Trigonometry
Trigonometry
Trigonometry
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
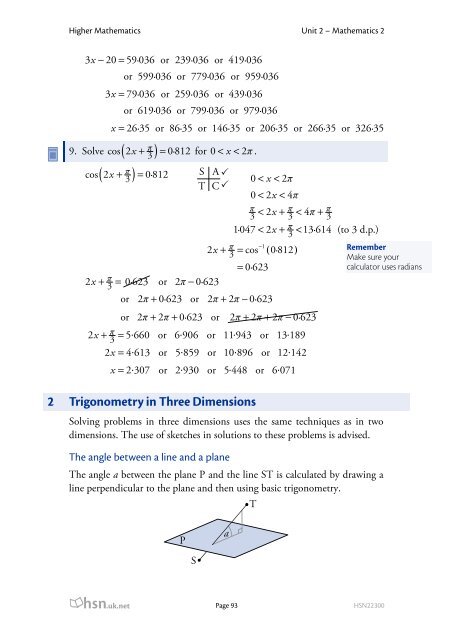
Higher Mathematics Unit 2 – Mathematics 23x− 20 = 59·036 or 239·036 or 419·036or 599·036 or 779·036 or 959·0363x= 79·036 or 259·036 or 439·036or 619·036 or 799·036 or 979·036x = 26·35 or 86·35 or 146·35 or 206·35 or 266·35 or 326·359. Solve ( x π3 )( x π)cos 2 + = 0·812 for 0 < x < 2π.cos 2 + 3 = 0·812 S A ̌0 < x < 2πT C ̌0 < 2x< 4ππ < + π < π + π3 2x3 4 31·047 < 2x+ π3 < 13·614 (to 3 d.p.)12x π −+ 3 = cos ( 0·812 )RememberMake sure your= 0·623calculator uses radians2x+ π3 = 0·623 or 2π− 0·623or 2π + 0·623 or 2π + 2π− 0·623or 2π + 2π + 0·623 or 2π + 2π + 2π− 0·6232x+ π . . . .3 = 5 660 or 6 906 or 11 943 or 13 1892x= 4. 613 or 5. 859 or 10. 896 or 12.142x = 2. 307 or 2. 930 or 5. 448 or 6.0712 <strong>Trigonometry</strong> in Three DimensionsSolving problems in three dimensions uses the same techniques as in twodimensions. The use of sketches in solutions to these problems is advised.The angle between a line and a planeThe angle a between the plane P and the line ST is calculated by drawing aline perpendicular to the plane and then using basic trigonometry.TPaShsn.uk.netPage 93HSN22300