(D) HK Normalien Aktuell [GB]
(D) HK Normalien Aktuell [GB]
(D) HK Normalien Aktuell [GB]
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
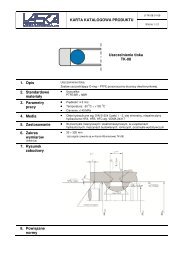
Oilless Guide ElementsGeneral DescriptionOilless Guide Elements with embeddedsolid lubricants are used in applicationsof linear or rotary motion in toolmaking,general machine construction andsimilar engineering uses. The structureof the base material provides closelyspaced deposits of solid lubricant –properties and specifications as per tablebelow.The elements satisfy highest demandsin terms of load bearing capacity atlow sliding speeds, within an extensivetemperature band.The lubricant deposits are arranged instaggered geometrical patterns, thus en -suring optimal lubrication effect alongthe sliding motion, especially withcounter bearings which are hardenedand ground.The sliding surfaces should be lightlygreased with lithium grease emulsion,prior to commissioning.On flat guideways and pillar guides, from25 to 30 per cent of the sliding surfacesconsist of lubricant deposits. Surfacesof counter bearings must have a groundfinish, preferably with a lay parallel withthe sliding motion.Choice of Element-TypeStandard:– for general uses at temperaturesup to 200°CSpecial Types on requestAdvantages of Oilless GuideElements– good emergency sliding properties– highest carrying capacity at low speed– use under water or with chemicalsolutions– extremely wide temperatureresistance – hot and cold– damping properties in presenceof vibrationPV valueThe permissible bearing load is determinedfrom the pressure and the PV value, whichdefines the bearing wear.The PV value is the product of surfacepressure (P) and running velocity (V).The permissible bearing load is determinedfrom the PV value.PV = P × V (N/cm 2 × m/min.)P = F/A (N/cm 2 )F = max. load (N)A = projected area of the bearingSurface pressure, temperature,speed and lubricationSurface pressure Temp. Speed PV valuemax. (N/cm 2 ) (C°) (m/min.) (N/cm 2 × m/min) Lubrication5000 80 15 10000 Initial3000 150 60 20000 Pressure IubricationOilless Guide Elements – Material Datachemical composition % CU 60–66 Brinell hardness HB 10 180–210 stroking velocity m/min 15 electric conductanceAl 5,0–7,5 shear strength N/mm 2 560 co-efficient of friction 0,04–0,10 m/(Ω × mm 2 ) 7–8Fe 2,0–4,0 yield limit temperature conductance alt. flexural strengthMn 2,5–5,0 Rp 0,2 N/mm 2 450 W/(m × K) 45–55 N/mm 2 ±150balance: Zn elongation to fracture A5 % 8 temperature resistance °C +300 ratio sliding surfacespecific density kg/dm 3 8,2 elongation % 12 co-efficient of thermal to lubricanttensile strength Rm N/mm 2 770 modulus of elasticity expansion 1,6–2,0 × 10 –5 /°C deposits (%) 25–30kN/mm 2 105–115 co-efficient of shrinkage % 1,8–2,3d100subject to alterations2·9207·8·6 °


![(D) HK Normalien Aktuell [GB]](https://img.yumpu.com/42904226/2/500x640/d-hk-normalien-aktuell-gb.jpg)





![(E) HK Normalien Aktuell [GB]](https://img.yumpu.com/48932549/1/184x260/e-hk-normalien-aktuell-gb.jpg?quality=85)