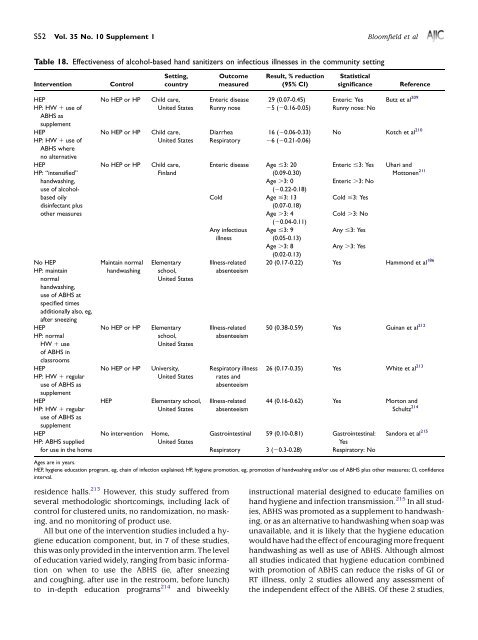
S52 Vol. 35 No. 10 Supplement 1 Bloomfield et alTable 18. Effectiveness <strong>of</strong> alcohol-based <strong>hand</strong> sanitizers on <strong>in</strong>fectious illnesses <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> community sett<strong>in</strong>gInterventionControlSett<strong>in</strong>g,countryOutcomemeasuredResult, % reduction(95% CI)StatisticalsignificanceReferenceHEPHP: HW 1 use <strong>of</strong>No HEP or HP Child care,United StatesABHS assupplementHEP No HEP or HP Child care,HP: HW 1 use <strong>of</strong>United StatesABHS whereno alternativeHEP No HEP or HP Child care,HP: ‘‘<strong>in</strong>tensified’’F<strong>in</strong>land<strong>hand</strong>wash<strong>in</strong>g,use <strong>of</strong> alcoholbasedoilydis<strong>in</strong>fectant pluso<strong>the</strong>r measuresNo HEPHP: ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong>normalMa<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong> normal<strong>hand</strong>wash<strong>in</strong>gElementaryschool,United States<strong>hand</strong>wash<strong>in</strong>g,use <strong>of</strong> ABHS atspecified timesadditionally also, eg,after sneez<strong>in</strong>gHEP No HEP or HP ElementaryHP: normalschool,HW 1 useUnited States<strong>of</strong> ABHS <strong>in</strong>classroomsHEP No HEP or HP University,HP: HW 1 regularUnited Statesuse <strong>of</strong> ABHS assupplementHEP HEP Elementary school,HP: HW 1 regularUnited Statesuse <strong>of</strong> ABHS assupplementHEP No <strong>in</strong>tervention Home,HP: ABHS suppliedUnited StatesEnteric disease 29 (0.07-0.45) Enteric: Yes Butz et al 209Runny nose 25 (20.16-0.05) Runny nose: NoDiarrhea 16 (20.06-0.33) No Kotch et al 210Respiratory 26 (20.21-0.06)Enteric disease Age #3: 20(0.09-0.30)Enteric #3: Yes Uhari andMottonen 211Age .3: 0Enteric .3: No(20.22-0.18)Cold Age #3: 13Cold #3: Yes(0.07-0.18)Age .3: 4Cold .3: No(20.04-0.11)Any <strong>in</strong>fectious Age #3: 9Any #3: Yesillness(0.05-0.13)Age .3: 8Any .3: Yes(0.02-0.13)Illness-related 20 (0.17-0.22) Yes Hammond et al 186absenteeismIllness-relatedabsenteeismRespiratory illnessrates andabsenteeismIllness-relatedabsenteeism50 (0.38-0.59) Yes Gu<strong>in</strong>an et al 21226 (0.17-0.35) Yes White et al 21344 (0.16-0.62) Yes Morton andSchultz 214Gastro<strong>in</strong>test<strong>in</strong>al 59 (0.10-0.81) Gastro<strong>in</strong>test<strong>in</strong>al:Yesfor use <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> home Respiratory 3 (20.3-0.28) Respiratory: NoSandora et al 215Ages are <strong>in</strong> years.HEP, <strong>hygiene</strong> education program, eg, cha<strong>in</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>fection expla<strong>in</strong>ed; HP, <strong>hygiene</strong> promotion, eg, promotion <strong>of</strong> <strong>hand</strong>wash<strong>in</strong>g and/or use <strong>of</strong> ABHS plus o<strong>the</strong>r measures; CI, confidence<strong>in</strong>terval.residence halls. 213 However, this study suffered fromseveral methodologic shortcom<strong>in</strong>gs, <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g lack <strong>of</strong>control for clustered units, no randomization, no mask<strong>in</strong>g,and no monitor<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> product use.All but one <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>tervention studies <strong>in</strong>cluded a <strong>hygiene</strong>education component, but, <strong>in</strong> 7 <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se studies,this was only provided <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>tervention arm. <strong>The</strong> level<strong>of</strong> education varied widely, rang<strong>in</strong>g from basic <strong>in</strong>formationon when to use <strong>the</strong> ABHS (ie, after sneez<strong>in</strong>gand cough<strong>in</strong>g, after use <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> restroom, before lunch)to <strong>in</strong>-depth education programs 214 and biweekly<strong>in</strong>structional material designed to educate families on<strong>hand</strong> <strong>hygiene</strong> and <strong>in</strong>fection transmission. 215 In all studies,ABHS was promoted as a supplement to <strong>hand</strong>wash<strong>in</strong>g,or as an alternative to <strong>hand</strong>wash<strong>in</strong>g when soap wasunavailable, and it is likely that <strong>the</strong> <strong>hygiene</strong> educationwould have had <strong>the</strong> effect <strong>of</strong> encourag<strong>in</strong>g more frequent<strong>hand</strong>wash<strong>in</strong>g as well as use <strong>of</strong> ABHS. Although almostall studies <strong>in</strong>dicated that <strong>hygiene</strong> education comb<strong>in</strong>edwith promotion <strong>of</strong> ABHS can reduce <strong>the</strong> <strong>risks</strong> <strong>of</strong> GI orRT illness, only 2 studies allowed any assessment <strong>of</strong><strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>dependent effect <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> ABHS. Of <strong>the</strong>se 2 studies,
Bloomfield et al December 2007 S53<strong>the</strong> study by Hammond et al 186 did not provide any educationalcomponent to ei<strong>the</strong>r arm, and <strong>the</strong> study byMorton and Schultz 214 provided education to both <strong>in</strong>terventionand control arms. Both studies showed a significantreduction <strong>in</strong> illness-related absences (20% and44%, respectively), but it is not clear whe<strong>the</strong>r <strong>the</strong> illnesseswere predom<strong>in</strong>antly GI or RT because <strong>the</strong>se studiesused a loose def<strong>in</strong>ition <strong>of</strong> absence-related illnesses.Sandora et al 215 was <strong>the</strong> only study carried out <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong>household sett<strong>in</strong>g and, <strong>of</strong> all <strong>the</strong> studies, reported <strong>the</strong>highest reduction for GI illness. <strong>The</strong> trial <strong>in</strong>volved 292families with children enrolled <strong>in</strong> 26 child care centers.Intervention families received a supply <strong>of</strong> ABHS andbiweekly <strong>hand</strong> <strong>hygiene</strong> educational materials for 5months; control families received only materials promot<strong>in</strong>ggood nutrition. A total <strong>of</strong> 252 GI illnesses occurreddur<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> study; 11% were secondaryillnesses. <strong>The</strong> secondary GI illness rate was significantlylower (59%) <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>tervention families comparedwith control families (see Table 18). A total <strong>of</strong> 1802RT illnesses occurred dur<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> study; 25% were secondaryillnesses. Although RT illness rates were not significantlydifferent between groups, families withhigher ABHS usage had marg<strong>in</strong>ally lower RT illnessrate than those with less usage (19% reduction). Sandoraet al 215 suggested that <strong>the</strong> difference may be dueto heightened diligence associated with us<strong>in</strong>g ABHS aftera GI-related <strong>in</strong>cident compared with an RT <strong>in</strong>cident,such as sneez<strong>in</strong>g.Overall, based on relatively limited data available,<strong>the</strong> results <strong>in</strong> Table 18 suggest that <strong>the</strong> impact <strong>of</strong>ABHS promotion, as part <strong>of</strong> a <strong>hygiene</strong> education andpromotion program <strong>in</strong> reduc<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>cidence <strong>of</strong> GI <strong>in</strong>fections<strong>in</strong> young children, is similar to that observedfor promotion <strong>of</strong> <strong>hand</strong>wash<strong>in</strong>g with soap. Promotion<strong>of</strong> ABHS <strong>in</strong> this manner also produced some reduction<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>cidence <strong>of</strong> RT <strong>in</strong>fections, which was less thanthat associated with promotion <strong>of</strong> <strong>hand</strong>wash<strong>in</strong>g alone.Assess<strong>in</strong>g whe<strong>the</strong>r <strong>the</strong>re might be an added health benefit<strong>of</strong> us<strong>in</strong>g ABHS above and beyond <strong>the</strong> effect <strong>of</strong> <strong>hygiene</strong>education is hampered by <strong>the</strong> fact that moststudies used <strong>hygiene</strong> education and ABHS <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>terventionarm but did not provide an educational componentto <strong>the</strong> control arm.Several important methodologic issues were evident,although more recent studies have improved designsand conduct. In most studies, ei<strong>the</strong>r parents or schoolpersonnel provided <strong>in</strong>formation on ID among children<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> study populations. In all but one study, 34 <strong>the</strong> parents,participants, or personnel monitor<strong>in</strong>g and report<strong>in</strong>g<strong>in</strong>fections were not masked as to <strong>the</strong>ir own or<strong>the</strong>ir child’s <strong>in</strong>tervention status. Although mask<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong>participants and <strong>in</strong>terviewers to <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>tervention statusis important, because it might <strong>in</strong>fluence report<strong>in</strong>g, it is<strong>of</strong>ten difficult to conduct masked <strong>hygiene</strong> <strong>in</strong>terventionsand may not be ethical. Sandora et al determ<strong>in</strong>ed that itwas nei<strong>the</strong>r feasible nor ethical to mask subjects or <strong>in</strong>terviewersbecause it is difficult to devise a formulationthat could act as a ‘‘placebo’’ for ABHS, and us<strong>in</strong>g a placeboABHS product might endanger <strong>the</strong> control groupvia <strong>in</strong>adequate <strong>hand</strong> <strong>hygiene</strong>. 215In many <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> ABHS studies, especially <strong>the</strong> recentones, efforts were made to control for potential confound<strong>in</strong>gfactors. However, many <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> studies didnot collect <strong>in</strong>formation on basel<strong>in</strong>e <strong>hand</strong> <strong>hygiene</strong> practices(nor methods and frequency <strong>of</strong> clean<strong>in</strong>g/dis<strong>in</strong>fect<strong>in</strong>gsoiled/contam<strong>in</strong>ated environmental surfaces <strong>in</strong>homes) as well as ABHS use. <strong>The</strong> studies also excludedparticipants who reported current ABHS use <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong>home. Fur<strong>the</strong>rmore, participants were asked to refra<strong>in</strong>from us<strong>in</strong>g ABHS <strong>in</strong> sett<strong>in</strong>gs outside <strong>the</strong> home. <strong>The</strong>seare all important design strategies m<strong>in</strong>imiz<strong>in</strong>g bias associatedwith noncompliance or differential usage. Two<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> 8 <strong>in</strong>tervention studies failed to use systematicmonitor<strong>in</strong>g for <strong>hygiene</strong> practices, such as frequency<strong>of</strong> <strong>hand</strong>-sanitiz<strong>in</strong>g episodes, frequency <strong>of</strong> <strong>hand</strong>wash<strong>in</strong>g,or duration <strong>of</strong> <strong>hand</strong>wash<strong>in</strong>g. 212,213 This is especiallyconcern<strong>in</strong>g because <strong>the</strong> study by Sandora et alsuggests that <strong>the</strong> quantity <strong>of</strong> ABHS <strong>in</strong>fluences <strong>the</strong> risk<strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>fection <strong>in</strong> a dose-response manner. 215 Moreover,if frequency <strong>of</strong> <strong>hand</strong>wash<strong>in</strong>g and ABHS use is not recorded,it is impossible to isolate <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>dependent effects<strong>of</strong> ABHS from that <strong>of</strong> <strong>hand</strong>wash<strong>in</strong>g on <strong>in</strong>fectionrates. In <strong>the</strong>se studies <strong>of</strong> ABHS use, surveillance measures<strong>in</strong>cluded calculat<strong>in</strong>g use from monthly demand,total amount supplied, observation by research assistants,participant report, and reported use by primarycaregivers <strong>in</strong> households. 186,209,212,214,215THE HEALTH IMPACT OF HAND HYGIENEOverall, <strong>the</strong> microbiologic data, toge<strong>the</strong>r with <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>terventionstudy data (both those <strong>in</strong>volv<strong>in</strong>g ABHS aswell as those <strong>in</strong>volv<strong>in</strong>g <strong>hand</strong>wash<strong>in</strong>g) as presented <strong>in</strong>this review, provide consistent evidence <strong>of</strong> a strongcausal l<strong>in</strong>k between <strong>hygiene</strong> and <strong>the</strong> spread <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>fection<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> home and community, and suggest thatprobably <strong>the</strong> s<strong>in</strong>gle most important route for <strong>the</strong>spread <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>fection is <strong>the</strong> <strong>hand</strong>s. If <strong>the</strong> data from <strong>in</strong>terventionstudies (summarized <strong>in</strong> Table 19) are an accuratereflection <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> true picture, it is suggested that,for up to 60% <strong>of</strong> GI illnesses, <strong>the</strong> <strong>hand</strong>s are <strong>the</strong> ‘‘sufficient,’’or a ‘‘component’’ (see earlier for def<strong>in</strong>itions),cause <strong>of</strong> spread <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>fection. This correlates with microbiologicand o<strong>the</strong>r data reviewed <strong>in</strong> this report,which suggest that, although <strong>the</strong>re is a tendency to assumethat GI <strong>in</strong>fections are mostly foodborne and resultfrom <strong>in</strong>adequate cook<strong>in</strong>g and <strong>in</strong>adequate storage<strong>of</strong> food, <strong>in</strong> reality, most GI <strong>in</strong>fections <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> home resultfrom person-to-person spread or contam<strong>in</strong>ation <strong>of</strong>