Theory of Nuclear Matter for Neutron Stars and ... - Graduate Physics
Theory of Nuclear Matter for Neutron Stars and ... - Graduate Physics
Theory of Nuclear Matter for Neutron Stars and ... - Graduate Physics
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
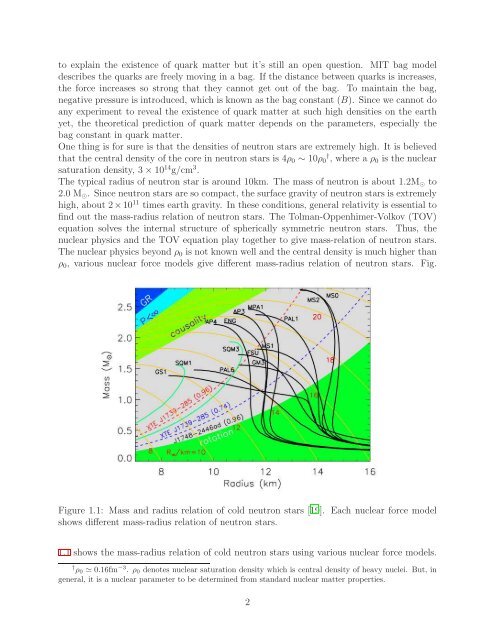
to explain the existence <strong>of</strong> quark matter but it’s still an open question. MIT bag modeldescribes the quarks are freely moving in a bag. If the distance between quarks is increases,the <strong>for</strong>ce increases so strong that they cannot get out <strong>of</strong> the bag. To maintain the bag,negative pressure is introduced, which is known as the bag constant (B). Since we cannot doany experiment to reveal the existence <strong>of</strong> quark matter at such high densities on the earthyet, the theoretical prediction <strong>of</strong> quark matter depends on the parameters, especially thebag constant in quark matter.One thing is <strong>for</strong> sure is that the densities <strong>of</strong> neutron stars are extremely high. It is believedthat the central density <strong>of</strong> the core in neutron stars is 4ρ 0 ∼ 10ρ 0 † , where a ρ 0 is the nuclearsaturation density, 3×10 14 g/cm 3 .The typical radius <strong>of</strong> neutron star is around 10km. The mass <strong>of</strong> neutron is about 1.2M ⊙ to2.0 M ⊙ . Since neutron stars are so compact, the surface gravity <strong>of</strong> neutron stars is extremelyhigh, about 2×10 11 times earth gravity. In these conditions, general relativity is essential t<strong>of</strong>ind out the mass-radius relation <strong>of</strong> neutron stars. The Tolman-Oppenhimer-Volkov (TOV)equation solves the internal structure <strong>of</strong> spherically symmetric neutron stars. Thus, thenuclear physics <strong>and</strong> the TOV equation play together to give mass-relation <strong>of</strong> neutron stars.The nuclear physics beyond ρ 0 is not known well <strong>and</strong> the central density is much higher thanρ 0 , various nuclear <strong>for</strong>ce models give different mass-radius relation <strong>of</strong> neutron stars. Fig.Figure 1.1: Mass <strong>and</strong> radius relation <strong>of</strong> cold neutron stars [19]. Each nuclear <strong>for</strong>ce modelshows different mass-radius relation <strong>of</strong> neutron stars.1.1 shows the mass-radius relation <strong>of</strong> cold neutron stars using various nuclear <strong>for</strong>ce models.† ρ 0 ≃ 0.16fm −3 . ρ 0 denotes nuclear saturation density which is central density <strong>of</strong> heavy nuclei. But, ingeneral, it is a nuclear parameter to be determined from st<strong>and</strong>ard nuclear matter properties.2