218100 - Frederiksen
218100 - Frederiksen
218100 - Frederiksen
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
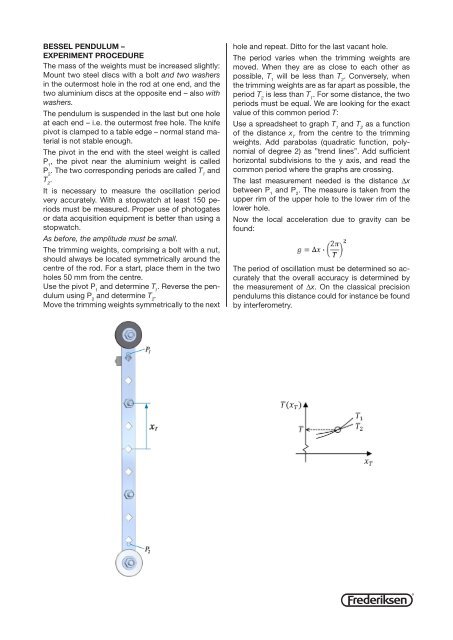
Bessel pendulum –experiment procedureThe mass of the weights must be increased slightly:Mount two steel discs with a bolt and two washersin the outermost hole in the rod at one end, and thetwo aluminium discs at the opposite end – also withwashers.The pendulum is suspended in the last but one holeat each end – i.e. the outermost free hole. The knifepivot is clamped to a table edge – normal stand materialis not stable enough.The pivot in the end with the steel weight is calledP 1, the pivot near the aluminium weight is calledP 2. The two corresponding periods are called T 1andT 2.It is necessary to measure the oscillation periodvery accurately. With a stopwatch at least 150 periodsmust be measured. Proper use of photogatesor data acquisition equipment is better than using astopwatch.As before, the amplitude must be small.The trimming weights, comprising a bolt with a nut,should always be located symmetrically around thecentre of the rod. For a start, place them in the twoholes 50 mm from the centre.Use the pivot P 1and determine T 1. Reverse the pendulumusing P 2and determine T 2.Move the trimming weights symmetrically to the nexthole and repeat. Ditto for the last vacant hole.The period varies when the trimming weights aremoved. When they are as close to each other aspossible, T 1will be less than T 2. Conversely, whenthe trimming weights are as far apart as possible, theperiod T 2is less than T 1. For some distance, the twoperiods must be equal. We are looking for the exactvalue of this common period T:Use a spreadsheet to graph T 1and T 2as a functionof the distance x Tfrom the centre to the trimmingweights. Add parabolas (quadratic function, polynomialof degree 2) as ”trend lines”. Add sufficienthorizontal subdivisions to the y axis, and read thecommon period where the graphs are crossing.The last measurement needed is the distance Δxbetween P 1and P 2. The measure is taken from theupper rim of the upper hole to the lower rim of thelower hole.Now the local acceleration due to gravity can befound:The period of oscillation must be determined so accuratelythat the overall accuracy is determined bythe measurement of Δx. On the classical precisionpendulums this distance could for instance be foundby interferometry.®