Institute of Membrane & Systems Biology - Faculty of Biological ...
Institute of Membrane & Systems Biology - Faculty of Biological ...
Institute of Membrane & Systems Biology - Faculty of Biological ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Dan Donnelly<br />
BSc <strong>Biological</strong> Chemistry, University <strong>of</strong> Leicester (1988)<br />
PhD, University <strong>of</strong> London 1992, supervisor Pr<strong>of</strong> TL Blundell<br />
Post doc with Pr<strong>of</strong> J.B.C. Findlay (1991-1995)<br />
Lecturer (1995-2004) & Senior Lecturer (2004-), University <strong>of</strong> Leeds<br />
Contact: d.donnelly@leeds.ac.uk<br />
G Protein-Coupled<br />
Receptors<br />
My research group studies the structure<br />
& function <strong>of</strong> G protein-coupled<br />
receptors - one <strong>of</strong> the most diverse<br />
and ubiquitous families <strong>of</strong> integral<br />
membrane proteins. GPCRs play a<br />
pivotal role in many cellular signalling<br />
pathways and are prime targets for<br />
the development <strong>of</strong> therapeutic agents<br />
designed to either block or activate the<br />
receptors. The aim <strong>of</strong> this laboratory is<br />
to elucidate the mechanism by which<br />
these receptors bind their ligands<br />
and transduce the signal across the<br />
plasma membrane.<br />
The control <strong>of</strong> the body’s blood sugar<br />
level requires keeping an intricate<br />
balance between the levels and<br />
actions <strong>of</strong> the two opposing pancreatic<br />
hormones, insulin and glucagon. While<br />
low glucose levels result in glucagon<br />
secretion from pancreatic alpha cells, in<br />
the high glucose situation the action <strong>of</strong><br />
glucose on pancreatic beta cells results<br />
in increased plasma insulin levels.<br />
However, high blood glucose levels are<br />
not solely responsible for increased<br />
insulin secretion. Two hormones,<br />
glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and<br />
glucose-dependent-insulinotropic<br />
polypeptide (GIP), are responsible<br />
sensing food intake and consequently<br />
sensitizing the pancreatic beta cells’<br />
insulin secretory system to glucose.<br />
Using truncated and mutated receptors<br />
alongside modified peptide ligands, our<br />
group has defined a two-stage model for<br />
peptide binding at the GLP-1 receptor<br />
(Al-Sabah & Donnelly, 2003; Lopez de<br />
Maturana et al. 2003).<br />
The GLP-1 work in my laboratory<br />
is currently funded by an Industrial<br />
Partnership award from BBSRC &<br />
AstraZeneca, part <strong>of</strong> which involves<br />
the design & synthesis <strong>of</strong> small<br />
molecules ligands (Dr. Colin Fishwick,<br />
School <strong>of</strong> Chemistry).<br />
As part <strong>of</strong> a collaboration with GSK, our<br />
group also study the calcitonin receptorlike<br />
receptor (e.g. Miller et al., 2010) and<br />
the receptors for parathyroid hormone<br />
(e.g. Mann et al., 2008).<br />
Current Funding: BBSRC; GSK,<br />
AstraZeneca<br />
Past Funding: Novo Nordisk, Knoll, Royal<br />
Society, BBSRC, Wellcome<br />
Trust, British Heart Foundation<br />
and Diabetes UK.<br />
More information:<br />
www.fbs.leeds.ac.uk/staff/pr<strong>of</strong>ile.<br />
php?staff=DD<br />
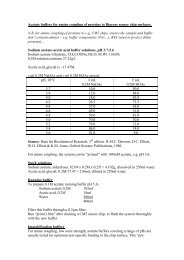
Figure 1: Schematic figure <strong>of</strong> how GLP-1 bind to its<br />
receptor (left) and a competition binding experiment<br />
using three different ligands at the GLP-1 receptor<br />
expressed in HEK-293 cells (right).<br />
Representative Publications<br />
Mann RJ, Nasr NE, Sinfield JK, Paci E, Donnelly<br />
D (2010) The major determinant <strong>of</strong> exendin-4/<br />
GLP-1 differential affinity at the rat GLP-1<br />
receptor N-terminal domain is a hydrogen bond<br />
from SER-32 <strong>of</strong> exendin-4. Brit. J. Pharmacol doi:<br />
10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00834.x<br />
Miller PS, Barwell J, Poyner DR, Wigglesworth<br />
MJ, Garland SL, Donnelly D (2010) Non-peptidic<br />
antagonists <strong>of</strong> the CGRP receptor, BIBN4096BS<br />
and MK-0974, interact with the calcitonin<br />
receptor-like receptor via methionine-42 and<br />
RAMP1 via tryptophan-74. Biochem Biophys Res<br />
Commun 391(1): 437-442<br />
Mann R, Wigglesworth MJ, Donnelly D (2008)<br />
Ligand-receptor interactions at the parathyroid<br />
hormone receptors: subtype binding selectivity is<br />
mediated via an interaction between residue 23<br />
on the ligand and residue 41 on the receptor. Mol<br />
Pharmacol 74(3): 605-613<br />
Al-Sabah S, Donnelly D (2003) A model for<br />
receptor-peptide binding at the glucagon-like<br />
peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor through the analysis<br />
<strong>of</strong> truncated ligands and receptors British Journal<br />
<strong>of</strong> Pharmacology 140: 339-346<br />
Lopez de Maturana R, Willshaw A, Kuntzsch<br />
A, Rudolph R, Donnelly D (2003) The isolated<br />
N-terminal domain <strong>of</strong> the glucagon-like<br />
peptide-1 receptor binds exendin peptides<br />
with much higher affinity than GLP-1 Journal <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>Biological</strong> Chemistry 278: 10195-10200