Notes on Differentiation - Michigan State University
Notes on Differentiation - Michigan State University
Notes on Differentiation - Michigan State University
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
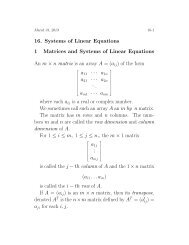
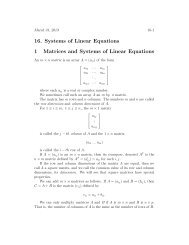
Math 829 Spring 19994.3 Analytic statement of the problem. It’s pretty clear that the stereographicprojecti<strong>on</strong> preserves the sense of angles, so we will c<strong>on</strong>centrate <strong>on</strong> preservati<strong>on</strong> ofmagnitudes of angles. Here is the analytic expressi<strong>on</strong> of what needs to be d<strong>on</strong>e.Suppose p ∈ S 2 \{N} and v, w ∈ R 3 with〈p, v〉 =0 and 〈p, w〉 =0, (9)(i.e. v and w are orthog<strong>on</strong>al to the line from the origin to p, and hence tangent to S 2at p). Let A =[Dσ(p)], the matrix of Df(p) with respect to the standard basis. Wedesire to show that〈Av, Aw〉|Av||Aw|=〈v, w〉|v||w| . (10)The quantities that show up <strong>on</strong> the left and right hand sides of this last equati<strong>on</strong>are, you will recall, the cosines of the angles between the respective pairs of vectors 1 .4.4 Exercise—reducti<strong>on</strong> of problem. Show that in order to prove (10) you need<strong>on</strong>ly show that there is a positive c<strong>on</strong>stant c such thatfor all v, w ∈ R 3 satisfying (9).In order to prove (11) we observe that〈Av, Aw〉 = c〈v, w〉 (11)〈Av, Aw〉 = 〈A ∗ Av, w〉where A ∗ is the linear transformati<strong>on</strong> R 2 → R 3 whose matrix is the transpose of thematrix of A. This is just a matrix calculati<strong>on</strong> based <strong>on</strong> the fact that 〈x, y〉 =[x] T [y](matrix product), where x and y are any vectors in the same Euclidean space, [x]and [y] are their respective column vectors, and the superscript “T ” denotes matrixtranspose. Thus:〈Aw, Av〉 = [Aw] T [Av] =([A][w]) T [A][v]= [w] T [A] T [A][v] =[w] T [A ∗ A][v]= 〈w, A ∗ Av〉from which the desired result follows by the symmetry of the inner product (it isunchanged if the order of its entries is reversed). Note that this calculati<strong>on</strong> works aswell for any m × n matrix and any pair of vectors in R n .1 Remember that the inner product <strong>on</strong> the left-hand side of the equati<strong>on</strong> is the <strong>on</strong>e for R 3 , andthe <strong>on</strong>e <strong>on</strong> the right is that of R 2 .-6-