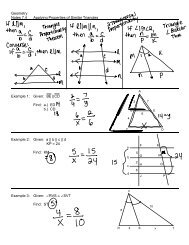
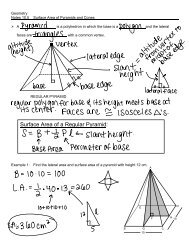
Geometry Notes 10.1 Solid Geometry Intro â Classify each polygon ...
Geometry Notes 10.1 Solid Geometry Intro â Classify each polygon ...
Geometry Notes 10.1 Solid Geometry Intro â Classify each polygon ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Geometry</strong><br />
<strong>Notes</strong> <strong>10.1</strong> <strong>Solid</strong> <strong>Geometry</strong><br />
<strong>Intro</strong> – <strong>Classify</strong> <strong>each</strong> <strong>polygon</strong>.<br />
1. a <strong>polygon</strong> with three congruent sides<br />
2. a <strong>polygon</strong> with six congruent sides and six congruent angles<br />
3. a <strong>polygon</strong> with four sides and with opposite sides parallel and congruent<br />
Types of <strong>Solid</strong>s (3-D figures):<br />
Prism Pyramid Cone Cylinder Sphere<br />
Cube:<br />
Other prisms and pyramids are names for the shape of their bases<br />
Face<br />
Edge<br />
Vertex
Example 1: Decide whether the solid is a polyhedron. If so, count the number of faces, vertices,<br />
and edges of the polyhedron.<br />
a.) b.) c.)<br />
Euler’s Theorem (Only applies to Polyhedrons)<br />
Example 2: Calculate the number of vertices of the solid using the given information.<br />
a.) 20 faces b.) 14 faces c.) 8 faces<br />
all triangles 8 hexagons 4 hexagons<br />
6 squares 4 triangles<br />
Nets
Cross Section<br />
Regular Polyhedron