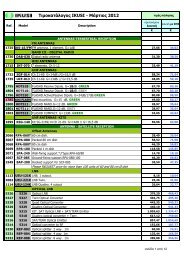
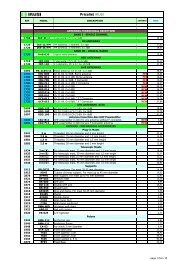
ClassA - tridimas electronics
ClassA - tridimas electronics
ClassA - tridimas electronics
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>ClassA</strong>MTI HEADEND• Digital transmodulation (QPSK/8PSK toCOFDM) with Transport Stream Processing.The QPSK or 8PSK channels locatedin the Sat-IF frequency band (950-2150MHz) are transformed to COFDM channelslocated in the 47-862 MHz band. Rangeincludes two transmodulators: MTI-900and MTI-800. The MTI-900 has CommonInterface (EN 50221) for discretionary deencryptingof TV programmes.• A MTI headend includes:- As many MTI tansmodulators as COFDMchannels to be distributed. At MTI-900module, one CAM (Conditional AccessModule) containing the Operator's SmartCard must fit the front panel slot.- One HPA that amplifies the sum of theoutput COFDM channels from the transmodulators.- One or more CFP Power Supplies.- One or more Rack-Frames or wall-fixingBase-Plates. The base-plates can bejoined horizontally.- Usually, housing units for the base-plates.- If the headend is large, one or moreAMX-400 combiners.The MTI headends provide a COFDM multichannelsignal whose level is appropriate tofeed the distribution network. An extensioninput at the HPA amplifier allows easycoupling of the wideband 47-862 MHz signalprovided by another existing headend.You can use your TV DTT (Digital TerrestrialTelevision) for programs receiving satellitechannels treated at the station MTI.FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION OF THE MTITRANSMODULATORSAn MTI transmodulator carries out the completechannel processing from the input tothe output:- tunes a QPSK/8PSK digital channel of the950-2150 MHz band, demodulates thesignal being received,- processes the transport stream (withprogramme de-encrypting in the MTI-900,if this one has a “CAM + Operator Card”couple is installed), and- re-modulates it in COFDM format on an RFchannel that is selectable within the 47-862MHz frequency range.Main features:- Central xPSK Input Frequency (1 MHzsteps)- Input Symbol Rate (0.001 MS/s steps)- Central COFDM Output Frequency (1 kHzsteps)- Output Channel Bandwidth (6, 7 or 8 MHz;also 5 MHz on DVB-H)- Output Operation Mode (2K or 8K; also 4Kon DVB-H)- RF Output Level- FFT Window (Fast Fourier Transform), toreduce interference on adjacent channel- In-depth interleaving (only on DVB-H; with2K and 4K modes)- Discretionary de-encrypting of one or moreServices (only for MTI-900)- Optional Blockade of Services, PIDs andConditional Accesses, with Regenerationof Tables- NIT AdaptationSimple cabling of MTI headendsThe MTI transmodulators feature two directionallycoupled input and output ports.Sat-IF signal can therefore be directly fedinto the input port of the first module, whichin turn passes in through the coupler tothe next and so forth. On the output side,the same procedure is repeated whichforms the channel coupling. The sum of thecombined channels is turn connected in thesame way to the drive amplifier_ the HPAmodule or an external wideband amplifier_which then feeds the distribution network.For power connection, each module hastwo DC banana sockets that allow to builda +12 VDC cascade. A third banana socketis available to connect the power for theattached LNB.Local programming is carried out eitherwith the SPI-300 unit, which is connectedto each module individually. In order to performNIT adaptation, the IKUSUP bus mustbe installed. The last module at the rightend of the IKUSUP cascade carries out thecontrol function.Remote programming may by carried outonly if the HMS control unit is installed in theheadend.FUNCTIONS OF THE TS PROCESSING• Bit Rate adaptation with PCR restamping• Adaptation of NIT tableAdaptation to the particular adjustmentsof the headend is automatic. Name andidentifier of the new network can be edited.• Service and CA blockadeBlockade is at service level and at conditionalaccess level.Automatic regeneration of PAT, SDT andCAT tables.• TS monitoringUsage level of the Transport Stream —percentage of null packets— is presentedalong the programming process.• LCN insertion.• TS_ID, SID, ONID and NID edition.2HeadendsIKUSI · CATALOGUE 201351