A Pediatric Care Provider Oral Health Assessment Form
A Pediatric Care Provider Oral Health Assessment Form
A Pediatric Care Provider Oral Health Assessment Form
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
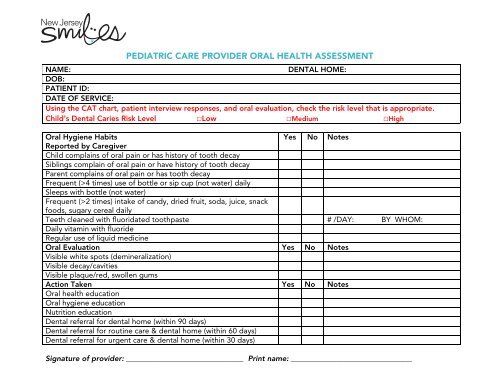
PEDIATRIC CARE PROVIDER ORAL HEALTH ASSESSMENTNAME: DENTAL HOME:DOB:PATIENT ID:DATE OF SERVICE:Using the CAT chart, patient interview responses, and oral evaluation, check the risk level that is appropriate.Child’s Dental Caries Risk Level □Low □Medium □High<strong>Oral</strong> Hygiene HabitsYes No NotesReported by <strong>Care</strong>giverChild complains of oral pain or has history of tooth decaySiblings complain of oral pain or have history of tooth decayParent complains of oral pain or has tooth decayFrequent (>4 times) use of bottle or sip cup (not water) dailySleeps with bottle (not water)Frequent (>2 times) intake of candy, dried fruit, soda, juice, snackfoods, sugary cereal dailyTeeth cleaned with fluoridated toothpaste # /DAY: BY WHOM:Daily vitamin with fluorideRegular use of liquid medicine<strong>Oral</strong> Evaluation Yes No NotesVisible white spots (demineralization)Visible decay/cavitiesVisible plaque/red, swollen gumsAction Taken Yes No Notes<strong>Oral</strong> health education<strong>Oral</strong> hygiene educationNutrition educationDental referral for dental home (within 90 days)Dental referral for routine care & dental home (within 60 days)Dental referral for urgent care & dental home (within 30 days)Signature of provider: _______________________________ Print name: ________________________________
American Academy of <strong>Pediatric</strong> Dentistry Caries Risk <strong>Assessment</strong> Tool (CAT*)ClinicalConditionsEnvironmentalCharacteristicsGeneral <strong>Health</strong>ConditionsLow risk Moderate risk High risk• No caries• No enamel demineralization• No visible plaque• No gingivitis• Optimal systemic topicalfluoride exposure• Consumption of simple sugarsor foods strongly associatedwith caries initiation primarily atmealtimes• High caregiver socioeconomicstatus• Regular use of dental care in anestablished dental home• Carious teeth in past 24 months• 1 area of enameldemineralization (enamel• Caries “white spots lesions”)• Gingivitis• Suboptimal systemic fluorideexposure with optimal topicalexposure• Occasional (1-2) between-mealexposures to simple sugars orfoods strongly associated withcaries• Mid-level caregiversocioeconomic status (i.e.,eligible for school lunchprogram or SCHIP)• Irregular use of dental services• Carious teeth in the past 12 months• More than 1 area of enameldemineralization• (enamel caries, “white spot lesions”• Visible plaque on anterior frontteeth• Radiographic enamel caries• High titers of mutans streptococci• Wearing dental or orthodonticappliances• Enamel hypoplasia• Suboptimal topical fluorideexposure• Frequent (i.e. 3 or more) betweenmealexposures to simple sugars orfoods strongly associated withcaries• Low-level caregiver socioeconomicstatus (i.e. Eligible for Medicaid)• No usual source of dental care• Active caries present in the mother• Children with special health careneeds• Conditions impairing salivacomposition/flow*AAPD, Council on Clinical Affairs, www.aapd.org