Orthopedic Tests
Orthopedic Tests
Orthopedic Tests
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
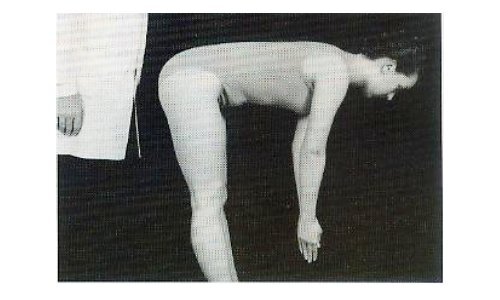
Adam’s TestFor ScoliosisFunctional Scoliosis:if Patient exhibits rib hump while standing, but itdisappears with forward bendingStructural Scoliosis:if Patient exhibits rib hump while standing, and it remainswith forward bending (more serious)
Antalgia SignLateral disc protrusion:Antalgic position is to lean Away from the side of lesionMedial disc protrusion:Antalgic position is to lean Toward from the side of lesion
Becheterrews TestExtend each leg, apply downward pressure, then both legs.Positive test can indicate sciatica, disc lesion, spasm orsubluxation.
Trendelenberg TestHip Joint PathologyNormal:Iliac crest will be higher on the side of flexed legAbnormal:Iliac crest will be lower on the side of flexed leg
Straight Leg RaisePositive Test:Pain on the side of raised leg.The greater the angle is when patient feels pain, the higherthe location of the problemWell Leg Raise - Fajerstan’s TestPositive Test:Pain on the side of complaint when well leg is raised
Braggard’s TestIf SLR is positive, lower affected leg below the angle ofpain and dorsiflex the foot.Positive sign can indicate Sciatic neuritis, spinal cordtumors, IVD lesions, or Spinal nerve irritations
Sicard’s TestIf SLR is positive, lower affected leg below the angle ofpain and dorsiflex the big toe of the affected leg.Positive sign may indicate Sciatic neuropathy
Turyn’s TestDorsiflexion of big toe – No leg raisePositive sign of pain may indicate Sciatic nerve rootirritation
Sacroiliac Stretch TestExaminer places crossed hands on opposite ASISs andapplies downward lateral pressureUnilateral gluteal pain indicates sprain of the anterior SIligament
Patrick FABERE Test(AKA: Sign of Four)
Laquerre’s Test(AKA: Fabere in the Air)
Goldthwait Test
Gaenslen Test
Cox SignDuring Straight Leg RaisePositive if pelvis arises from the table instead of hip flexingMay indicate a prolapse of the nucleus into the IVF
Laseque Differential TestLeg is brought to degree obtained with SLRWith hip and leg flexed, pain is relieved, this rules out HipJoint disease.Sciatic pain returns or is exacerbated when leg is extendedsuspect sciatic problem
Milgram’s TestInability to raise legs to 6 inches off table, due to L/S pain,may indicate a space occupying lesion such as a herniateddisc
Bowstring SignIf exerting pressure on the hamstring is painful,exert pressure into popliteal fossa.Pain in Lumbar region or radiculopathy is positive fornerve root compression
Lindner’s SignPain in lumbosacral region upon flexing head, suspectnerve root irritation
Thomas TestHip Flexor ContractureIf the Lumbar spine maintains lordosis and the affected legflexes so that the patient is unable to lay the leg flat on thetable, this may indicate a shortened Iliopsoas muscle.
Soto-HallWhile head is flexed toward the chest, flexion of the kneesand thighs may indicate spinal meningitis.
Beevor’s SignDeviation of the belly button while legs are raised orpatient does a sit up indicates weak muscles on the side thatthe belly button deviated away from.
SI Resisted Abduction TestPerformed with myotome testing
Variation on Gaenslen’s TestLewin-Gaenslen Test
Iliac Compression Test
Yeoman’s Test
Nachlas TestHeel to Buttock Test
Hibbs TestHeel to Buttock TestLateral
Ely’s TestHeel to Buttock TestCross medially toward opposite buttock
CoughSneezePain during defecationDejerine’s Triadmay indicate a space-occupying lesion
Valsalva Test
Tripod Test
Belt Test - Supported Forward Bending
Minors SignLumbosacral LesionsPositive if the patient supports their weight on theunaffected side while standing up from a seated position.
Kemp’s TestStanding or SittingPerforming the test while patient is seated reduces SIinvolvementMed./Lat. Disc Bulge or Facet IrritationNOTE: Kemps can also produce localized pain from facetirritation
Chest Expansion TestMeasure Patient at level of nipplePatient exhales and record measurementThen Patient inhales record change in measurementNormal male = 2 inchesNormal female 1 ½ inchesIf measurement is less suspectAnkylosing condition such as Ankylosing Spondylitis
Sternal Compression
Schepelmann’s Sign