SWOT Analysis Report Matrix - Final (4th Revision) - Strategic ...
SWOT Analysis Report Matrix - Final (4th Revision) - Strategic ...
SWOT Analysis Report Matrix - Final (4th Revision) - Strategic ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
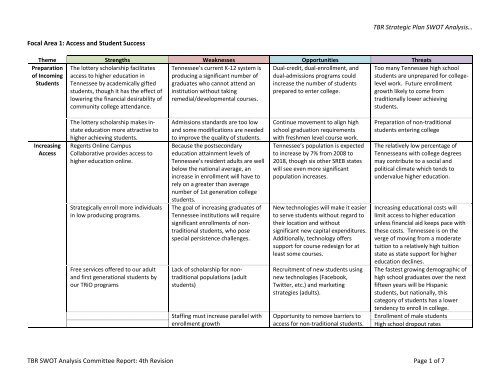
TBR <strong>Strategic</strong> Plan <strong>SWOT</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong>…Focal Area 2: Institution Quality (continued)Theme Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities ThreatsAcademicProgramQualityPass rates on licensure exams arecompetitive with national averagesStrong business and nursingprograms of study at the communitycollegesStrong transition programs [generaleducation, AA and AS] of study tothe four‐year institutions at thecommunity collegesArticulation policy to move studentsfrom the TTC’s to the communitycolleges and then to theuniversities. Smooth articulationprocess.Good DSP programs experimentingwith making the remediationprograms stronger, and more timeand economically viable for studentsthus moving the student morerapidly toward occupational goalsMany academic programs enjoy anational reputation for excellence.Dynamic online learning statewidecollaborative: ROCCPhilosophical move of TBR andcommunity college leadership fromthe comprehensive mission of thecommunity collegeInconsistent vocational andacademic counseling of studentsLack of funding for upgrades tofacilities for student learning andresearchRetention and graduation rates arelower than our peers‐‐indicative ofproblems in getting studentsconnected, in overcoming theirfinancial problems or other barriersto success, or academicperformanceInstitutions need to increase therigor of some of their academicprograms in order to attainexcellence, to help ensure theirgraduates acquire the knowledgeand skills that will give them acompetitive advantage.Loss of institution identity whencommercializing.Need more cross‐discipline teachingfor courses that have the samegeneral content except for a smalldepartment‐specific component.New emphasis beginning withemphases to raise academic level ofincoming freshmen through multipleinitiatives (e.g. Tennessee DiplomaProject, Ramp‐up, Gear‐up, math“bridge” courses, etc.)New technology in student successresearch.Ability to do data driven research.We need to find a way for TBR toassist the academic community inasserting itself through the electoralprocess.E learning pilotsWhat appears to be a general lack ofunderstanding on the part of thelegislature as to the mission ofhigher education in TennesseeState budget seeing diminishedrevenues for the foreseeable futureContinued need for remediation onhigh percentage of incomingtraditional‐age freshmenThe political climate will impact howthe governor and legislature chooseto fund the TBR system.Gubernatorial support of only oneor two research‐level institutions.Too much politicking at the statelevel with regards to new programs.TBR <strong>SWOT</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong> Committee <strong>Report</strong>: <strong>4th</strong> <strong>Revision</strong> Page 4 of 7
TBR <strong>Strategic</strong> Plan <strong>SWOT</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong>…Focal Area 3: Affordability, Awareness, and AspirationTheme Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities ThreatsLottery Scholarships have provided Lack of need‐based opportunities Implementation of cost estimatorsawareness and opportunities for available to adult students. Lack of at community colleges andhigher education.scholarships for transfer, adult, universities.Cost ofattendingCollegeResourcefulnessLower costs of TTC’s and communitycolleges.Cost of education is centralized andcan be coordinated via CentralOfficeImplementing models to reducetextbook costs, such as open‐sourcemodels and campus initiatives.Tuition and fees in Tennessee areaverage among SREB states andbelow the US average.Regents Online CampusCollaborative eliminates duplicationof online classes by campuses.Room for growth in developmentand private donations (local color)Growth in Sponsored Researchprograms in the last five years.Most funds available are for fouryear universitiesLibraries have partnerships forreducing costs of materials.returning studentsOnline course costs are aboveaverage.Cost of textbooks and other learningmaterials.System level administrative costsneed review.Progressively rising tuition costs.Under‐utilization of potential grantwritingopportunitiesNeed more faculty involvement inefforts to gain support from externalfunding sources. Faculty/programsneed to become more involved inthe public face of the institutions.Partnership with K‐12 to stimulatediscussions of affordability, costestimates, types of available aid,etc., at the middle‐school level toplant seeds early.Campaign to our legislators andother elected officials the need for,and benefits of, need based aidprograms for adult students.Federal Requirement that textbookcosts and processes will have to beclearly stated by bookstore.Partner with THEC on the annualtuition cost increasesThe public understands that highereducation is tuition drivenInject more resources into fundraising. TBR could help educatecampuses on how to improve fundraising efforts Utilize or maximizeprospecting methods or tools.Potential to expand research anddevelopment funding with industry,etc.Implement plans to grow our grantwritingprograms. Grants for needbasedopportunities and/oraffordability programs for ruralareas or for adult students.Expand revenue by licensing ofintellectual propertyDeclining value of the US dollar andunstable economy could furtherimpact the cost of educationCompetition for students from otherstates, competition between instate‐institutionsfor RODP students.State appropriations per FTEstudent need to be increasedsubstantially while minimizingincreases in tuition and student feesFailure of higher education systemsand institutions to explain risingcosts will threaten public support.Lack of financial planning andresearch of cost by families whohave the income resources.Decrease in out‐of‐state studentsdue to rising costs.Reduced levels of private donationsSlow/limited growth of NIH and NSFresearch support.Ability of financial aid to covertuition gap could decrease.TBR <strong>SWOT</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong> Committee <strong>Report</strong>: <strong>4th</strong> <strong>Revision</strong> Page 5 of 7
TBR <strong>Strategic</strong> Plan <strong>SWOT</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong>…Focal Area 4: Environmental ConditionsTheme Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities ThreatsCompetitiveEnvironmentEducational environment attractiveto out‐of‐state studentsSize of adult populations withoutdegreesStudent achievement initiative;Momentum Point CalculationTN traditionally one of the leasteducated states.Per FTE funding in lower rangecompared to SREB statesCompare TN system level data toother system level dataSome areas of the state are growingwhile others are losing population.Behind in delivery of alternatemethods of course delivery.Growing Hispanic population withcorresponding educational needsLower per capita income comparedto SREB and national indexGetting to potential adult students Increase in for‐profit schools.Low state tax rate, compared toSREB and national index, favorableto attracting industriesUncertain status of pool ofinternational students.External scholarship GPArequirementsLeadershipAndGovernanceCommunity confidence inPresidential leadershipWorking with sister institutions tocoordinate TTC graduates tocontinue educationPresence of institution leaders incommunity. Communityinvolvement and enhancement byinstitution leadership.System governance structureshould facilitate the possibility ofcoordination between universitiesand community colleges to increasegraduation rates througharticulation agreements, etc.Program and service duplicationUncertainty in future leadershipand direction of higher educationsystemIncreased bureaucracy/reportingrequirements for compliance withregulations and mandates at alllevels.Current funding formula diminishescapacity of the state to allocateresources appropriately toinstitutions with increasingenrollments or graduation rates.Funding formulas based ongraduation rates withoutconsidering particular subcategoriesof students such as nontraditional,low income, or minority studentswill undermine the larger goal ofincreasing the number of degrees.Opportunity to rethink internalgovernance and decision makingprocessesOpportunity to rethink externalgovernance and decision makingprocessesTBR institutional locations aroundthe state, nation, and worldwide.Right‐sizing the number and types ofprograms at each school—politicalwill to get this right.Commercialization of collegecampuses“Methods” based education andrigid basis for credentialing teachersmay inhibit opportunity to enlistretirees.Funding formulae of the State (i.e.THEC) that under‐fundsoccupational, technical andworkforce programs of study, bothcredit and non‐creditProducing more graduates inTennessee will almost certainlyrequire creativity and innovation atthe campus level, though this is notalways encouraged by currentnorms within the Board of Regentssystem.TBR <strong>SWOT</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong> Committee <strong>Report</strong>: <strong>4th</strong> <strong>Revision</strong> Page 6 of 7
TBR <strong>Strategic</strong> Plan <strong>SWOT</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong>…Focal Area 4: Environmental Conditions (continued)Theme Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities ThreatsEconomicLeadershipTTC‐Regents online professionaldevelopment and Regents OnlineContinuing Education – workforcedevelopmentStudents who complete a programof study in the health sciences,business, or technology generallyhave marketable skills.TTC’s and community collegesemphasize job placement for theircommunities. Placement rates ofcomm. college grads arecomparable to peers.Some universities have increaseddoctoral and professional degreesawarded, especially in the healthsciences, to meet regional andnational demands.HOPE Scholarships and TELS Wilder‐Naifeh Technical Skills Grant.Colleges ,universities andTechnology Centers seen as criticalto their local regionsLarge number of high schoolstudents and adults who mightenroll in community colleges andtechnology centers who want quicktraining for a new careerNew value placed on education asan advantage in the employmentmarketplace, recognized need toimprove college going rates.Short turn around for thedevelopment of special industryprograms to meet needs.Limited or isolated partnershipswith business, industry, and otherstate agencies.Non‐equitable service to businessand industry throughout the stateCurrently, there are not enoughqualified faculty to train studentsfor the career areas in whichworkers are most needed in thisstate.Lack of quantifiable data reportingeconomic leadership elementsSchool’s outreach to thecommunitiesWorkforce viewed asunderprepared for demands ofcurrent/future technology jobs2 year schools and 4 year schoolshave very different IT needs andchallenges.Through partnerships with business,industry, the creation of new facultyendowments for new programs maybe possible.New federal funding sources foreconomic leadership initiatives suchas in green job education andtrainingTBR beginning to renew economicand labor department ties for alllevels of higher education,partnerships with secondaryeducation, career and technicalclasses, and dept of education.Place more emphasis uponeconomic development byanticipating workforce needs andthen by modifying their programs tomatch those needs.Intervention by higher education toassist in STEM areasRise in unemployment. Size of adultpopulations without degrees.Changing industry needs provideopportunities for working togetherNew Veterans BenefitsAttractive to high skills industriesLimited vision by other stateagencies that only the TTC’s are theeconomic leadership elements ofthe TBRLack of statewide vision foreconomic leadership, particularly inthe area of integration of thecommunity colleges within a planOff‐shore outsourcing of high‐skill,high‐wage jobsOff‐shore outsourcing of high‐skill,high‐wage jobsSpikes in enrollment based oneconomyTBR <strong>SWOT</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong> Committee <strong>Report</strong>: <strong>4th</strong> <strong>Revision</strong> Page 7 of 7