IFSM 310 A+ Demo Installing Windows 95 A+ OS Domain 1.0
IFSM 310 A+ Demo Installing Windows 95 A+ OS Domain 1.0
IFSM 310 A+ Demo Installing Windows 95 A+ OS Domain 1.0
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
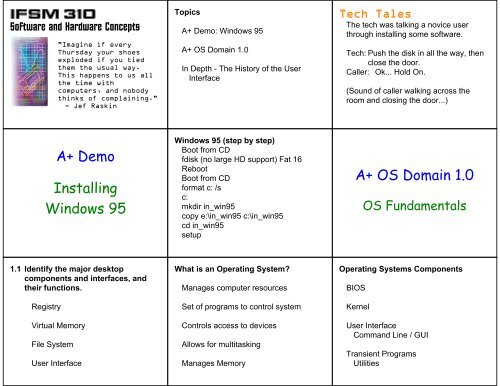
<strong>IFSM</strong> <strong>310</strong>Software and Hardware Concepts"Imagine if everyThursday your shoesexploded if you tiedthem the usual way.This happens to us allthe time withcomputers, and nobodythinks of complaining."- Jef RaskinTopics<strong>A+</strong> <strong>Demo</strong>: <strong>Windows</strong> <strong>95</strong><strong>A+</strong> <strong>OS</strong> <strong>Domain</strong> <strong>1.0</strong>In Depth - The History of the UserInterfaceTech TalesThe tech was talking a novice userthrough installing some software.Tech: Push the disk in all the way, thenclose the door.Caller: Ok... Hold On.(Sound of caller walking across theroom and closing the door...)<strong>A+</strong> <strong>Demo</strong><strong>Installing</strong><strong>Windows</strong> <strong>95</strong><strong>Windows</strong> <strong>95</strong> (step by step)Boot from CDfdisk (no large HD support) Fat 16RebootBoot from CDformat c: /sc:mkdir in_win<strong>95</strong>copy e:\in_win<strong>95</strong> c:\in_win<strong>95</strong>cd in_win<strong>95</strong>setup<strong>A+</strong> <strong>OS</strong> <strong>Domain</strong> <strong>1.0</strong><strong>OS</strong> Fundamentals1.1 Identify the major desktopcomponents and interfaces, andtheir functions.RegistryVirtual MemoryFile SystemUser InterfaceWhat is an Operating System?Manages computer resourcesSet of programs to control systemControls access to devicesAllows for multitaskingManages MemoryOperating Systems ComponentsBI<strong>OS</strong>KernelUser InterfaceCommand Line / GUITransient ProgramsUtilities
Where is the <strong>OS</strong>? The Heart of the <strong>OS</strong> - The Kernel Common <strong>Windows</strong> ComponentsDesktopIconsTask Bar (Start menu)Shortcut MenuMultitaskingMultitaskingConventional MemoryMemory below 640KUsed by MS/D<strong>OS</strong>Early System LimitUpper memory use for devicesVideo Memory, BI<strong>OS</strong>Conventional MemoryUpper MemoryExpanded MemoryEarly systems hampered by 640kLotus-Intel-Microsoft developedExpanded memory (board)Paged memoryLegacy ApplicationsExpanded Memoryconfig.sysDEVICE=C:\D<strong>OS</strong>\HIMEM.SYSDEVICE=C:\D<strong>OS</strong>\EMM386.EXED<strong>OS</strong>=HIGH,UMB
Extended MemoryMaking use of "real" memoryAbove 1 MegabyteConfig.sysDEVICE=C:\D<strong>OS</strong>\HIMEM.SYSD<strong>OS</strong>=HIGHExtended MemoryVirtual MemoryWe never have enough memorySimulate RAM on hard driveSlower, but allows more programs torun.Virtual Memory<strong>Windows</strong> Virtual Memory<strong>Windows</strong> 9xWIN386.SWP<strong>Windows</strong> 2000 PAGEFILE.SYSSize set automatically, can change inPerformance TabThrashingContrast Between 9x and 2000<strong>Windows</strong> 9x, MeDesigned for Home UseShare level security<strong>Windows</strong> 2000, XPTrue <strong>OS</strong>User Level SecuritySystem Files and UtilitiesSystem FilesPart of the Operating SystemTypically in C:\<strong>Windows</strong>HiddenApplicationsAdd on programsTypically in C:\Program FilesMajor <strong>OS</strong> Interfaces<strong>Windows</strong> ExplorerMy ComputerControl PanelComputer Management ConsoleAccessories / System ToolsCommand LineNetwork NeighborhoodTask Bar / System TrayStart MenuDevice ManagerControl Panel
Device Manager Computer Management 1.2 Identify major system files<strong>Windows</strong> 9x is almost an <strong>OS</strong>Still requires D<strong>OS</strong> 7 and Fat 16Another step towards single <strong>OS</strong>Win 9x Booting SequenceBoot SectorIO.SYSMSD<strong>OS</strong>.SYSDRVSPACE.BINSYSTEM.DATUSER.DATCONFIG.SYSAUTOEXEC.BATSYSTEM.INIVMM32.VXDWIN.COMKERNAL32.DLLGDI.EXE/GDI32.EXEUSER.EXE/USER32.DLLWIN.INIStartup GroupIO.SYSSmall D<strong>OS</strong> core module. It starts the<strong>Windows</strong> 9X boot process and looks forMSD<strong>OS</strong>.SYS.MSD<strong>OS</strong>.SYSASCII text file that contains bootconfiguration options.DRVSPACE.BINIf DRVSPACE.INI file is present, itallows for disk compression.SYSTEM.DATPart of the Registry, contains systemconfiguration.Similar to the SYSTEM.INI file.USER.DATPart of the Registry, containsuser-specific information.Similar to the WIN.INI file.CONFIG.SYSText file for MS/D<strong>OS</strong> device drivers andsystem setup values.AUTOEXEC.BATText file for MS/D<strong>OS</strong> system variables torun D<strong>OS</strong> applications.SYSTEM.INIContains hardware settings. It must bein the <strong>Windows</strong> folder for <strong>Windows</strong> tostart.VMM32.VXDThe virtual machine manager loadingother virtual device drivers.WIN.COMSwitches from Real Mode to ProtectedMode, initializing the devices andloading the following files.
KERNEL32.DLLContains most the Operating System for<strong>Windows</strong>9X.GDI.EXE/GDI32.EXEThese files are the graphics engines forboth 16-bit and 32-bit graphics displays.USER.EXE/USER32.DLLUser Interface and control the inputinformation.WIN.INIContains application informationconfiguration.STARTUP GroupContains programs that will start everytime the <strong>OS</strong> starts.<strong>Windows</strong> 2000 Boot FilesTrue <strong>OS</strong>BOOT.ININTLDRNTDETECT.COMNTBOOTDD.SYSNTUSER.DATRegistry Data FilesBOOT.INIUsed for dual-boot. Select which <strong>OS</strong> torun.NTLDRUsed to coordinate the system’s startupprocedure and locates and initializesother required startup files.NTDETECT.COMChecks system hardware, writes theinformation in the registry.NTBOOTDD.SYSAllows for booting from a SCSI device.1.3 Command Line FilesInternal / External CommandsInternal: Built into the <strong>OS</strong>DIR, COPYExternal: On the DiskFDISK, FORMATCommon CommandsCommand/CMD SETVERDIRSCANREGATTRIBMD/CD/RDVERDEL / RENMEMDELTREESCANDISK TYPEDEFRAG ECHOEDITSETXCOPYPINGFORMAT MSCDEXFDISK1.4 Disk ManagementDisk PreparationFDISK defines the partitionsFormat prepares for data useWhat file format should us use?FAT, FAT32, NTFS?ParititionsActive - bootablePrimary - Up to 4Extended - OneLogical Drives
FAT16 bit file systemCan only access 2 GB of dataLarger hard drives broken into multiple2GB partitionsWasted Space, Cluster SizesIf you have a 1k file1k clusters - no waste2k clusters - 1k lost4k clusters - 3k lost16k clusters - 15k lost32k clusters - 31k lostFAT3232 bit file system2 TB data limit (2048 Gigabytes)4k clustersNTFSIntroduced with NT 4.032 bit file systemFile CompressionSpanned Disks (Volume Sets)NTFS 5 (<strong>Windows</strong> 2000)EncryptionDisk QuotasHPFSLegacy use for <strong>OS</strong>/2Can not be used by 9x or 2000Drive Converter<strong>Windows</strong> UtilityConvert drive from FAT to FAT32<strong>Windows</strong> 2000Computer ManagementConvert to NTFSFile and Folder ManagementCreating FoldersManaging FoldersNavigating FoldersFile PropertiesFile AttributesRead OnlyHiddenArchiveSystemFilename ConventionsFull Path - Max 255 charactersCan not include: \ / ? * : “ < > |Common File ExtensionsEXE BAT COM MDBDOC BMP SYS PIFCFG INI XLS JPG
Backup and RestoreBackupCan compress dataBackup MediaTape, CD, ZIP, Hard DriveFloppyExtractUtility to pull files from .CABsCABs are compressed filesSimilar to ZIPCommand:EXTRACT D:\WIN98_4.CAB DRIVER.DLL C:\WINDOWSDone automatically when needed<strong>Windows</strong> 2000 Compression andEncryptionCompression of files and foldersMust be enabledEncryption of files and foldersOther users can not read1.5 Major <strong>OS</strong> UtilitiesDisk management ToolsDEFRAGFDISKSCANDISKCHKDSKDisk CleanupFORMATSystem Management ToolsDevice ManagerSystem MonitorComputer ManagerMSCONFIGEvent ViewerTask ManagerSYSEDITMSCONFIGThe Registry<strong>Windows</strong> 3.1: REG.DATThen a lot of .INI files<strong>Windows</strong> <strong>95</strong> / 98SYSTEM.DATUSER.DATEdit with REGEDIT.EXECheck with SCANREG.EXEREGEDIT.EXENo icons, use the RUN commandBE CAREFULNO UNDO OPTION!!!Changes are made right away, withoutthe FILE / SAVE optionMost registry modification can be madeusing the control panel.
The Registry KeysHKEY_CLASSES_ROOTFile extension and applicationsHKEY_USERSUser configuration optionsHKEY_CURRENT_USERCopy of HKEY_USERS for the currentuserThe Registry KeysHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINEHardware / Software config, includingmultiple configurationsHKEY_CURRENT_CONFIGCurrent configurationHKEY_DYN_DATADynamic data for this sessionRegistry OrganizationEditing the RegistryCopies of the RegistrySYSTEM.NEW When installing windows.DAT Current registry.DA0 Backup of last good boot.1ST 1st reboot of systemREGEDT32Advanced version of REGEDITSecurity on KeysUSER.DATUSER.DA0Current User fileBackup of User fileIn DepthThe History of theUser InterfaceUser InterfaceHelp the user use the computer systemproductivelyProvide consistent user interfaceservices to application programs tolower learning curves and increaseproductivityChoice of user interface depends on thekind of userWriting programs vs. runningapplicationsCommand Line Interfacecommand … …example: dir *.exe /pOperandskeyword (switches) and/or positionalAdvantagesMore flexible and powerfulFaster for experienced usersCan combine commands
Command Line Interface<strong>Windows</strong> InterfacesGraphical User Interfaces (GUIs)Mouse-driven and icon-based<strong>Windows</strong>Are allocated to the use of a particularprogram or processContain a title bar, menu bar, andwidgetsAKA: WIMP Interface(<strong>Windows</strong>, Icons, Menus, Pointers)Xerox Alto - 1973Original AltoMouseXerox Star - 1981 MS/D<strong>OS</strong> - 1981<strong>Windows</strong> <strong>1.0</strong>1 - 1985 <strong>Windows</strong> 2.11 - 1987 <strong>Windows</strong> 3.1 - 1992
<strong>Windows</strong> 9x - 19<strong>95</strong>Blue Screen of Death - Singapore, 1999 <strong>Windows</strong> XP - 2001Video: Watch Bill Gates Crash Win98<strong>Windows</strong> Longhorn - 2004...2006 The Next <strong>Windows</strong> <strong>OS</strong>... <strong>OS</strong>/21983 Microsoft and IBMMS and IBM SplitVersion 2.0 and later, only IBMVersion 3 - <strong>OS</strong>/2 Warp<strong>Windows</strong> compatible3.1, Win32Couldn't keep up with MSInterface <strong>OS</strong>/2 1.3 Interface <strong>OS</strong>/2 Warp Linux KDE
Mac - 1984Mac <strong>OS</strong> X Amiga - 1985VMAC emulatorSystem 8Solaris 9 - 2002GUI vs. CLIGUIAdvantagesEasy to learn and useLittle trainingAmenable to multi-taskingDisadvantagesHarder to implementMore HW/SW requirementsRequires lots of memorySW is complex and difficult to writeGUI vs. CLICLIAdvantagesMore flexible and powerfulFaster for experienced usersCan combine commandsDisadvantagesMore difficult to learn and useParting Thought"On the keyboard of life,always keep one fingeron the escape key."- AnonymousEnd of Lesson