Chapter 16 Recap - Honors Chemistry Coursework
Chapter 16 Recap - Honors Chemistry Coursework
Chapter 16 Recap - Honors Chemistry Coursework
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
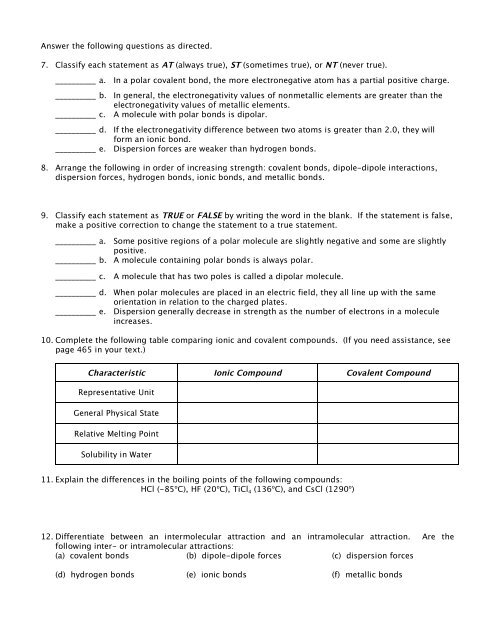
Answer the following questions as directed.7. Classify each statement as AT (always true), ST (sometimes true), or NT (never true).__________ a. In a polar covalent bond, the more electronegative atom has a partial positive charge.__________ b. In general, the electronegativity values of nonmetallic elements are greater than theelectronegativity values of metallic elements.__________ c. A molecule with polar bonds is dipolar.__________ d. If the electronegativity difference between two atoms is greater than 2.0, they willform an ionic bond.__________ e. Dispersion forces are weaker than hydrogen bonds.8. Arrange the following in order of increasing strength: covalent bonds, dipole-dipole interactions,dispersion forces, hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and metallic bonds.9. Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE by writing the word in the blank. If the statement is false,make a positive correction to change the statement to a true statement.__________ a. Some positive regions of a polar molecule are slightly negative and some are slightlypositive.__________ b. A molecule containing polar bonds is always polar.__________ c. A molecule that has two poles is called a dipolar molecule.__________ d. When polar molecules are placed in an electric field, they all line up with the sameorientation in relation to the charged plates.__________ e. Dispersion generally decrease in strength as the number of electrons in a moleculeincreases.10. Complete the following table comparing ionic and covalent compounds. (If you need assistance, seepage 465 in your text.)Characteristic Ionic Compound Covalent CompoundRepresentative UnitGeneral Physical StateRelative Melting PointSolubility in Water11. Explain the differences in the boiling points of the following compounds:HCl (-85 o C), HF (20 o C), TiCl 4 (136 o C), and CsCl (1290 o )12. Differentiate between an intermolecular attraction and an intramolecular attraction. Are thefollowing inter- or intramolecular attractions:(a) covalent bonds (b) dipole-dipole forces (c) dispersion forces(d) hydrogen bonds (e) ionic bonds (f) metallic bonds