KPL Antibodies and Conjugates Catalog
KPL Antibodies and Conjugates Catalog
KPL Antibodies and Conjugates Catalog
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
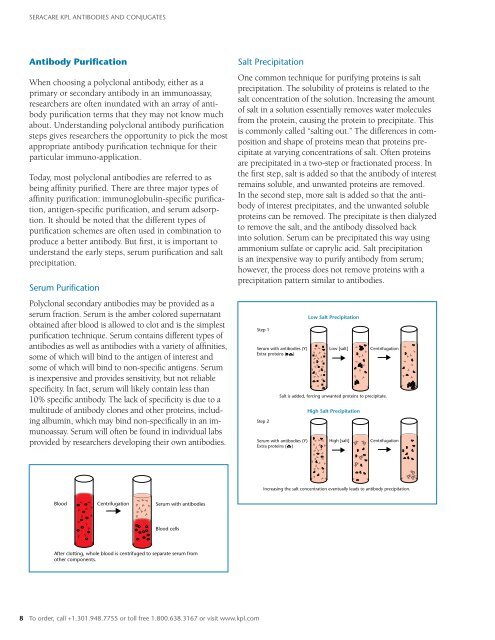
YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYSERACARE <strong>KPL</strong> ANTIBODIES AND CONJUGATESAntibody PurificationWhen choosing a polyclonal antibody, either as aprimary or secondary antibody in an immunoassay,researchers are often inundated with an array of antibodypurification terms that they may not know muchabout. Underst<strong>and</strong>ing polyclonal antibody purificationsteps gives researchers the opportunity to pick the mostappropriate antibody purification technique for theirparticular immuno-application.Today, most polyclonal antibodies are referred to asbeing affinity purified. There are three major types ofaffinity purification: immunoglobulin-specific purification,antigen-specific purification, <strong>and</strong> serum adsorption.It should be noted that the different types ofpurification schemes are often used in combination toproduce a better antibody. But first, it is important tounderst<strong>and</strong> the early steps, serum purification <strong>and</strong> saltprecipitation.Serum PurificationPolyclonal secondary antibodies may be provided as aserum fraction. Serum is the amber colored supernatantobtained after blood is allowed to clot <strong>and</strong> is the simplestpurification technique. Serum contains different types ofantibodies as well as antibodies with a variety of affinities,some of which will bind to the antigen of interest <strong>and</strong>some of which will bind to non-specific antigens. Serumis inexpensive <strong>and</strong> provides sensitivity, but not reliablespecificity. In fact, serum will likely contain less than10% specific antibody. The lack of specificity is due to amultitude of antibody clones <strong>and</strong> other proteins, includingalbumin, which may bind non-specifically in an immunoassay.Serum will often be found in individual labsprovided by researchers developing their own antibodies.Salt PrecipitationOne common technique for purifying proteins is saltprecipitation. The solubility of proteins is related to thesalt concentration of the solution. Increasing the amountof salt in a solution essentially removes water moleculesfrom the protein, causing the protein to precipitate. Thisis commonly called “salting out.” The differences in composition<strong>and</strong> shape of proteins mean that proteins precipitateat varying concentrations of salt. Often proteinsare precipitated in a two-step or fractionated process. Inthe first step, salt is added so that the antibody of interestremains soluble, <strong>and</strong> unwanted proteins are removed.In the second step, more salt is added so that the antibodyof interest precipitates, <strong>and</strong> the unwanted solubleproteins can be removed. The precipitate is then dialyzedto remove the salt, <strong>and</strong> the antibody dissolved backinto solution. Serum can be precipitated this way usingammonium sulfate or caprylic acid. Salt precipitationis an inexpensive way to purify antibody from serum;however, the process does not remove proteins with aprecipitation pattern similar to antibodies.Step 1Serum with antibodies (Y)Extra proteins ( )Step 2Serum with antibodies (Y)Extra proteins ( )Low Salt PrecipitationYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYLow [salt]High [salt]CentrifugationSalt is added, forcing unwanted proteins to precipitate.Y YY YYHigh Salt PrecipitationYYYYYYYYYYYYYCentrifugationY YY YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYIncreasing the salt concentration eventually leads to antibody precipitation.BloodYYYYYYCentrifugationYYYYYYYYSerum with antibodiesYYYYBlood cellsAfter clotting, whole blood is centrifuged to separate serum fromother components.8 To order, call +1.301.948.7755 or toll free 1.800.638.3167 or visit www.kpl.com