Bond and Note Valuation and Related Interest Rate Formulas
Bond and Note Valuation and Related Interest Rate Formulas
Bond and Note Valuation and Related Interest Rate Formulas
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
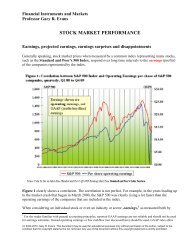
<strong>Bond</strong> <strong>Valuation</strong> - Page 7series. Therefore the elementary bond formula can be reduced to a simpler formula that is easierto calculate on a calculator or in a computer program:12.MV 1 C 11rrn Par 1 n1r The hypothetical problem used in this section would be solved as 1 1201.10 1 13. MV 8 100 82. 9720 0.10 1.10 The derivation of this formula is shown in the Appendix A.<strong>Note</strong> that the values for equations (11) <strong>and</strong> (13) agree, as they should.VII. Elementary <strong>Bond</strong> <strong>Valuation</strong> - Periodic <strong>Interest</strong> PaymentsThe formula above is just a beginning approximation. It does not take into account the facts thatbonds usually pay interest either twice per year, quarterly or monthly. For example U.S. Treasury<strong>Bond</strong>s pay interest twice per year. The formula for periodic payments is a slight modification offormula (9) above:MV Cm1mC m1rmC m1rmC m1rmC m1rmPar1r14. 3 n 1r n n m2where variables have the same values as above exceptm = the number of times per year that interest is paid.n = number of remaining coupon payments rather than number of remaining years.<strong>Note</strong> that C still equals the annual value of the coupon payment (the coupon rate times par) <strong>and</strong>that the final term is unchanged from formula (9), given that n is equal to m times the number ofyears.The summation notation version of this equation needs only a small modification of equation(10):