Comprehensive Study Guide For Physics 101 Laboratory Exams
Comprehensive Study Guide For Physics 101 Laboratory Exams
Comprehensive Study Guide For Physics 101 Laboratory Exams
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
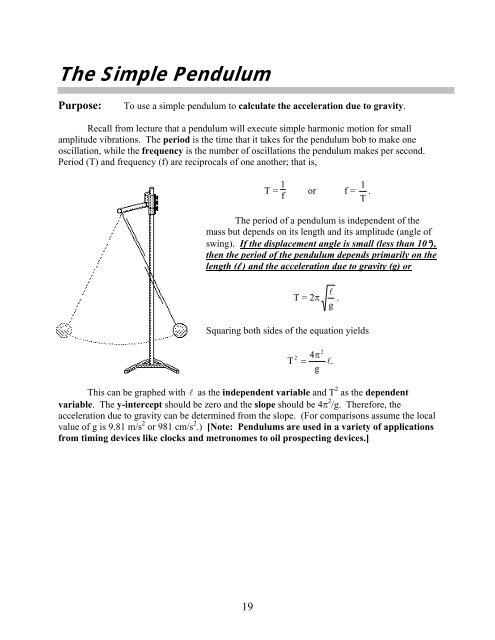
The Simple PendulumPurpose:To use a simple pendulum to calculate the acceleration due to gravity.Recall from lecture that a pendulum will execute simple harmonic motion for smallamplitude vibrations. The period is the time that it takes for the pendulum bob to make oneoscillation, while the frequency is the number of oscillations the pendulum makes per second.Period (T) and frequency (f) are reciprocals of one another; that is,T = 1 for f = T1 .The period of a pendulum is independent of themass but depends on its length and its amplitude (angle ofswing). If the displacement angle is small (less than 10),then the period of the pendulum depends primarily on thelength (l ) and the acceleration due to gravity (g) orT = 2 g .Squaring both sides of the equation yieldsT24g2.This can be graphed with as the independent variable and T 2 as the dependentvariable. The y-intercept should be zero and the slope should be 4 2 /g. Therefore, theacceleration due to gravity can be determined from the slope. (<strong>For</strong> comparisons assume the localvalue of g is 9.81 m/s 2 or 981 cm/s 2 .) [Note: Pendulums are used in a variety of applicationsfrom timing devices like clocks and metronomes to oil prospecting devices.]19











![[pdf] physics 110 fundamentals of electronics](https://img.yumpu.com/29312006/1/190x245/pdf-physics-110-fundamentals-of-electronics.jpg?quality=85)