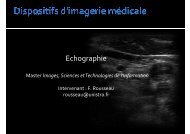
Presentation - MIV
Presentation - MIV
Presentation - MIV
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
ACI’s GRID – IDHA & MDA<br />
Reduction Methods for Multiband<br />
Image Analysis<br />
F. Flitti 1 , C. Collet 1 and F.Bonnarel 2<br />
1<br />
LSIIT, Strasbourg Univ.<br />
2<br />
Strasbourg Astronomic Observatory<br />
1<br />
http://picabia.u-strasbg.fr/lsiit/<br />
2<br />
http://cdsweb.u-strasbg.fr/
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Plan<br />
Pattern recognition<br />
* Classification task<br />
* Curse of dimensionality<br />
* Data reduction<br />
Multi-super-hyperspectral analysis<br />
* goals<br />
* limits<br />
Data reduction<br />
* Superspectral images in radio-astronomy context<br />
* 1 st method : Reduction using local projections<br />
* 2 nd method : Reduction using spectrum gaussian modeling<br />
Conclusion and Perspectives
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Pattern recognition<br />
Guessing / predicting the unknown nature<br />
of an observation<br />
* discrete quantity<br />
* definition of pattern<br />
Methods<br />
* template matching<br />
* statistical classification<br />
* neural networks<br />
Recognition<br />
* supervised classification<br />
* unsupervised classification<br />
>> Set of features
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Classification<br />
Space spanned by feature vectors<br />
* is subdivided using decision boundaries<br />
* which are established by statistical decision theory<br />
* Bayes decision theory : average risk is minimized<br />
Performances of a classifier<br />
* sample size<br />
* nb of features<br />
* classifier complexity (criterion function)<br />
Classification of high dimensional vector<br />
* curse of dimensionality<br />
* main factor affecting the classification task
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Hughe phenomenon<br />
Inherent sparsity of high dimensional spaces<br />
* in the absence of simplifying assumptions, the amount of data needed<br />
to get reasonably low variance estimators is really high<br />
* N-band observations >> N times more data but in R N space<br />
Dimensionality reduction<br />
* appropriate dimensionality of the reduced feature space<br />
* Important structure in the data actually lies in a much smaller<br />
dimensional space, and will therefore try to reduce the<br />
dimensionality before attempting the classification.<br />
This approach can be successful if the dimensionality reduction/feature<br />
extraction method loses as little relevant information as possible in the<br />
transformation from high-dimensional space to the low-dimensional one.
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Dimensionality reduction<br />
PCA (Karhunen-Loève expansion) and so on…<br />
* rotates the original feature space before projecting the feature<br />
vectors onto a limited number of axe<br />
* Energy based criterion (variance)<br />
* PCA seeks to minimize the mean squared reconstruction error<br />
* Maximization of the projection variance<br />
* Probabilistic PCA (PPCA, 1999) :<br />
gaussian a priori
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Dimensionality reduction<br />
ICA principles<br />
* Model of source mixture (« cocktail party problem »)<br />
* linear transform making the data components independent<br />
* Mutual information measured by Kullback-Leibler distance<br />
* Weak mutual information between sources : Neguentropy<br />
(non gaussianity criterion)<br />
* pre-processing : centered data, spherical noise<br />
* loss of source order<br />
*lossof source power<br />
ICA’s methods<br />
* Cumulant-based approach (Comon)<br />
* Jade (4th order cumulant + joint diagonalization), (Carodoso, Souloumiac)<br />
* Infomax : Neural Network (Bell, Sejnowski) ;<br />
* FastICA (Oja & Hyvärinen),<br />
* SOBI : cross-correlation + joint diagonalization (Belouchrani)…
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Dimensionality reduction<br />
Multidimensional scaling<br />
* multivariate data analysis techniques : any method searching<br />
for a low dimensional representation of objects given<br />
their high-dimensional representation<br />
Projection pursuit<br />
* Battacharya distance between 2 distributions<br />
* Subspaces max this distance<br />
Kohonen’s self organizing map
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Dimensionality reduction<br />
Limits<br />
A reduction in the number of features may lead to a loss in the<br />
discrimination power and thereby lower the accuracy of the resulting<br />
recognition system.<br />
Dimensionality reduction<br />
* feature selection : selects best subset of the input feature set<br />
* feature extraction : creates new features based on<br />
transformation or combination of the original feature<br />
The main issue in dimensionality reduction is the choice of a criterion<br />
function.<br />
A commonly used criterion is the classification error of a feature subset.
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Vector valued images<br />
Multispectral data<br />
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Mueller Imaging<br />
Mueller matrix describes interaction between<br />
light source and raw materials<br />
Segmentation : vein of the leaf are well detected<br />
Paper to appear : J. Zallat, Ch. Collet and Y. Takakura, “Polarization Images Clustering”,<br />
Applied Optics, to appear, January 2004
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
MRI<br />
3D MARSIAA Software<br />
(Markovian Quadtree or Markov Chain)<br />
For classification tasks<br />
Markov Chain<br />
3D Markovian<br />
Quadtree<br />
Magnetic Resonance Imagery<br />
Multimodal imagery by using different imaging modalities
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
MRI
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Vector valued images
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Vector valued images
The images to be reduced<br />
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
48 bands<br />
around CO ray<br />
of the GG<br />
tauri system<br />
from the<br />
IRAM<br />
interferometer
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Reduction using local projections<br />
(1 st technique)<br />
Multispectral /<br />
Superspectral<br />
cube<br />
Grouping<br />
Bottom to up clustering algorithm using<br />
multiscale similarity measure based on<br />
normalized histograms and barycenters<br />
Local projections on each cluster obtained by<br />
the grouping :<br />
PCA /ICA<br />
1 st axe of the Principal Component Analysis<br />
1 st axe of the fastICA with deflationary<br />
orthogonalization<br />
Segmentation<br />
Markov modelling on the quadtree
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Reduction using local projections<br />
(1 st technique)<br />
Grouping<br />
Multispectral /<br />
Superspectral<br />
Image<br />
Grouping<br />
S 2<br />
S 1<br />
S 0<br />
Difference between normalized histograms &<br />
barycenters at each scale<br />
Summing over all scales and normalizing<br />
similarity measure<br />
Illustration of the<br />
bottom to up<br />
clustering algorithm:<br />
Grouping the closest<br />
two clusters at each<br />
iteration
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Reduction using local projections<br />
(1 st technique)<br />
Local projections<br />
On each cluster established by the grouping step, we perform one<br />
of the two projections:<br />
PCA:<br />
Seeks data variance maximisation. Projection matrix given by the<br />
eigen vectors of the covariance matrix of data.<br />
PCA /ICA<br />
ICA:<br />
We use the fastICA algorithm with deflationary orthogonalization<br />
which seeks maximisation of the nongaussianity<br />
Finally, one keeps only the first image corresponding to the higher<br />
eigenvalue (PCA) or to the higher nongaussianity criterion (ICA).
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
The images reduced by the<br />
1 st technique with PCA
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
The images reduced by the<br />
1 st technique with PCA<br />
Grouping<br />
Hierarchical Markovian<br />
Segmentation (MARSIAA)
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Segmentation Results of The images<br />
reduced by the 1 st technique with PCA<br />
Map on each reduced image
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Segmentation Results of The images<br />
reduced by the 1 st technique with PCA<br />
Combined maps
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
The images reduced by the<br />
1 st technique with ICA
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
The images reduced by the<br />
1 st technique with ICA<br />
Grouping<br />
Hierarchical Markovian<br />
Segmentation (MARSIAA)
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Segmentation Results of The images<br />
reduced by the 1 st technique with ICA<br />
Map on each reduced image
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Segmentation Results of The images<br />
reduced by the 1 st technique with ICA<br />
Combined maps
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Reduction using spectrum<br />
gaussian modeling<br />
(2 nd technique)<br />
Superspectral<br />
Image (N bands)<br />
Spectrum in<br />
each pixel<br />
Spectrum Gaussian<br />
Modeling<br />
(a 1 ,a 2 , … ,a M )<br />
The N original bands are<br />
reduced to M parameter<br />
images. In our case N = 48<br />
and M=6.<br />
Segmentation<br />
We choose the decomposition<br />
base as a set of M uniformly<br />
distributed gaussians on the λ<br />
interval. Then only<br />
M parameters are used to<br />
represent the spectrum on<br />
each pixel.
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
The images reconstructed using<br />
Gaussian modeling (2 nd technique)<br />
The original 48 images (256 x 256)<br />
rearranged as 48 vectors of 256 2<br />
elements<br />
The 48 images reconstructed using<br />
gaussian modeling (M=6) rearranged<br />
as the originals
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
The images reduced by the<br />
2 nd technique, M=6
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
The images reduced by the<br />
2 nd technique, M=6<br />
Gaussian<br />
Model<br />
Hierarchical Markovian<br />
Segmentation (MARSIAA)
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Segmentation Results of The images<br />
reduced by the 2 nd technique, M=6<br />
Map on each reduced image
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Segmentation Results of The images<br />
reduced by the 2 nd technique, M=6<br />
Combined maps
collet@lsiit.u-strasbg.fr<br />
iAstro Workshop - Nice Observatory<br />
16/17 October 2003<br />
Conclusion & further works<br />
1 st technique with ICA<br />
1 st technique with PCA<br />
2 nd technique, M=6<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
Rotation of the disk detected especially with<br />
Gaussian modeling<br />
Unsupervised algorithms<br />
The central zone seems interesting and need more<br />
investigations<br />
More investigations on the segmentation maps on<br />
each reduced image