T cell Receptor
T cell Receptor
T cell Receptor
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
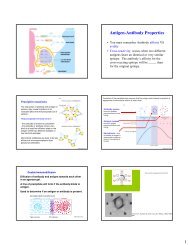
Accessory Molecules Involvedin Cell-Cell InteractionsCell Adhesion:T CellCD2- (LFA-2)LFA-1Ligand on APCLFA-3ICAM-1, ICAM-2LFA = Leukocyte Function-associatedAntigenICAM = InterCellular Adhesion MoleculeCostimulatory Molecules• Molecules on T <strong>cell</strong> and 2 nd <strong>cell</strong> that engageto deliver 2 nd signal required for activation ofT <strong>cell</strong>• Most important co-stimulatory molecules:T <strong>cell</strong> Ligand on 2 nd <strong>cell</strong>CD28 B7-1 (CD80), B7-2 (CD86)CTLA-4 B7-1 (CD80), B7-2 (CD86)CD45RCD22CD4/CD8 MHC-I/IIT <strong>cell</strong>APCAlloreactive T <strong>cell</strong>s• Allogeneic – genetically different individual of thesame species (humans!!)• MHC molecules are alloantigens: CD4 T <strong>cell</strong>s arealloreactive to MHC-II alloantigens and CD8 T<strong>cell</strong>s are alloreactive to MHC-I alloantigens• Direct and Indirect recognition of alloantigens: a)nonself MHC moleucle on foreign <strong>cell</strong> recognizedin its native form; b) peptides from allogeneicMHC after processing are prpresented by self-MHC molecules• The End6