No. 12. GILPAT.pdf - Marine Institute Open Access Repository
No. 12. GILPAT.pdf - Marine Institute Open Access Repository
No. 12. GILPAT.pdf - Marine Institute Open Access Repository
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
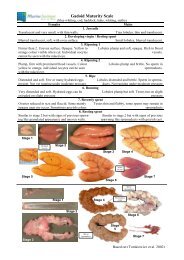
NDP <strong>Marine</strong> Research Sub-Programme 2007-20132004). Since 2003, gill disorders have emerged as the most serious cause of mortality in Irishfarmed salmon (Rodger 2007). Average mortalities in marine farms due to gill disorders duringthe period 2003-2005 have been 12%, ranging from 1-79%. All marine stages of production areaffected, however preliminary investigations showed that the younger, post-smolt stage salmonappear to be more severely affected in terms of mortality and that the majority of gillproblems occur in the summer or autumn months with S1 smolts (Rodger 2007). In 2005 aprotracted bloom of Karenia mikimotoi resulted in mortalities of both farmed and wild fishalong the west coast of Ireland (Silke et al. 2005).The aetiology of gill disorders are believed to be multifactorial and can originate with oneprimary insult which then allows secondary opportunistic pathogens to infect, resulting inepithelial damage and respiratory distress for the host fish. As the infectious agents remainundefined, medication and vaccination are not feasible and preventive measures taken againstgill pathologies have proven insufficient. This study aimed to clarify the role of potentiallyharmful water borne organisms and pathogens which should then lead to strategies ormethods to reduce the impact or exposure on aquaculture sites.1.2. Possible Causes of Gill PathologiesThe possible causes of gill pathologies have been grouped into a number of broad categories(Rodger 2007). The two major categories of significance to Ireland are 1) phytoplanktonblooms and 2) zooplankton blooms. Two other categories include 3) gill parasites and 4)bacterial and viral pathogens, of which there is limited information available in Ireland and theirrole in the development of gill pathologies is unknown.1.2.1. Phytoplankton bloomsAlgal blooms can give rise to gill pathologies through direct physical damage e.g. Chaetocerossp., where the diatom skeletons or silicacaeous spicules cause irritation of the gill epithelia(Kent et al. 1995; Treasurer et al. 2003). In addition, the production of toxins from speciessuch as Karenia mikimotoi can cause high mortalities (Silke et al. 2005; Mitchell & Rodger 2007)and through deoxygenation following phytoplankton die-off (Richardson 1997).1.2.2. Zooplankton bloomsHarmful zooplankton swarms such as siphonophores (pelagic hydrozoans e.g. Apolemia uvaria,Muggiaea atlantica), scyphozoans (jellyfish e.g. Cyanea capillata, Pelagia noctiluca), and hydrozoans(e.g. Solmaris corona) can cause direct damage to the gill tissue through the effects of their2