Calculation of Eddy Current Losses in Permanent Magnets of ...
Calculation of Eddy Current Losses in Permanent Magnets of ...
Calculation of Eddy Current Losses in Permanent Magnets of ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
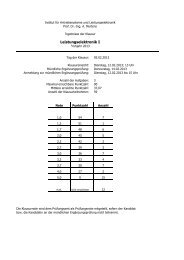
OverviewFachbereich Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik- Introduction- Considered PM synchronous motors- Loss calculation methods- Loss estimation from thermal measurements- ConclusionsInstitut für ElektrischeEnergiewandlungDipl.-Ing. Csaba Deak 1
Loss calculation methodsFachbereich Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik1000 rpm, no-load operationFlux density for Motor AB(x) at upper surfaceInstitut für ElektrischeEnergiewandlungFEMAG-DC(no eddy currents considered!)Dipl.-Ing. Csaba Deak 5
Loss calculation methodsFachbereich Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik1000 rpm, no-load operationUppersurfaceMiddlesurfaceBottomsurfaceFlux density for Motor AInstitut für ElektrischeEnergiewandlungFEMAG-DC(no eddy currents considered!)Dipl.-Ing. Csaba Deak 6
Loss calculation methodsFachbereich Elektrotechnik und InformationstechnikFlux density at no-load operationMotor AFlux densityMotor BMotor C1000 rpm, upper surfaceMotor DInstitut für ElektrischeEnergiewandlungFEMAG-DC(no eddy currents considered!)Dipl.-Ing. Csaba Deak 7
Loss calculation methodsFachbereich Elektrotechnik und InformationstechnikInstitut für ElektrischeEnergiewandlungFlux density at load operationMotor AS<strong>in</strong>usoidal currentMotor BMotor C Motor D1000 rpm, upper surfaceFEMAG-DC(no eddy currents considered!)Dipl.-Ing. Csaba Deak 8
Loss calculation methodsMethod 1: 1 FEMAG-DC & Analytical FormulaFachbereich Elektrotechnik und InformationstechnikVector potential<strong>Current</strong> densityAlternat<strong>in</strong>g current density∫b M<strong>Losses</strong> <strong>in</strong> magnetsb~Jz( x)⋅dx=b0Considered <strong>in</strong> each <strong>of</strong> the three surfaces (upper, middle, bottom)~Institut für ElektrischeEnergiewandlungDipl.-Ing. Csaba Deak 9
Loss calculation methodsMethod 2: 2 FEMAG DC - Version 05/2007Fachbereich Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik- No reaction field <strong>of</strong> eddy currents considered- Maxwell equations- Fast calculation rotE= −∂B/ ∂t J = κE- For magnets with rather low conductivity (small eddy currents)Method 2 is similar to Method 1, butis considered over the magnet cross section and not only<strong>in</strong> the three surfaces∫A MJz( x,y)⋅ dx ⋅dy= 0Institut für ElektrischeEnergiewandlungDipl.-Ing. Csaba Deak 10
Loss calculation methodsInfluence <strong>of</strong> eddy current reaction fieldFachbereich Elektrotechnik und InformationstechnikPenetration depth:dE=κMg⋅π⋅1fB,Mg⋅ µRatio b Mg/ d E≤ 1 → no eddy current reaction fieldEx.: n = 3000 rpm; f s= 400 Hz; f B,Mg= 1200 Hz (q = ½)Motor A Motor Bb Mg,A= 3.6 mmb Mg,B= 27.3 mmκ Mg,A= 0.62 · 10 6 S/m κ Mg,B= 0.43 · 10 6 S/md E,A= 17.8 mmd E,B= 21.6 mmb Mg,A/ d E,A= 0.2 b Mg,B/ d E,B= 1.26MgMotor Ab Mg,AMotor Bb Mg,BInstitut für ElektrischeEnergiewandlungDipl.-Ing. Csaba Deak 11
Loss calculation methodsMethod 3: 3 2D Time-step calculationFachbereich Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik- Reaction field <strong>of</strong> eddy currents considered- Full set <strong>of</strong> Maxwell equationsrotErotH= −∂B/ ∂t= κE- For general purpose up to medium frequencies valid- Very time consum<strong>in</strong>gJ=JB= µ HInstitut für ElektrischeEnergiewandlungDipl.-Ing. Csaba Deak 12
Loss calculation methodsFachbereich Elektrotechnik und InformationstechnikP Mg [W]350300250200150100500Motor ANo-load 1000 rpmMethod1: FEMAG + AnalyticalMethod2: FEMAGMethod3: Time stepp<strong>in</strong>gA B C D G HComparisonP Mg [W]350300250200150100500No-load 3000 rpmMethod1: FEMAG + AnalyticalMethod2: FEMAGMethod3: Time stepp<strong>in</strong>gA B C D G HMotor B Motor C Motor D Motor G Motor HInstitut für ElektrischeEnergiewandlungq = ½q = ¼Dipl.-Ing. Csaba Deak 13
Loss calculation methodsFachbereich Elektrotechnik und InformationstechnikP Mg [W]2000180016001400120010008006004002000Load 1000 rpmMethod1: FEMAG + AnalyticalMethod2: FEMAGMethod3: Time stepp<strong>in</strong>gA B C D G HComparisonS<strong>in</strong>usoidal currentP Mg [W]22002000180016001400120010008006004002000Load 3000 rpmMethod1: FEMAG + AnalyticalMethod2: FEMAGMethod3: Time stepp<strong>in</strong>gA B C D G HMotor A Motor B Motor C Motor D Motor G Motor HInstitut für ElektrischeEnergiewandlungq = ½q = ¼Dipl.-Ing. Csaba Deak 14
Loss estimation from thermal measurements<strong>Losses</strong> at adiabatic heat<strong>in</strong>gFachbereich Elektrotechnik und InformationstechnikTemperature [°C]1009080706050403020100<strong>Losses</strong>:∆tMagnet temperature∆ϑ0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240Time [m<strong>in</strong>]P = m·c·dϑ/dtMotor A: 1000 rpmload operationUseful only as the ratio <strong>of</strong> the dϑ/dt valuesby the different motor configuration!!Motor ATemperature sensorMotor GInstitut für ElektrischeEnergiewandlungDipl.-Ing. Csaba Deak 15
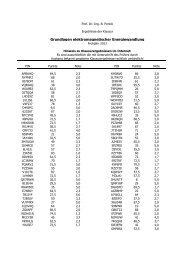
Fachbereich Elektrotechnik und InformationstechnikP Mg / P Mg0,A9080706050403020100Loss estimation from thermal measurementsNo- load 1000 rpmCalculatedMeasuredA B C E F GComparison(all values related to Motor A, 1000 rpm, no-load operation P Mg0,A)<strong>Losses</strong> <strong>in</strong> rotor iron. bridge and magnetsP Mg / P Mg0,A9080706050403020100No- load 3000 rpmCalculatedMeasured<strong>Losses</strong> <strong>in</strong> rotor iron. bridge and magnetsA B C E F GMotor A Motor B Motor C Motor E Motor F Motor Gq = ½Institut für ElektrischeEnergiewandlungq = ¼Dipl.-Ing. Csaba Deak 16
Loss estimation from thermal measurementsFachbereich Elektrotechnik und InformationstechnikP Mg / P Mg0,A9080706050403020100Comparison(all values related to Motor A, 1000 rpm, no-load operation P Mg0,A )Load 1000 rpmCalculatedMeasured<strong>Losses</strong> <strong>in</strong> rotor iron. bridge and magnetsA B C E F GP Mg / P Mg0,A200180160140120100806040200Load 3000 rpmCalculatedMeasured<strong>Losses</strong> <strong>in</strong> rotor iron. bridge and magnetsA B C E F GMotor A Motor B Motor C Motor E Motor F Motor Gq = ½Institut für ElektrischeEnergiewandlungq = ¼Dipl.-Ing. Csaba Deak 17
ConclusionsFachbereich Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik- 3 loss calculation methods: FEMAG-DC & analytical formulaFEMAG-DC- 8 motors : 2 Stators (q = ½ ; q = ¼ )Time stepp<strong>in</strong>g4 Rotors (segmented/non-segmented; surface/buried)- eddy-current losses <strong>in</strong> magnets are possible to be calculatedwith DC method (no eddy current reaction field) due to the ratherlow conductivity <strong>of</strong> rare-earth magnets- loss estimation from adiabatic thermal heat<strong>in</strong>g is possiblema<strong>in</strong>ly for surface-mounted permanent magnets- for buried magnets: <strong>in</strong>fluence <strong>of</strong> bridge losses to be<strong>in</strong>vestigated furtherInstitut für ElektrischeEnergiewandlungDipl.-Ing. Csaba Deak 18
<strong>Calculation</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Eddy</strong> <strong>Current</strong> <strong>Losses</strong><strong>in</strong> <strong>Permanent</strong> <strong>Magnets</strong>Fachbereich Elektrotechnik und InformationstechnikThank you for your attention!Institut für ElektrischeEnergiewandlungcdeak@ew.tu-darmstadt.deDipl.-Ing. Csaba Deak 19