Chapter 21 Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday's Law
Chapter 21 Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday's Law
Chapter 21 Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday's Law
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
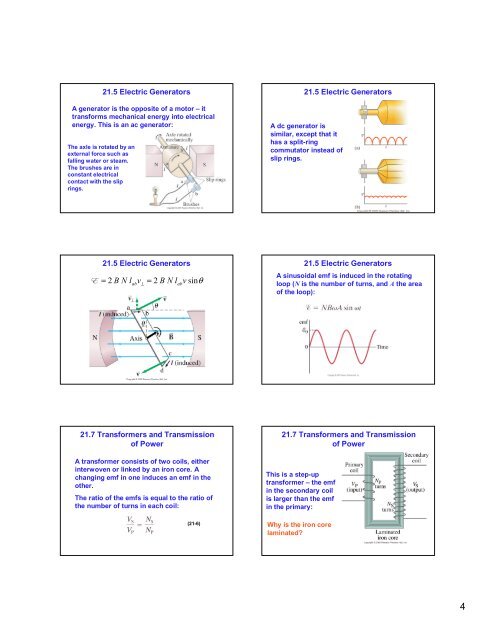
<strong>21</strong>.5 Electric Generators<br />
A generator is the opposite of a motor – it<br />
transforms mechanical energy into electrical<br />
energy. This is an ac generator:<br />
The axle is rotated by an<br />
external force such as<br />
falling water or steam.<br />
The brushes are in<br />
constant electrical<br />
contact with the slip<br />
rings.<br />
<strong>21</strong>.5 Electric Generators<br />
A dc generator is<br />
similar, except that it<br />
has a split-ring<br />
commutator instead of<br />
slip rings.<br />
<br />
<strong>21</strong>.5 Electric Generators<br />
=<br />
ab ⊥<br />
=<br />
2 B N l v 2 B N l v sinθ<br />
ab<br />
<strong>21</strong>.5 Electric Generators<br />
A sinusoidal emf is induced in the rotating<br />
loop (N is the number of turns, <strong>and</strong> A the area<br />
of the loop):<br />
<strong>21</strong>.7 Transformers <strong>and</strong> Transmission<br />
of Power<br />
A transformer consists of two coils, either<br />
interwoven or linked by an iron core. A<br />
changing emf in one induces an emf in the<br />
other.<br />
The ratio of the emfs is equal to the ratio of<br />
the number of turns in each coil:<br />
(<strong>21</strong>-6)<br />
<strong>21</strong>.7 Transformers <strong>and</strong> Transmission<br />
of Power<br />
This is a step-up<br />
transformer – the emf<br />
in the secondary coil<br />
is larger than the emf<br />
in the primary:<br />
Why is the iron core<br />
laminated?<br />
4