Digital Terrestrial Broadcasting: Innovation and Development or a ...
Digital Terrestrial Broadcasting: Innovation and Development or a ...
Digital Terrestrial Broadcasting: Innovation and Development or a ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
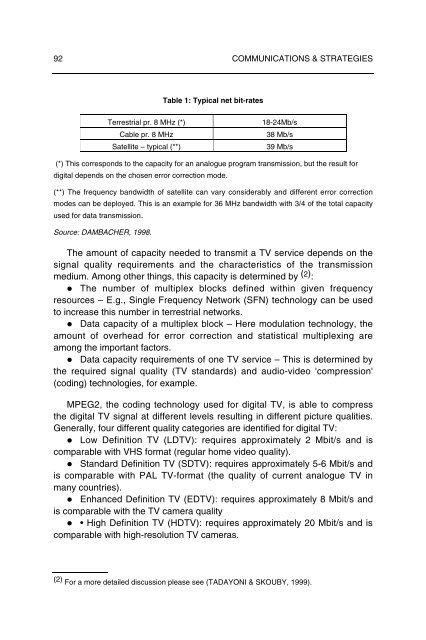
92 COMMUNICATIONS & STRATEGIESTable 1: Typical net bit-rates<strong>Terrestrial</strong> pr. 8 MHz (*)Cable pr. 8 MHzSatellite – typical (**)18-24Mb/s38 Mb/s39 Mb/s(*) This c<strong>or</strong>responds to the capacity f<strong>or</strong> an analogue program transmission, but the result f<strong>or</strong>digital depends on the chosen err<strong>or</strong> c<strong>or</strong>rection mode.(**) The frequency b<strong>and</strong>width of satellite can vary considerably <strong>and</strong> different err<strong>or</strong> c<strong>or</strong>rectionmodes can be deployed. This is an example f<strong>or</strong> 36 MHz b<strong>and</strong>width with 3/4 of the total capacityused f<strong>or</strong> data transmission.Source: DAMBACHER, 1998.The amount of capacity needed to transmit a TV service depends on thesignal quality requirements <strong>and</strong> the characteristics of the transmissionmedium. Among other things, this capacity is determined by (2) :• The number of multiplex blocks defined within given frequencyresources – E.g., Single Frequency Netw<strong>or</strong>k (SFN) technology can be usedto increase this number in terrestrial netw<strong>or</strong>ks.• Data capacity of a multiplex block – Here modulation technology, theamount of overhead f<strong>or</strong> err<strong>or</strong> c<strong>or</strong>rection <strong>and</strong> statistical multiplexing areamong the imp<strong>or</strong>tant fact<strong>or</strong>s.• Data capacity requirements of one TV service – This is determined bythe required signal quality (TV st<strong>and</strong>ards) <strong>and</strong> audio-video 'compression'(coding) technologies, f<strong>or</strong> example.MPEG2, the coding technology used f<strong>or</strong> digital TV, is able to compressthe digital TV signal at different levels resulting in different picture qualities.Generally, four different quality categ<strong>or</strong>ies are identified f<strong>or</strong> digital TV:• Low Definition TV (LDTV): requires approximately 2 Mbit/s <strong>and</strong> iscomparable with VHS f<strong>or</strong>mat (regular home video quality).• St<strong>and</strong>ard Definition TV (SDTV): requires approximately 5-6 Mbit/s <strong>and</strong>is comparable with PAL TV-f<strong>or</strong>mat (the quality of current analogue TV inmany countries).• Enhanced Definition TV (EDTV): requires approximately 8 Mbit/s <strong>and</strong>is comparable with the TV camera quality• • High Definition TV (HDTV): requires approximately 20 Mbit/s <strong>and</strong> iscomparable with high-resolution TV cameras.(2) F<strong>or</strong> a m<strong>or</strong>e detailed discussion please see (TADAYONI & SKOUBY, 1999).