Chapter 1 Discrete Probability Distributions - DIM
Chapter 1 Discrete Probability Distributions - DIM
Chapter 1 Discrete Probability Distributions - DIM
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
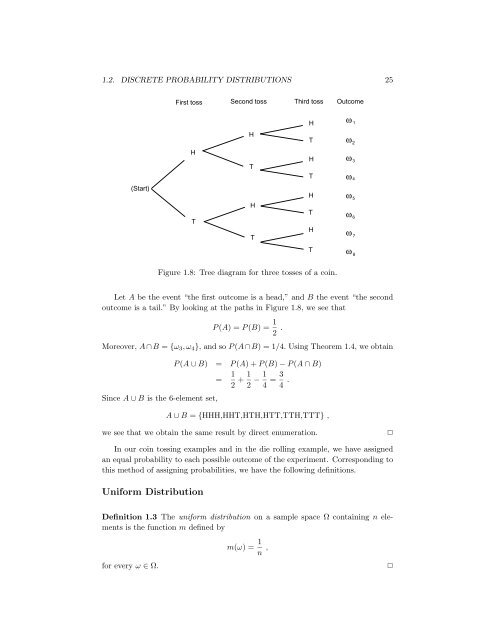
1.2. DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS 25First toss Second toss Third toss OutcomeHω1HTω2HTHTωω34(Start)THTHTHωωω567Tω8Figure 1.8: Tree diagram for three tosses of a coin.Let A be the event “the first outcome is a head,” and B the event “the secondoutcome is a tail.” By looking at the paths in Figure 1.8, we see thatP (A) =P(B)= 1 2 .Moreover, A ∩ B = {ω 3 ,ω 4 }, and so P (A ∩ B) =1/4.Using Theorem 1.4, we obtainSince A ∪ B is the 6-element set,P (A ∪ B) = P(A)+P(B)−P(A∩B)= 1 2 +1 2 −1 4 = 3 4 .A ∪ B = {HHH,HHT,HTH,HTT,TTH,TTT} ,we see that we obtain the same result by direct enumeration.✷In our coin tossing examples and in the die rolling example, we have assignedan equal probability to each possible outcome of the experiment. Corresponding tothis method of assigning probabilities, we have the following definitions.Uniform DistributionDefinition 1.3 The uniform distribution on a sample space Ω containing n elementsis the function m defined bym(ω) = 1 n ,for every ω ∈ Ω.✷