SEMESTER – II (17 WEEKS) - IHM Gwalior
SEMESTER – II (17 WEEKS) - IHM Gwalior
SEMESTER – II (17 WEEKS) - IHM Gwalior
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
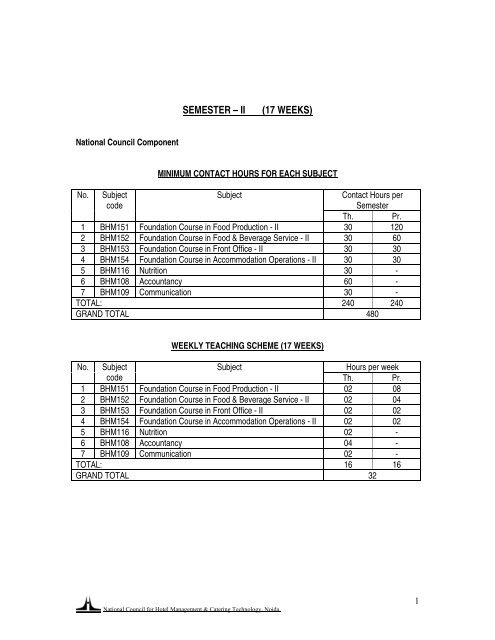
<strong>SEMESTER</strong> <strong>–</strong> <strong>II</strong>(<strong>17</strong> <strong>WEEKS</strong>)National Council ComponentMINIMUM CONTACT HOURS FOR EACH SUBJECTNo. SubjectcodeSubjectContact Hours perSemesterTh. Pr.1 BHM151 Foundation Course in Food Production - <strong>II</strong> 30 1202 BHM152 Foundation Course in Food & Beverage Service - <strong>II</strong> 30 603 BHM153 Foundation Course in Front Office - <strong>II</strong> 30 304 BHM154 Foundation Course in Accommodation Operations - <strong>II</strong> 30 305 BHM116 Nutrition 30 -6 BHM108 Accountancy 60 -7 BHM109 Communication 30 -TOTAL: 240 240GRAND TOTAL 480WEEKLY TEACHING SCHEME (<strong>17</strong> <strong>WEEKS</strong>)No. SubjectSubjectHours per weekcodeTh. Pr.1 BHM151 Foundation Course in Food Production - <strong>II</strong> 02 082 BHM152 Foundation Course in Food & Beverage Service - <strong>II</strong> 02 043 BHM153 Foundation Course in Front Office - <strong>II</strong> 02 024 BHM154 Foundation Course in Accommodation Operations - <strong>II</strong> 02 025 BHM116 Nutrition 02 -6 BHM108 Accountancy 04 -7 BHM109 Communication 02 -TOTAL: 16 16GRAND TOTAL 32National Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.1
EXAMINATION SCHEMENo. SubjectSubjectTerm Marks*codeTh. Pr.1 BHM151 Foundation Course in Food Production - <strong>II</strong> 100 1002 BHM152 Foundation Course in Food & Beverage Service <strong>–</strong> <strong>II</strong> 100 1003 BHM153 Foundation Course in Front Office - <strong>II</strong> 100 1004 BHM154 Foundation Course in Accommodation Operations <strong>–</strong> <strong>II</strong> 100 1005 BHM116 Nutrition 100 -6 BHM108 Accountancy 100 -7 BHM109 Communication 50 -TOTAL: 650 400GRAND TOTAL 1050* Term marks will comprise 30% Incourse & 70% Term end exam marks.IGNOU ComponentNo. SubjectSubjectCounselling sessionscode01 BHM110 Foundation Course in Tourism 10-12 counselling sessions of twohours each per group per yearNational Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.2
BHM151 - FOUNDATION COURSE IN FOOD PRODUCTION <strong>–</strong> <strong>II</strong> (THEORY)HOURS ALLOTED: 30 MAXIMUM MARKS: 100S.No. Topic Hours Weightage01 SOUPS02 10%A. Basic recipes other than consommé with menu examples• Broths• Bouillon• Puree• Cream• Veloute• Chowder• Bisque etcB. Garnishes and accompanimentsC. International soups02 SAUCES & GRAVIES03 10%A. Difference between sauce and gravyB. Derivatives of mother saucesC. Contemporary & Proprietary03 MEAT COOKERY04 15%A. Introduction to meat cookeryB. Cuts of beef/vealC. Cuts of lamb/muttonD. Cuts of porkE. Variety meats (offals)F. Poultry(With menu examples of each)04 FISH COOKERY03 10%A. Introduction to fish cookeryB. Classification of fish with examplesC. Cuts of fish with menu examplesD. Selection of fish and shell fishE. Cooking of fish (effects of heat)05 RICE, CEREALS & PULSES01 5%A. IntroductionB. Classification and identificationC. Cooking of rice, cereals and pulsesD. Varieties of rice and other cereals06 i) PASTRYA. Short crustB. LaminatedC. ChouxD. Hot water/Rough puff02 5%• Recipes and methods of preparation• Differences• Uses of each pastry• Care to be taken while preparing pastry• Role of each ingredient• Temperature of baking pastryNational Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.3
ii) FlourA. Structure of wheatB. Types of WheatC. Types of FlourD. Processing of Wheat <strong>–</strong> FlourE. Uses of Flour in Food ProductionF. Cooking of Flour (Starch)iii) SIMPLE BREADSA. Principles of bread makingB. Simple yeast breadsC. Role of each ingredient in break makingD. Baking temperature and its importance07 PASTRY CREAMSA. Basic pastry creamsB. Uses in confectioneryC. Preparation and care in production08 BASIC COMMODITIES:i) MilkA. IntroductionB. Processing of MilkC. Pasteurisation <strong>–</strong> HomogenisationD. Types of Milk <strong>–</strong> Skimmed and CondensedE. Nutritive Value03 10%02 5%15%02ii)CreamA. IntroductionB. Processing of CreamC. Types of Cream01iii) CheeseA. IntroductionB. Processing of CheeseC. Types of CheeseD. Classification of CheeseE. Curing of CheeseF. Uses of Cheeseiv) ButterA. IntroductionB. Processing of ButterC. Types of Butter09 BASIC INDIAN COOKERY020102 5%i) CONDIMENTS & SPICESA. Introduction to Indian foodB. Spices used in Indian cookeryC. Role of spices in Indian cookeryD. Indian equivalent of spices (names)National Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.4
ii) MASALASA. Blending of spicesB. Different masalas used in Indian cookery• Wet masalas• Dry masalasC. Composition of different masalasD. Varieties of masalas available in regional areasE. Special masala blends10 KITCHEN ORGANIZATION AND LAYOUT02 10%A. General layout of the kitchen in various organisationsB. Layout of receiving areasC. Layout of service and wash upTOTAL 30 100%National Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.5
FOUNDATION COURSE IN FOOD PRODUCTION <strong>–</strong> <strong>II</strong> (PRACTICAL)PART A - COOKERYHOURS ALLOTED: 60 MAXIMUM MARKS: 50S.No Topic Method Hours1 • Meat <strong>–</strong> Identification of various cuts, Carcassdemonstration• Preparation of basic cuts-Lamb and PorkChops , Tornado, Fillet, Steaks and Escalope• Fish-Identification & Classification• Cuts and Folds of fish2 • Identification, Selection and processing ofMeat, Fish and poultry.• Slaughtering and dressing3 Preparation of menuSalads & soups- waldrof salad, Fruit salad, Russiansalad, salade nicoise,Cream (Spinach, Vegetable, Tomato),Puree (Lentil, Peas Carrot)International soupsDemonstrations &simple applicationsDemonstrations atthe site in localArea/Slaughteringhouse/Market0404Chicken, Mutton and Fish Preparations-Fish orly, a la anglaise, colbert, meuniere, poached,bakedEntrée-Lamb stew, hot pot, shepherd’s pie, grilledsteaks & lamb/Pork chops, Roast chicken, grilledchicken, Leg of Lamb, BeefSimple potato preparations-Basic potato dishesVegetable preparations-Basic vegetable dishesDemonstration byinstructor andapplications bystudents52Indian cookery-Rice dishes, Breads, Main course, Basic Vegetables,Paneer PreparationsTOTAL 60National Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.6
PART B - BAKERY & PATISSERIEHOURS ALLOTED: 60 MAXIMUM MARKS: 50S.No Topic Method Hours1 PASTRY:Demonstration and Preparation of dishes usingvarieties of Pastry• Short Crust <strong>–</strong> Jam tarts, Turnovers• Laminated <strong>–</strong> Palmiers, Khara Biscuits, DanishPastry, Cream Horns• Choux Paste <strong>–</strong> Eclairs, Profiteroles2 COLD SWEETDemonstration byinstructor andapplications bystudents20• Honeycomb mould• Butterscotch sponge• Coffee mousse• Lemon sponge• Trifle• Blancmange• Chocolate mousse• Lemon soufflé3 HOT SWEET• Bread & butter pudding• Caramel custard• Albert pudding• Christmas pudding4 INDIAN SWEETSSimple ones such as chicoti, gajjar halwa, kheerDemonstration byinstructor andapplications bystudentsDemonstration byinstructor andapplications bystudentsDemonstration byinstructor andapplications bystudentsTOTAL 60201208National Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.7
152 - FOUNDATION COURSE IN FOOD & BEVERAGE SERVICE <strong>–</strong> <strong>II</strong> (THEORY)HOURS ALLOTED: 30 MAXIMUM MARKS: 100S.No. Topic Hours Weightage01 MEALS & MENU PLANNING:A. Origin of MenuB. Objectives of Menu PlanningC. Types of MenuD. Courses of French Classical Menu• Sequence• Examples from each course• Cover of each course• AccompanimentsE. French Names of dishesF. Types of Meals• Early Morning Tea• Breakfast (English, American Continental, Indian)• Brunch• Lunch• Afternoon/High Tea• Dinner• Supper02 I PREPARATION FOR SERVICE01020105030302A. Organising Mise-en-sceneB. Organising Mise en place<strong>II</strong> TYPES OF FOOD SERVICE04A. Silver serviceB. Pre-plated serviceC. Cafeteria serviceD. Room serviceE. Buffet serviceF. Gueridon serviceG. Lounge service03 SALE CONTROL SYSTEM06A. KOT/Bill Control System (Manual)• Triplicate Checking System• Duplicate Checking System• Single Order Sheet• Quick Service Menu & Customer BillB. Making billC. Cash handling equipmentD. Record keeping (Restaurant Cashier)National Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.8
04 TOBACCO03A. HistoryB. Processing for cigarettes, pipe tobacco & cigarsC. Cigarettes <strong>–</strong> Types and Brand namesD. Pipe Tobacco <strong>–</strong> Types and Brand namesE. Cigars <strong>–</strong> shapes, sizes, colours and Brand namesF. Care and Storage of cigarettes & cigarsTOTAL 30 100%National Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.9
FOUNDATION COURSE IN FOOD & BEVERAGE SERVICE <strong>–</strong> <strong>II</strong> (PRACTICAL)HOURS ALLOTED: 60 MAXIMUM MARKS: 100S.No Topic Hours01 REVIEW OF <strong>SEMESTER</strong> -1 0402 TABLE LAY-UP & SERVICETask-01: A La Carte CoverTask-02: Table d’ Hote CoverTask-03: English Breakfast CoverTask-04: American Breakfast CoverTask-05: Continental Breakfast CoverTask-06: Indian Breakfast CoverTask-07: Afternoon Tea CoverTask-08: High Tea CoverTRAY/TROLLEY SET-UP & SERVICE16Task-01: Room Service Tray SetupTask-02: Room Service Trolley Setup03 PREPARATION FOR SERVICE (RESTAURANT)A. Organizing Mise-en-sceneB. Organizing Mise-en-PlaceC. Opening, Operating & Closing duties04 PROCEDURE FOR SERVICE OF A MEALTask-01: Taking Guest ReservationsTask-02: Receiving & Seating of GuestsTask-03: Order taking & RecordingTask-04: Order processing (passing orders to the kitchen)Task-05: Sequence of serviceTask-06: Presentation & Encashing the BillTask-07: Presenting & collecting Guest comment cardsTask-08: Seeing off the Guests05 Social SkillsTask-01: Handling Guest ComplaintsTask-02: Telephone mannersTask-03: Dining & Service etiquettes06 Special Food Service - (Cover, Accompaniments & Service)04080412Task-01: Classical Hors d’ oeuvre• Oysters• Caviar• Smoked Salmon• Pate de Foie GrasTask-02: CheeseTask-03: Dessert (Fresh Fruit & Nuts)• Snails• Melon• Grapefruit• AsparagusNational Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.10
Service of Tobacco• Cigarettes & Cigars07 Restaurant French: To be taught by a professional French language teacher.12• Restaurant Vocabulary (English & French)• French Classical Menu Planning• French for Receiving, Greeting & Seating Guests• French related to taking order & description of dishesTOTAL 60National Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.11
153 - FOUNDATION COURSE IN FRONT OFFICE OPERATIONS <strong>–</strong> <strong>II</strong> (THEORY)HOURS ALLOTED: 30 MAXIMUM MARKS: 100S.No. Topic Hours Weightage01 TARIFF STRUCTURE04 10%A. Basis of chargingB. Plans, competition, customer’s profile, standards of service &amenitiesC. Hubbart formulaD. Different types of tariffs• Rack Rate• Discounted Rates for Corporates, Airlines, Groups & TravelAgents02 FRONT OFFICE AND GUEST HANDLING• Introduction to guest cycle• Pre arrival• Arrival• During guest stay• Departure• After departure03 RESERVATIONSA. Importance of reservationB. Modes of reservationC. Channels and sources (FITs, Travel Agents, Airlines, GITs)D. Types of reservations (Tentative, confirmed, guaranteed etc.)E. Systems (non automatic, semi automatic fully automatic)F. CancellationG. AmendmentsH. Overbooking04 ROOM SELLING TECHNIQUESA. Up sellingB. Discounts05 ARRIVALSA. Preparing for guest arrivals at Reservation and Front OfficeB. Receiving of guestsC. Pre-registrationD. Registration (non automatic, semi automatic and automatic)E. Relevant records for FITs, Groups, Air crews & VIPs06 DURING THE STAY ACTIVITIES04 10%07 25%02 05%05 20%06 20%A. Information servicesB. Message and Mail HandlingC. Key HandlingD. Room selling techniqueNational Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.12
E. Hospitality deskF. Complaints handlingG. Guest handlingH. Guest history07 FRONT OFFICE CO-ORDINATION02 10%With other departments of hotelTOTAL 30 100FOUNDATION COURSE IN FRONT OFFICE OPERATIONS <strong>–</strong> <strong>II</strong> (PRACTICALS)HOURS ALLOTED: 30 MAXIMUM MARKS: 100Hands on practice of computer applications on PMS.S.No.Suggested tasks on Fidelio1 Hot function keys2 Create and update guest profiles3 Make FIT reservation4 Send confirmation letters5 Printing registration cards6 Make an Add-on reservation7 Amend a reservation8 Cancel a reservation-with deposit and without deposit9 Log onto cashier code10 Process a reservation deposit11 Pre-register a guest12 Put message and locator for a guest13 Put trace for guest14 Check in a reserved guest15 Check in day use16 Check <strong>–</strong>in a walk-in guest<strong>17</strong> Maintain guest history18 Issue a new key19 Verify a key20 Cancel a key21 Issue a duplicate key22 Extend a key23 Programme keys continuously24 Re-programme keys25 Programme one key for two roomsNational Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.13
BHM154 - FOUNDATION COURSE IN ACCOMMODATION OPERATIONS <strong>–</strong> <strong>II</strong> (THEORY)HOURS ALLOTED: 30 MAXIMUM MARKS: 100S.No. Topic Hours Weightage01 ROOM LAYOUT AND GUEST SUPPLIES04 15%A. Standard rooms, VIP ROOMSB. Guest’s special requests02 AREA CLEANINGA. Guest roomsB. Front-of-the-house AreasC. Back-of-the house AreasD. Work routine and associated problems e.g. high traffic areas,Façade cleaning etc.03 ROUTINE SYSTEMS AND RECORDS OF HOUSE KEEPINGDEPARTMENT06 20%10 35%A. Reporting Staff placementB. Room Occupancy ReportC. Guest Room InspectionD. Entering Checklists, Floor Register, Work Orders, Log Sheet.E. Lost and Found Register and Enquiry FileF. Maid’s Report and Housekeeper’s ReportG. Handover RecordsH. Guest’s Special Requests RegisterI. Record of Special CleaningJ. Call RegisterK. VIP Lists04 TYPES OF BEDS AND MATTRESSES 02 5%05 PEST CONTROL20%A. Areas of infestationB. Preventive measures and Control measure06 KEYSA. Types of keysB. Computerised key cardsC. Key control030302 5%TOTAL 30 100%National Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.14
• Guest special request register• Record of special cleaning• Call register• VIP list• Floor linen book/ register05 Guest room inspection 206 Minibar management2• Issue• stock taking• checking expiry date07 Handling room linen/ guest supplies4• maintaining register/ record• replenishing floor pantry• stock taking08 Guest handling2• Guest request• Guest complaintsNational Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.16
BHM116 - NUTRITIONHOURS ALLOTED: 30 MAXIMUM MARKS: 100S.No. Topic Hours Weightage01 BASIC ASPECTS01 5%A. Definition of the terms Health, Nutrition and NutrientsB. Importance of Food <strong>–</strong> (Physiological, Psychological and Socialfunction of food) in maintaining good health.C. Classification of nutrients02 ENERGY03 10%A. Definition of Energy and Units of its measurement (Kcal)B. Energy contribution from macronutrients (Carbohydrates, Proteinsand Fat)C. Factors affecting energy requirementsD. Concept of BMR, SDA, Thermodynamic action of foodE. Dietary sources of energyF. Concept of energy balance and the health hazards associated withUnderweight, Overweight03 MACRO NUTRIENTSCarbohydrates• Definition• Classification ( mono, di and polysaccharides)• Dieteary Sources• Functions• Significance of dietary fibre (Prevention/treatment of diseases)Lipids040410%10%• Definition• Classification : Saturated and unsaturated fats• Dietary Sources• Functions• Significance of Fatty acids (PUFAs, MUFAs, SFAs, EFA) inmaintaining health• Cholesterol <strong>–</strong> Dietary sources and the Concept of dietary and bloodcholesterolProteins• Definition• Classification based upon amino acid composition• Dietary sources• Functions• Methods of improving quality of protein in food (special emphasison Soya proteins and whey proteins)0410%National Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.<strong>17</strong>
04 MACRO NUTRIENTSA. Vitamins• Definition and Classification (water and fats soluble vitamins)• Food Sources, function and significance of:1. Fat soluble vitamins (Vitamin A, D, E, K)2. Water soluble vitamins (Vitamin C, Thiamine, Riboflavin,Niacin, Cyanocobalamin Folic acidB. MINERALS• Definition and Classification (major and minor)• Food Sources, functions and significance of :Calcium, Iron, Sodium, Iodine & Flourine05 WATER• Definition• Dietary Sources (visible, invisible)• Functions of water• Role of water in maintaining health (water balance)06 BALANCED DIET• Definition• Importance of balanced diet• RDA for various nutrients <strong>–</strong> age, gender, physiological state07 MENU PLANNING• Planning of nutritionally balanced meals based upon the three foodgroup system• Factors affecting meal planning• Critical evaluation of few meals served at the Institutes/Hotelsbased on the principle of meal planning.• Calculation of nutritive value of dishes/meals.08 MASS FOOD PRODUCTION• Effect of cooking on nutritive value of food (QFP)09 NEWER TRENDS IN FOOD SERVICE INDUSTRY IN RELEVANCE TONUTRITION AND HEALTH• Need for introducing nutritionally balanced and health specificmeals• Critical evaluation of fast foods• New products being launched in the market (nutritional evaluation)050315%10%01 5%01 5%02 10%01 5%01 5%TOTAL 30 100%National Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.18
B. MethodsC. AdvantagesD. LimitationsE. Practicals08 FINAL ACCOUNTSA. MeaningB. Procedure for preparation of Final AccountsC. Difference between Trading Accounts, Profit & Loss Accounts andBalance SheetD. Adjustments (Only four)• Closing Stock• Pre-paid Expenses• Outstanding Expenses• Depreciation09 CAPITAL AND REVENUE EXPENDITURE12 25%02 5%A. MeaningB. Definition of Capital and Revenue ExpenditureTOTAL 60 100%NOTE: USE OF CALCULATORS IS PERMITTEDNational Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.20
BHM109 - COMMUNICATIONHOURS ALLOTED: 30 MAXIMUM MARKS: 50S.No. Topic Hours Weightage01 BUSINESS COMMUNICATION7 20%A. NeedB. PurposeC. NatureD. ModelsE. Barriers to communicationF. Overcoming the barriers02 LISTENING ON THE JOB6 20%A. DefinitionB. Levels and types of listeningC. Listening barriersD. Guidelines for effective listeningE. Listening computerization and note taking03 EFFECTIVE SPEAKING7 20%A. Restaurant and hotel EnglishB. Polite and effective enquiries and responsesC. Addressing a groupD. Essential qualities of a good speakerE. Audience analysisF. Defining the purpose of a speech, organizing the ideas anddelivering the speech04 NON VERBAL COMMUNICATION4 15%A. Definition, its importance and its inevitabilityB. Kinesics: Body movements, facial expressions, posture, eyecontact etc.C. Protemies: The communication use of spaceD. Paralanguage: Vocal behaviour and its impact on verbalcommunicationE. Communicative use of artifacts <strong>–</strong> furniture, plants, colours,architects etc.05 SPEECH IMPROVEMENT4 15%A. Pronunciation, stress, accentB. Important of speech in hotelsC. Common phonetic difficultiesD. Connective drills exercisesE. Introduction to frequently used foreign sounds06 USING THE TELEPHONE2 10%A. The nature of telephone activity in the hotel industryB. The need for developing telephone skillsC. Developing telephone skillsTOTAL 30 100%National Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.21
FOUNDATION COURSE IN TOURISM (BHM110)Tourism has been acknowledged as one of the most rapidly growing industries in recent years.Yet it has not received adequate attention as an academic discipline which it rightly deserves. Thiscourse has been designed with the objective of making up for this lacuna by introducing to you somefoundational concepts of tourism studies. The emphasis here has been on the situation obtaining inIndia, though we have not been unduly different about borrowing concepts and terms from similarstudies undertaken in other parts of the world. You will thus find details on the historical evolution oftourism along with core definitions of tourism industry in this course. Tourism services and operations,planning and policy, and marketing and communications form other Blocks of the course. Finally wehave also dealt with the geography and tourism and the relationship between cultural heritage andtourism development in this course.SyllabusBlock-1Tourism PhenomenonUnit 1 Understanding Tourism <strong>–</strong> IUnit 2 Understanding Tourism <strong>–</strong> <strong>II</strong>Unit 3 Historical Evolution and DevelopmentBlock-2Tourism IndustryUnit 4 Tourism SystemUnit 5 Constituents of Tourism Industry and Tourism OrganisationsUnit 6 Tourism RegulationsUnit 7 Statistics and MeasurementsBlock-3 Tourism Services and Operations <strong>–</strong> 1Unit 8 Modes of TransportUnit 9 Tourist AccommodationUnit 10 Informal Services in TourismUnit 11 Subsidiary Services: Categories and RolesUnit 12 Shops, Emporiums and Melas (Fairs)Block-4 Tourism Services and Operations <strong>–</strong> 2Unit 13 Travel AgencyUnit 14 Tour OperatorsUnit 15 Guides and EscortsUnit 16 Tourism InformationNational Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.22
Block-5Geography and TourismUnit <strong>17</strong> India’s Biodiversity: Landscape, Environment and EcologyUnit 18 Seasonality and DestinationsUnit 19 Map and Chart WorkBlock-6Tourism Marketing and CommunicationsUnit 20 Tourism Marketing <strong>–</strong> 1: Relevance, Product Design, Market ResearchUnit 21 Tourism Marketing <strong>–</strong> 2: Promotional Events, Advertising Publicity, SellingUnit 22 Role of MediaUnit 23 Writing for TourismUnit 24 Personality Development and Communicating SkillsBlock-7Tourism: The Cultural HeritageUnit 25 Use of HistoryUnit 26 Monuments and MuseumsUnit 27 Living Culture and Performing ArtsUnit 28 Religions of IndiaBlock-8Tourism: Planning and PolicyUnit 29 Tourism Policy and PlanningUnit 30 Infrastructural DevelopmentUnit 31 Local Bodies, Officials and TourismUnit 32 Development, Dependency and Manila DeclarationBlock-9Tourism ImpactUnit 33 Economic ImpactUnit 34 Social, Environmental and Political ImpactsUnit 35 Threats and Obstacles to Tourism*****National Council for Hotel Management & Catering Technology, Noida.23