Applying the Concepts 10 - McGraw-Hill Ryerson
Applying the Concepts 10 - McGraw-Hill Ryerson
Applying the Concepts 10 - McGraw-Hill Ryerson
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
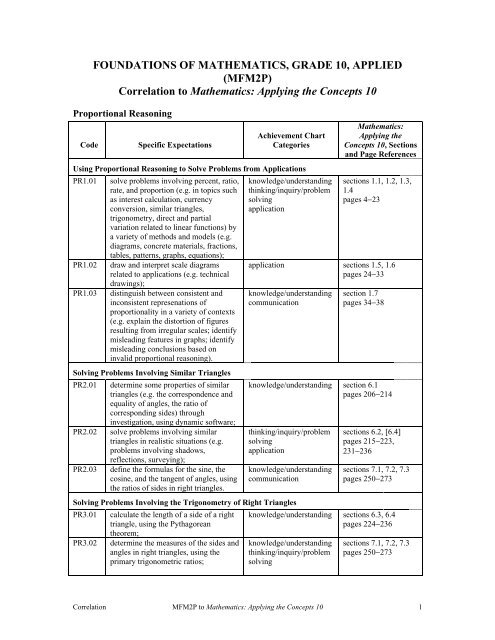
FOUNDATIONS OF MATHEMATICS, GRADE <strong>10</strong>, APPLIED(MFM2P)Correlation to Ma<strong>the</strong>matics: <strong>Applying</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Concepts</strong> <strong>10</strong>Proportional ReasoningCodeSpecific ExpectationsAchievement ChartCategoriesUsing Proportional Reasoning to Solve Problems from ApplicationsPR1.01PR1.02PR1.03solve problems involving percent, ratio,rate, and proportion (e.g. in topics suchas interest calculation, currencyconversion, similar triangles,trigonometry, direct and partialvariation related to linear functions) bya variety of methods and models (e.g.diagrams, concrete materials, fractions,tables, patterns, graphs, equations);draw and interpret scale diagramsrelated to applications (e.g. technicaldrawings);distinguish between consistent andinconsistent represenations ofproportionality in a variety of contexts(e.g. explain <strong>the</strong> distortion of figuresresulting from irregular scales; identifymisleading features in graphs; identifymisleading conclusions based oninvalid proportional reasoning).Solving Problems Involving Similar TrianglesPR2.01PR2.02PR2.03determine some properties of similartriangles (e.g. <strong>the</strong> correspondence andequality of angles, <strong>the</strong> ratio ofcorresponding sides) throughinvestigation, using dynamic software;solve problems involving similartriangles in realistic situations (e.g.problems involving shadows,reflections, surveying);define <strong>the</strong> formulas for <strong>the</strong> sine, <strong>the</strong>cosine, and <strong>the</strong> tangent of angles, using<strong>the</strong> ratios of sides in right triangles.knowledge/understandingthinking/inquiry/problemsolvingapplicationMa<strong>the</strong>matics:<strong>Applying</strong> <strong>the</strong><strong>Concepts</strong> <strong>10</strong>, Sectionsand Page Referencessections 1.1, 1.2, 1.3,1.4pages 4−23application sections 1.5, 1.6pages 24−33knowledge/understandingcommunicationsection 1.7pages 34−38knowledge/understanding section 6.1pages 206−214thinking/inquiry/problemsolvingapplicationknowledge/understandingcommunicationSolving Problems Involving <strong>the</strong> Trigonometry of Right TrianglesPR3.01PR3.02calculate <strong>the</strong> length of a side of a righttriangle, using <strong>the</strong> Pythagorean<strong>the</strong>orem;determine <strong>the</strong> measures of <strong>the</strong> sides andangles in right triangles, using <strong>the</strong>primary trigonometric ratios;sections 6.2, [6.4]pages 215−223,231−236sections 7.1, 7.2, 7.3pages 250−273knowledge/understanding sections 6.3, 6.4pages 224−236knowledge/understandingthinking/inquiry/problemsolvingsections 7.1, 7.2, 7.3pages 250−273Correlation MFM2P to Ma<strong>the</strong>matics: <strong>Applying</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Concepts</strong> <strong>10</strong> 1
PR3.03PR3.04PR3.05solve problems involving <strong>the</strong> measuresof sides and angles in right triangles(e.g. in surveying, navigation);determine <strong>the</strong> height of an inaccessibleobject in <strong>the</strong> environment around <strong>the</strong>school, using <strong>the</strong> trigonometry of righttriangles;describe applications of trigonometry invarious occupations.thinking/inquiry/problemsolvingapplicationthinking/inquiry/problemsolvingapplicationcommunicationapplicationsections 7.1, 7.2, 7.3,7.4pages 250−278sections 7.1, 7.4pages 250−258,274−280sections 7.1, 7.2, 7.3,7.4pages 250−280Linear FunctionsCodeSpecific Expectations<strong>Applying</strong> Piecewise Linear FunctionsLF1.01LF1.02LF1.03explain <strong>the</strong> characteristics of situationsinvolving piecewise linear functions(e.g. pay scale variations, gasconsumption costs, water consumptioncosts, differentiated pricing, motion);construct tables of values and sketchgraphs to represent given descriptionsof realistic situations involvingpiecewise linear functions, with andwithout <strong>the</strong> use of graphing calculatorsor graphing software;answer questions about piecewiselinear functions by interpolation andextrapolation, and by consideringvariations on given conditions.Interpreting Systems of Linear EquationsLF2.01LF2.02LF2.03LF2.04determine <strong>the</strong> point of intersection oftwo linear relations arising from arealistic situation, using graphingcalculators or graphing software;interpret <strong>the</strong> point of intersection of twolinear relations within <strong>the</strong> context of arealistic situation;solve systems of two linear equations intwo variables by <strong>the</strong> algebraic methodsof substitution and elimination;solve problems represented by linearsystems of two equations in twovariables arising from realisticsituations, by using an algebraicmethod and by interpreting graphs.Manipulating Algebraic ExpressionsLF3.01write linear equations by generalizingfrom tables of values and by translatingwritten descriptions;Achievement ChartCategoriescommunicationapplicationknowledge/understandingapplicationknowledge/understandingthinking/inquiry/problemsolvingknowledge/understandingapplicationcommunicationapplicationMa<strong>the</strong>matics:<strong>Applying</strong> <strong>the</strong><strong>Concepts</strong> <strong>10</strong>, Sectionsand Page Referencessection 4.1pages 132−138sections 4.2, 4.3pages 139−152section 4.4pages 153−159section 5.1pages 168−174section 5.2pages 175−181knowledge/understanding sections 5.3, 5.4pages 182−196thinking/inquiry/problemsolvingapplicationsections 5.1, 5.2, .5.3,5.4pages 168−196knowledge/understanding sections 3.5, 3.6pages <strong>10</strong>4−113Correlation MFM2P to Ma<strong>the</strong>matics: <strong>Applying</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Concepts</strong> <strong>10</strong> 2
LF3.02LF3.03LF3.04rearrange equations from <strong>the</strong> formy = mx + b to <strong>the</strong> form Ax + By + C = 0,and vice versa;solve first-degree equations in onevariable, including those with fractionalcoefficients, using an algebraic method;isolate a variable in formulas involvingfirst-degree terms.knowledge/understanding section 3.7pages 114−118knowledge/understanding sections 2.1, 2.2, 2.3,2.4pages 48−71knowledge/understanding sections 2.1, 2.2, 2.3,2.4pages 48−71Quadratic FunctionsCodeSpecific ExpectationsManipulating Algebraic ExpressionsAchievement ChartCategoriesMa<strong>the</strong>matics:<strong>Applying</strong> <strong>the</strong><strong>Concepts</strong> <strong>10</strong>, Sectionsand Page ReferencesQF1.01 multiply two binomials and square abinomial;knowledge/understanding sections 9.1, 9.2pages 326−333QF1.02 expand and simplify polynomialexpressions involving <strong>the</strong> multiplyingknowledge/understanding section 9.3pages 334−337and squaring of binomials;QF1.03 describe intervals on quadraticfunctions using appropriate vocabulary(e.g. greater than, less than, between,from…to, less than 3 or greater than 7);communication throughout chapter 8and chapter <strong>10</strong>Pages 288−317,364−388QF1.04 factor polynomials by determining acommon factor;knowledge/understanding section 9.4pages 338−341QF1.05 factor trinomials of <strong>the</strong> formx 2 + bx + c;knowledge/understanding section 9.6pages 345−348QF1.06 factor <strong>the</strong> difference of squares; knowledge/understanding section 9.5pages 342−344QF1.07 solve quadratic equations by factoring. knowledge/understanding section 9.7pages 349−353Investigating <strong>the</strong> Connection Between <strong>the</strong> Graphs and <strong>the</strong> Equations of QuadraticFunctionsQF2.01QF2.02QF2.03construct tables of values, sketchgraphs, and write equationsof <strong>the</strong> formy = ax 2 + b to represent quadraticfunctions derived from descriptions ofrealistic situations (e.g. vary <strong>the</strong> sidelength of a cube and observe <strong>the</strong> effecton <strong>the</strong> surface area of <strong>the</strong> cube);identify <strong>the</strong> effect of simpletransformations (i.e. translations,reflections, vertical stretch factors) on<strong>the</strong> graph and <strong>the</strong> equation of y = x 2 ,using graphing calculators or graphingsoftware;explain <strong>the</strong> role of a, h, and k in <strong>the</strong>graph of y = a(x − h) 2 + k;knowledge/understandingapplicationknowledge/understandingcommunicationknowledge/understandingcommunicationsections 8.1, 8.2, 8.3pages 288−304sections 8.2, 8.3, 8.4pages 293−311section 8.5pages 312−317Correlation MFM2P to Ma<strong>the</strong>matics: <strong>Applying</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Concepts</strong> <strong>10</strong> 3
QF2.04expand and simplify an equation of <strong>the</strong>form y = a(x − h) 2 + k to obtain <strong>the</strong>form y = ax 2 + bx + c.Solving Problems Involving Quadratic FunctionsQF3.01QF3.02obtain <strong>the</strong> graphs of quadratic functionswhose equations are given in <strong>the</strong> formy = a(x − h) 2 + k or <strong>the</strong> formy = ax 2 + bx + c, using graphingcalculators or graphing software;determine <strong>the</strong> zeros and <strong>the</strong> maximumor minimum value of a quadraticfunction from its graph, using graphingcalculators or graphing software;knowledge/understanding section <strong>10</strong>.2pages 369−374knowledge/understanding section <strong>10</strong>.2pages 369−374knowledge/understandingthinking/inquiry/problemsolvingsections <strong>10</strong>.1, <strong>10</strong>.3,<strong>10</strong>.4pages 364−368,375−388LF3.03solve problems involving a givenquadratic function by interpreting itsgraph (e.g. given a formularepresenting <strong>the</strong> height of a ball overelapsed time, graph <strong>the</strong> function, usinga graphing calculator or graphingsoftware, and answer questions such as<strong>the</strong> following: What is <strong>the</strong> maximumheight of <strong>the</strong> ball? After what length oftime will <strong>the</strong> ball touch <strong>the</strong> ground?Over what interval is <strong>the</strong> height of <strong>the</strong>ball greater than 3 m?thinking/inquiry/problemsolvingapplicationsection<strong>10</strong>.4pages 381−388[also throughoutchapter 8 and chapter<strong>10</strong>]Correlation MFM2P to Ma<strong>the</strong>matics: <strong>Applying</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Concepts</strong> <strong>10</strong> 4