Biaxial tripod MEMS mirror and omnidirectional lens for a low cost ...
Biaxial tripod MEMS mirror and omnidirectional lens for a low cost ...
Biaxial tripod MEMS mirror and omnidirectional lens for a low cost ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
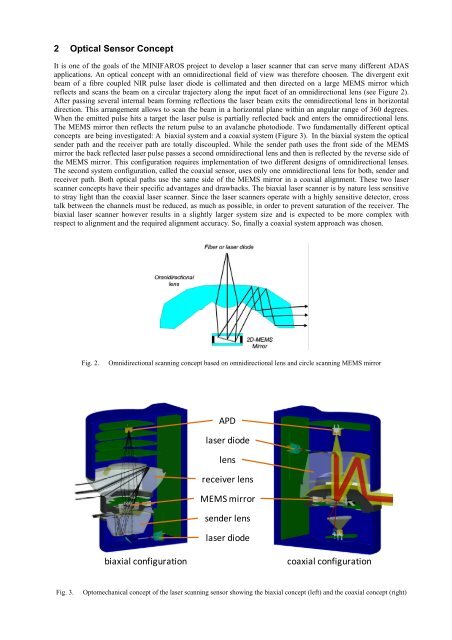
2 Optical Sensor ConceptIt is one of the goals of the MINIFAROS project to develop a laser scanner that can serve many different ADASapplications. An optical concept with an <strong>omnidirectional</strong> field of view was there<strong>for</strong>e choosen. The divergent exitbeam of a fibre coupled NIR pulse laser diode is collimated <strong>and</strong> then directed on a large <strong>MEMS</strong> <strong>mirror</strong> whichreflects <strong>and</strong> scans the beam on a circular trajectory along the input facet of an <strong>omnidirectional</strong> <strong>lens</strong> (see Figure 2).After passing several internal beam <strong>for</strong>ming reflections the laser beam exits the <strong>omnidirectional</strong> <strong>lens</strong> in horizontaldirection. This arrangement al<strong>low</strong>s to scan the beam in a horizontal plane within an angular range of 360 degrees.When the emitted pulse hits a target the laser pulse is partially reflected back <strong>and</strong> enters the <strong>omnidirectional</strong> <strong>lens</strong>.The <strong>MEMS</strong> <strong>mirror</strong> then reflects the return pulse to an avalanche photodiode. Two fundamentally different opticalconcepts are being investigated: A biaxial system <strong>and</strong> a coaxial system (Figure 3). In the biaxial system the opticalsender path <strong>and</strong> the receiver path are totally discoupled. While the sender path uses the front side of the <strong>MEMS</strong><strong>mirror</strong> the back reflected laser pulse passes a second <strong>omnidirectional</strong> <strong>lens</strong> <strong>and</strong> then is reflected by the reverse side ofthe <strong>MEMS</strong> <strong>mirror</strong>. This configuration requires implementation of two different designs of <strong>omnidirectional</strong> <strong>lens</strong>es.The second system configuration, called the coaxial sensor, uses only one <strong>omnidirectional</strong> <strong>lens</strong> <strong>for</strong> both, sender <strong>and</strong>receiver path. Both optical paths use the same side of the <strong>MEMS</strong> <strong>mirror</strong> in a coaxial alignment. These two laserscanner concepts have their specific advantages <strong>and</strong> drawbacks. The biaxial laser scanner is by nature less sensitiveto stray light than the coaxial laser scanner. Since the laser scanners operate with a highly sensitive detector, crosstalk between the channels must be reduced, as much as possible, in order to prevent saturation of the receiver. Thebiaxial laser scanner however results in a slightly larger system size <strong>and</strong> is expected to be more complex withrespect to alignment <strong>and</strong> the required alignment accuracy. So, finally a coaxial system approach was chosen.Fig. 2.Omnidirectional scanning concept based on <strong>omnidirectional</strong> <strong>lens</strong> <strong>and</strong> circle scanning <strong>MEMS</strong> <strong>mirror</strong>APDlaser diode<strong>lens</strong>receiver <strong>lens</strong><strong>MEMS</strong> <strong>mirror</strong>sender <strong>lens</strong>laser diodebiaxial configurationcoaxial configurationFig. 3.Optomechanical concept of the laser scanning sensor showing the biaxial concept (left) <strong>and</strong> the coaxial concept (right)