- Page 1 and 2: Neural Network ToolboxFor Use with
- Page 3: Printing History: June 1992 First p
- Page 6 and 7: PrefaceNeural NetworksNeural networ
- Page 8 and 9: PrefaceBasic ChaptersThe Neural Net
- Page 10 and 11: PrefaceInput Weight MatrixLayer Wei
- Page 12 and 13: PrefaceNeural Network Design BookPr
- Page 14 and 15: PrefaceOrlando De Jesús of Oklahom
- Page 16 and 17: Generalization and Speed Benchmarks
- Page 18 and 19: Introduction to the GUI . . . . . .
- Page 20 and 21: Mean and Stand. Dev. (prestd, posts
- Page 22 and 23: Graphical Example . . . . . . . . .
- Page 24 and 25: 11ApplicationsIntroduction . . . .
- Page 26 and 27: 14ReferenceFunctions — Categorica
- Page 28 and 29: Block Generation . . . . . . . . .
- Page 30 and 31: 1 IntroductionGetting StartedBasic
- Page 32 and 33: 1 IntroductionNote We no longer rec
- Page 34 and 35: 1 IntroductionDefense• Weapon ste
- Page 36 and 37: 1 Introduction1-8
- Page 38 and 39: 2 Neuron Model and Network Architec
- Page 40 and 41: 2 Neuron Model and Network Architec
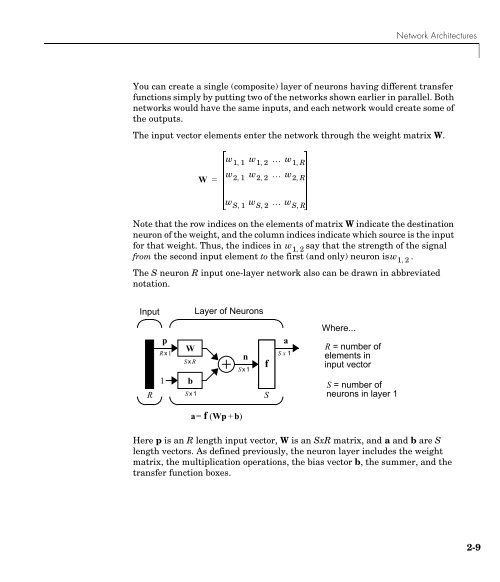
- Page 42 and 43: 2 Neuron Model and Network Architec
- Page 46 and 47: 2 Neuron Model and Network Architec
- Page 48 and 49: 2 Neuron Model and Network Architec
- Page 50 and 51: 2 Neuron Model and Network Architec
- Page 52 and 53: 2 Neuron Model and Network Architec
- Page 54 and 55: 2 Neuron Model and Network Architec
- Page 56 and 57: 2 Neuron Model and Network Architec
- Page 58 and 59: 2 Neuron Model and Network Architec
- Page 60 and 61: 2 Neuron Model and Network Architec
- Page 62 and 63: 2 Neuron Model and Network Architec
- Page 64 and 65: 2 Neuron Model and Network Architec
- Page 66 and 67: 2 Neuron Model and Network Architec
- Page 68 and 69: 2 Neuron Model and Network Architec
- Page 70 and 71: 3 PerceptronsIntroductionThis chapt
- Page 72 and 73: 3 PerceptronsNeuron ModelA perceptr
- Page 74 and 75: 3 PerceptronsPerceptron Architectur
- Page 76 and 77: 3 Perceptronsgivesbiases = net.bias
- Page 78 and 79: 3 Perceptronswhich givesbias =0Now
- Page 80 and 81: 3 PerceptronsLearning RulesWe defin
- Page 82 and 83: 3 PerceptronsCASE 1. If e = 0, then
- Page 84 and 85: 3 PerceptronsTraining (train)If sim
- Page 86 and 87: 3 PerceptronsOn this occasion, the
- Page 88 and 89: 3 PerceptronsTRAINC, Epoch 0/20TRAI
- Page 90 and 91: 3 PerceptronsBy changing the percep
- Page 92 and 93: 3 PerceptronsClick on Help to get s
- Page 94 and 95:
3 PerceptronsNext you might look at
- Page 96 and 97:
3 PerceptronsThus, the network was
- Page 98 and 99:
3 Perceptrons2 1Similarly,ANDNet.b{
- Page 100 and 101:
3 Perceptronswindow. Select the Loa
- Page 102 and 103:
3 PerceptronsPerceptron Transfer Fu
- Page 104 and 105:
3 PerceptronsOne Perceptron NeuronI
- Page 106 and 107:
4 Linear FiltersIntroductionThe lin
- Page 108 and 109:
4 Linear FiltersNetwork Architectur
- Page 110 and 111:
4 Linear FiltersWe can create a net
- Page 112 and 113:
4 Linear FiltersMean Square ErrorLi
- Page 114 and 115:
4 Linear FiltersLinear Networks wit
- Page 116 and 117:
4 Linear Filtersnet = newlind(P,T,P
- Page 118 and 119:
4 Linear FiltersFinally, the change
- Page 120 and 121:
4 Linear FiltersWe will use train t
- Page 122 and 123:
4 Linear FiltersLimitations and Cau
- Page 124 and 125:
4 Linear FiltersSummarySingle-layer
- Page 126 and 127:
4 Linear FiltersLinear Network Laye
- Page 128 and 129:
4 Linear FiltersTapped Delay LineTD
- Page 130 and 131:
4 Linear FiltersFunctionlearnwhpure
- Page 132 and 133:
5 BackpropagationIntroductionBackpr
- Page 134 and 135:
5 BackpropagationFundamentalsArchit
- Page 136 and 137:
5 BackpropagationThe three transfer
- Page 138 and 139:
5 Backpropagationweights, but you m
- Page 140 and 141:
5 BackpropagationBatch Gradient Des
- Page 142 and 143:
5 BackpropagationMomentum can be ad
- Page 144 and 145:
5 BackpropagationFaster TrainingThe
- Page 146 and 147:
5 BackpropagationThe function train
- Page 148 and 149:
5 Backpropagationdifferent search f
- Page 150 and 151:
5 BackpropagationPolak-Ribiére Upd
- Page 152 and 153:
5 Backpropagation[net,tr]=train(net
- Page 154 and 155:
5 BackpropagationThis procedure is
- Page 156 and 157:
5 BackpropagationThe backtracking a
- Page 158 and 159:
5 BackpropagationTRAINOSS-srchbac,
- Page 160 and 161:
5 Backpropagationequation is a buil
- Page 162 and 163:
5 BackpropagationSpeed and Memory C
- Page 164 and 165:
5 BackpropagationAlgorithmMeanTime
- Page 166 and 167:
5 BackpropagationSpeed Comparison o
- Page 168 and 169:
5 BackpropagationComparsion of Conv
- Page 170 and 171:
5 BackpropagationThe following figu
- Page 172 and 173:
5 Backpropagationon pattern recogni
- Page 174 and 175:
5 BackpropagationTime Comparison on
- Page 176 and 177:
5 BackpropagationComparsion of Conv
- Page 178 and 179:
5 BackpropagationAlgorithmMeanTime
- Page 180 and 181:
5 Backpropagationnumber of weights.
- Page 182 and 183:
5 Backpropagationgeneralization tha
- Page 184 and 185:
5 Backpropagationp = [-1:.05:1];t =
- Page 186 and 187:
5 Backpropagationprocess. If the er
- Page 188 and 189:
5 Backpropagationtraining parameter
- Page 190 and 191:
5 BackpropagationBayesian regulariz
- Page 192 and 193:
5 Backpropagationaccomplished with
- Page 194 and 195:
5 Backpropagationpnewn = trastd(pne
- Page 196 and 197:
5 BackpropagationSample Training Se
- Page 198 and 199:
5 Backpropagation3.532.5TrainingVal
- Page 200 and 201:
5 Backpropagation120Best Linear Fit
- Page 202 and 203:
5 Backpropagationcorrect weights fo
- Page 204 and 205:
5 BackpropagationFunctiontraincgftr
- Page 206 and 207:
5 Backpropagation5-76
- Page 208 and 209:
6 Control SystemsIntroductionNeural
- Page 211 and 212:
NN Predictive ControlThe neural net
- Page 213 and 214:
NN Predictive Controlw 1 w 2C b1C b
- Page 215 and 216:
NN Predictive ControlThe File menu
- Page 217 and 218:
NN Predictive Control5 Select the G
- Page 219 and 220:
NN Predictive Controlplant output a
- Page 221 and 222:
NARMA-L2 (Feedback Linearization) C
- Page 223 and 224:
NARMA-L2 (Feedback Linearization) C
- Page 225 and 226:
NARMA-L2 (Feedback Linearization) C
- Page 227 and 228:
NARMA-L2 (Feedback Linearization) C
- Page 229 and 230:
Model Reference ControlModel Refere
- Page 231 and 232:
Model Reference ControlUsing the Mo
- Page 233 and 234:
Model Reference ControlThe file men
- Page 235 and 236:
Model Reference Controlbecause the
- Page 237 and 238:
Importing and ExportingImporting an
- Page 239 and 240:
Importing and ExportingThis causes
- Page 241 and 242:
Importing and ExportingImporting an
- Page 243 and 244:
Importing and ExportingSelect MAT-f
- Page 245 and 246:
7Radial Basis NetworksIntroduction
- Page 247 and 248:
Radial Basis FunctionsRadial Basis
- Page 249 and 250:
Radial Basis FunctionsFortunately,
- Page 251 and 252:
Radial Basis Functionsacceptable so
- Page 253 and 254:
Generalized Regression NetworksGene
- Page 255 and 256:
Generalized Regression NetworksP =
- Page 257 and 258:
Probabilistic Neural NetworksThe se
- Page 259 and 260:
SummarySummaryRadial basis networks
- Page 261 and 262:
SummaryRadial Basis Network Archite
- Page 263 and 264:
SummaryFunctionnewpnnnewrbnewrbenor
- Page 265 and 266:
8Self-Organizing andLearn. Vector Q
- Page 267 and 268:
Competitive LearningCompetitive Lea
- Page 269 and 270:
Competitive LearningKohonen Learnin
- Page 271 and 272:
Competitive LearningThus, during ea
- Page 273 and 274:
Self-Organizing MapsSelf-Organizing
- Page 275 and 276:
Self-Organizing MapsHere neuron 1 h
- Page 277 and 278:
Self-Organizing Mapsplotsom(pos)to
- Page 279 and 280:
Self-Organizing Maps0 1 20 1 2We fi
- Page 281 and 282:
Self-Organizing MapsandP1= [1;1]P1
- Page 283 and 284:
Self-Organizing Maps2Weight Vectors
- Page 285 and 286:
Self-Organizing MapsLearning occurs
- Page 287 and 288:
Self-Organizing MapsWeight Vectors1
- Page 289 and 290:
Self-Organizing Maps1.51W(i,2)0.50-
- Page 291 and 292:
Self-Organizing Maps10.50-0.5-1-1 0
- Page 293 and 294:
Self-Organizing MapsAfter 120 cycle
- Page 295 and 296:
Learning Vector Quantization Networ
- Page 297 and 298:
Learning Vector Quantization Networ
- Page 299 and 300:
Learning Vector Quantization Networ
- Page 301 and 302:
Learning Vector Quantization Networ
- Page 303 and 304:
Learning Vector Quantization Networ
- Page 305 and 306:
SummaryFiguresCompetitive Network A
- Page 307 and 308:
SummaryFunctionnewlvqlearnlv1learnl
- Page 309 and 310:
9Recurrent NetworksIntroduction (p.
- Page 311 and 312:
Elman NetworksElman NetworksArchite
- Page 313 and 314:
Elman NetworksY = sim(net,Pseq)Y =C
- Page 315 and 316:
Elman NetworksT = [0 (P(1:end-1)+P(
- Page 317 and 318:
Hopfield Networka1(k-1) Dn1R 1pR 1
- Page 319 and 320:
Hopfield NetworkWe can execute the
- Page 321 and 322:
Hopfield Networkwhich givesW =0.692
- Page 323 and 324:
SummarySummaryElman networks, by ha
- Page 325 and 326:
SummaryNew FunctionsThis chapter in
- Page 327 and 328:
10Adaptive Filters andAdaptive Trai
- Page 329 and 330:
Linear Neuron ModelLinear Neuron Mo
- Page 331 and 332:
Adaptive Linear Network Architectur
- Page 333 and 334:
Mean Square ErrorMean Square ErrorL
- Page 335 and 336:
Adaptive Filtering (adapt)Adaptive
- Page 337 and 338:
Adaptive Filtering (adapt)InputLine
- Page 339 and 340:
Adaptive Filtering (adapt)bias = ne
- Page 341 and 342:
Adaptive Filtering (adapt)Pilot’s
- Page 343 and 344:
Adaptive Filtering (adapt)p(k)pd(k)
- Page 345 and 346:
SummaryPurelin Transfer Functiona0+
- Page 347 and 348:
SummaryLMS (Widrow-Hoff) AlgorithmT
- Page 349 and 350:
SummaryAdaptive Filter ExampleInput
- Page 351 and 352:
SummaryMultiple Neuron Adaptive Fil
- Page 353 and 354:
11ApplicationsIntroduction (p. 11-2
- Page 355 and 356:
Applin1: Linear DesignApplin1: Line
- Page 357 and 358:
Applin1: Linear Design1Output and T
- Page 359 and 360:
Applin2: Adaptive PredictionApplin2
- Page 361 and 362:
Applin2: Adaptive Prediction1.5Outp
- Page 363 and 364:
Appelm1: Amplitude DetectionAppelm1
- Page 365 and 366:
Appelm1: Amplitude DetectionThe fin
- Page 367 and 368:
Appelm1: Amplitude DetectionImprovi
- Page 369 and 370:
Appcr1: Character RecognitionPerfec
- Page 371 and 372:
Appcr1: Character RecognitionThen,
- Page 373 and 374:
Appcr1: Character Recognition50Perc
- Page 375 and 376:
12Advanced TopicsCustom Networks (p
- Page 377 and 378:
Custom NetworksTo create custom net
- Page 379 and 380:
Custom NetworksNote that net.numInp
- Page 381 and 382:
Custom NetworksSubobject Properties
- Page 383 and 384:
Custom Networksnet.layers{1}.initFc
- Page 385 and 386:
Custom Networkssize: 4userdata: [1x
- Page 387 and 388:
Custom Networksans =-0.3040 0.4703-
- Page 389 and 390:
Custom NetworksY =[3x1 double] [3x1
- Page 391 and 392:
Additional Toolbox FunctionsLearnin
- Page 393 and 394:
Custom Functionsoutput and net inpu
- Page 395 and 396:
Custom Functionsinput must have the
- Page 397 and 398:
Custom FunctionsTo be a valid weigh
- Page 399 and 400:
Custom FunctionsYour network initia
- Page 401 and 402:
Custom Functionsb = rands(S)where:
- Page 403 and 404:
Custom FunctionsWhen you set the ne
- Page 405 and 406:
Custom Functions• Tl is an N l ×
- Page 407 and 408:
Custom Functions- Each E{i,ts} is t
- Page 409 and 410:
Custom FunctionsWeight and Bias Lea
- Page 411 and 412:
Custom FunctionsOnce defined, you c
- Page 413 and 414:
Custom FunctionsTo be a valid dista
- Page 415 and 416:
13Network Object ReferenceNetwork P
- Page 417 and 418:
Network Propertiesnet.outputConnect
- Page 419 and 420:
Network PropertiesIt can be set to
- Page 421 and 422:
Network PropertiesInput Properties.
- Page 423 and 424:
Network Propertiesif the correspond
- Page 425 and 426:
Network PropertiesIt can be set to
- Page 427 and 428:
Network PropertiesThe fields of thi
- Page 429 and 430:
Network PropertiesLWThis property d
- Page 431 and 432:
Subobject PropertiesSubobject Prope
- Page 433 and 434:
Subobject Propertiesnet.layers{i}.d
- Page 435 and 436:
Subobject Propertiespositions (read
- Page 437 and 438:
Subobject PropertiesCustom function
- Page 439 and 440:
Subobject Propertiesnet.layers{i}.u
- Page 441 and 442:
Subobject PropertieslearnFcnThis pr
- Page 443 and 444:
Subobject PropertiesinitFcnThis pro
- Page 445 and 446:
Subobject Properties(net.trainFcn)
- Page 447 and 448:
Subobject PropertiesinitFcnThis pro
- Page 449 and 450:
Subobject Properties(net.trainFcn)
- Page 451 and 452:
14ReferenceFunctions — Categorica
- Page 453 and 454:
Functions — Categorical ListLearn
- Page 455 and 456:
Functions — Categorical ListNew N
- Page 457 and 458:
Functions — Categorical ListPre-
- Page 459 and 460:
Functions — Categorical ListTrans
- Page 461 and 462:
Functions — Categorical ListUtili
- Page 463 and 464:
Functions — Categorical ListWeigh
- Page 465 and 466:
Transfer Function Graphsa0+1-1a = l
- Page 467 and 468:
Transfer Function GraphsInput nOutp
- Page 469 and 470:
Functions — Alphabetical Listdtri
- Page 471 and 472:
Functions — Alphabetical Listplot
- Page 473 and 474:
adaptPurpose14adaptAllow a neural n
- Page 475 and 476:
adaptThe matrix format can be used
- Page 477 and 478:
oxdistPurpose14boxdistBox distance
- Page 479 and 480:
calcaHere the two initial layer del
- Page 481 and 482:
calca1Pc = [Pi P];Pd = calcpd(net,8
- Page 483 and 484:
calceHere we define the layer targe
- Page 485 and 486:
calce1[Ac,N,LWZ,IWZ,BZ] = calca(net
- Page 487 and 488:
calcgxnet.layerConnect(1,1) = 1;net
- Page 489 and 490:
calcjejjExamplesHere we create a li
- Page 491 and 492:
calcjxHere the two initial layer de
- Page 493 and 494:
calcperfPurpose14calcperfCalculate
- Page 495 and 496:
combvecPurpose14combvecCreate all c
- Page 497 and 498:
competTo model this type of layer e
- Page 499 and 500:
concurPurpose14concurCreate concurr
- Page 501 and 502:
dhardlimPurpose14dhardlimDerivative
- Page 503 and 504:
dispPurpose14dispDisplay a neural n
- Page 505 and 506:
distPurpose14distEuclidean distance
- Page 507 and 508:
dlogsigPurpose14dlogsigLog sigmoid
- Page 509 and 510:
dmsePurpose14dmseMean squared error
- Page 511 and 512:
dnetprodPurpose14dnetprodDerivative
- Page 513 and 514:
dotprodPurpose14dotprodDot product
- Page 515 and 516:
dpurelinPurpose14dpurelinLinear tra
- Page 517 and 518:
dsatlinPurpose14dsatlinDerivative o
- Page 519 and 520:
dssePurpose14dsseSum squared error
- Page 521 and 522:
dtribasPurpose14dtribasDerivative o
- Page 523 and 524:
formxPurpose14formxForm bias and we
- Page 525 and 526:
getxPurpose14getxGet all network we
- Page 527 and 528:
hardlimPurpose14hardlimHard limit t
- Page 529 and 530:
hardlimsPurpose14hardlimsSymmetric
- Page 531 and 532:
hextopPurpose14hextopHexagonal laye
- Page 533 and 534:
hintonwbPurpose14hintonwbHinton gra
- Page 535 and 536:
initPurpose14initInitialize a neura
- Page 537 and 538:
initconPurpose14initconConscience b
- Page 539 and 540:
initnwPurpose14initnwNguyen-Widrow
- Page 541 and 542:
initwbPurpose14initwbBy-weight-and-
- Page 543 and 544:
learnconPurpose14learnconConscience
- Page 545 and 546:
learncon(Note that learncon is able
- Page 547 and 548:
learngdExamples Here we define a ra
- Page 549 and 550:
learngdmlearngdm(code) returns usef
- Page 551 and 552:
learnhPurpose14learnhHebb weight le
- Page 553 and 554:
learnhdPurpose14learnhdHebb with de
- Page 555 and 556:
learnisPurpose14learnisInstar weigh
- Page 557 and 558:
learnkPurpose14learnkKohonen weight
- Page 559 and 560:
learnlv1Purpose14learnlv1LVQ1 weigh
- Page 561 and 562:
learnlv2Purpose14learnlv2LVQ2.1 wei
- Page 563 and 564:
learnlv2the input p is roughly equa
- Page 565 and 566:
learnosExamplesHere we define a ran
- Page 567 and 568:
learnpe = rand(3,1);Since learnp on
- Page 569 and 570:
learnpnPurpose14learnpnNormalized p
- Page 571 and 572:
learnpntargets of 1 cannot be separ
- Page 573 and 574:
learnsomlearnpn(code) returns usefu
- Page 575 and 576:
learnwhPurpose14learnwhWidrow-Hoff
- Page 577 and 578:
learnwhSee AlsoReferencesnewlin, ad
- Page 579 and 580:
logsigPurpose14logsigLog sigmoid tr
- Page 581 and 582:
maePurpose14maeMean absolute error
- Page 583 and 584:
mandistPurpose14mandistManhattan di
- Page 585 and 586:
maxlinlrPurpose14maxlinlrMaximum le
- Page 587 and 588:
minmaxPurpose14minmaxRanges of matr
- Page 589 and 590:
mseperf = mse(e)Note that mse can b
- Page 591 and 592:
mseregmsereg(code) returns useful i
- Page 593 and 594:
netprodPurpose14netprodProduct net
- Page 595 and 596:
networkPurpose14networkCreate a cus
- Page 597 and 598:
networkSubobject structure properti
- Page 599 and 600:
networknet.layers{1}.transferFcn =
- Page 601 and 602:
newcYc = vec2ind(Y)See Alsosim, ini
- Page 603 and 604:
newcfExamplesHere is a problem cons
- Page 605 and 606:
newelmExamples Here is a series of
- Page 607 and 608:
newffExamplesHere is a problem cons
- Page 609 and 610:
newfftdThe performance function can
- Page 611 and 612:
newgrnnSee AlsoReferencessim, newrb
- Page 613 and 614:
newhopIf you run the above code, Y{
- Page 615 and 616:
newlinP2 = {1 0 -1 -1 1 1 1 0 -1};T
- Page 617 and 618:
newlindT = {5.0 6.1 4.0 6.0 6.9 8.0
- Page 619 and 620:
newlvqThe target classes Tc are con
- Page 621 and 622:
newpHere we define a sequence of ta
- Page 623 and 624:
newpnnnewpnn sets the first layer w
- Page 625 and 626:
newrbsecond layer has purelin neuro
- Page 627 and 628:
newrbe[W{2,1} b{2}] * [A{1}; ones]
- Page 629 and 630:
newsomplotsom(net.layers{1}.positio
- Page 631 and 632:
nnt2cPurpose14nnt2cUpdate NNT 2.0 c
- Page 633 and 634:
nnt2ffPurpose14nnt2ffUpdate NNT 2.0
- Page 635 and 636:
nnt2linPurpose14nnt2linUpdate NNT 2
- Page 637 and 638:
nnt2pPurpose14nnt2pUpdate NNT 2.0 p
- Page 639 and 640:
nnt2somPurpose14nnt2somUpdate NNT 2
- Page 641 and 642:
normcPurpose14normcNormalize the co
- Page 643 and 644:
normrPurpose14normrNormalize the ro
- Page 645 and 646:
plotepPurpose14plotepPlot a weight-
- Page 647 and 648:
plotpcPurpose14plotpcPlot a classif
- Page 649 and 650:
plotpvPurpose14plotpvPlot perceptro
- Page 651 and 652:
plotvPurpose14plotvPlot vectors as
- Page 653 and 654:
pnormcPurpose14pnormcPseudo-normali
- Page 655 and 656:
poslinCall sim to simulate the netw
- Page 657 and 658:
postmnmxSee Alsopremnmx, prepca, po
- Page 659 and 660:
postregSee Alsopremnmx, prepca14-20
- Page 661 and 662:
poststdSee Alsopremnmx, prepca, pos
- Page 663 and 664:
prepcaPurpose14prepcaPrincipal comp
- Page 665 and 666:
prestd14prestdPurpose Preprocess da
- Page 667 and 668:
purelinTo change a network so a lay
- Page 669 and 670:
adbasPurpose14radbasRadial basis tr
- Page 671 and 672:
andncPurpose14randncNormalized colu
- Page 673 and 674:
andsPurpose14randsSymmetric random
- Page 675 and 676:
evertPurpose14revertChange network
- Page 677 and 678:
satlinCall sim to simulate the netw
- Page 679 and 680:
satlinsTo change a network so that
- Page 681 and 682:
setxPurpose14setxSet all network we
- Page 683 and 684:
simThe cell array format is easiest
- Page 685 and 686:
sim[y2,pf] = sim(net,p2,pf)Here new
- Page 687 and 688:
softmaxPurpose14softmaxSoft max tra
- Page 689 and 690:
srchbacPurpose14srchbacOne-dimensio
- Page 691 and 692:
srchbacp = [0 1 2 3 4 5];t = [0 0 0
- Page 693 and 694:
srchbrePurpose14srchbreOne-dimensio
- Page 695 and 696:
srchbreHere a two-layer feed-forwar
- Page 697 and 698:
srchchameanings for different searc
- Page 699 and 700:
srchgolPurpose14srchgolOne-dimensio
- Page 701 and 702:
srchgolhas one logsig neuron. The t
- Page 703 and 704:
srchhybmeanings for different searc
- Page 705 and 706:
ssePurpose14sseSum squared error pe
- Page 707 and 708:
sumsqrPurpose14sumsqrSum squared el
- Page 709 and 710:
tansigNetwork UseYou can create a s
- Page 711 and 712:
trainThe cell array format is easie
- Page 713 and 714:
trainy1 = sim(net,p)plot(p,t,'o',p,
- Page 715 and 716:
trainbTraining occurs according to
- Page 717 and 718:
trainbfgPurpose14trainbfgBFGS quasi
- Page 719 and 720:
trainbfgnet.trainParam.low_lim0.1 L
- Page 721 and 722:
trainbfgTo prepare a custom network
- Page 723 and 724:
trainbrPurpose14trainbrBayesian reg
- Page 725 and 726:
trainbrIf VV is not [], it must be
- Page 727 and 728:
trainbrThe adaptive value mu is inc
- Page 729 and 730:
traincTraining occurs according to
- Page 731 and 732:
traincgbPurpose14traincgbConjugate
- Page 733 and 734:
traincgbDimensions for these variab
- Page 735 and 736:
traincgbAlgorithmtraincgb can train
- Page 737 and 738:
traincgfTraining occurs according t
- Page 739 and 740:
traincgftraincgf(code) returns usef
- Page 741 and 742:
traincgfReferencesScales, L. E., In
- Page 743 and 744:
traincgpTraining occurs according t
- Page 745 and 746:
traincgptraincgp(code) returns usef
- Page 747 and 748:
traincgpReferencesScales, L. E., In
- Page 749 and 750:
traingdTraining occurs according to
- Page 751 and 752:
traingdaPurpose14traingdaGradient d
- Page 753 and 754:
traingdaValidation vectors are used
- Page 755 and 756:
traingdmPurpose14traingdmGradient d
- Page 757 and 758:
traingdmtraingdm(code) returns usef
- Page 759 and 760:
traingdxTraining occurs according t
- Page 761 and 762:
traingdx• The maximum amount of t
- Page 763 and 764:
trainlmTraining occurs according to
- Page 765 and 766:
trainlmwhere E is all errors and I
- Page 767 and 768:
trainossTraining occurs according t
- Page 769 and 770:
trainosstrainoss(code) returns usef
- Page 771 and 772:
trainrPurpose14trainrRandom order i
- Page 773 and 774:
trainr3 Set each net.layerWeights{i
- Page 775 and 776:
trainrpTraining occurs according to
- Page 777 and 778:
trainrpNetwork UseYou can create a
- Page 779 and 780:
trainsPurpose14trainsSequential ord
- Page 781 and 782:
trainsTo allow the network to adapt
- Page 783 and 784:
trainscgTraining occurs according t
- Page 785 and 786:
trainscgNetwork UseYou can create a
- Page 787 and 788:
tramnmxSee Alsopremnmx, prestd, pre
- Page 789 and 790:
trapcaAlgorithmSee AlsoPtrans = tra
- Page 791 and 792:
trastdSee Alsopremnmx, prepca, pres
- Page 793 and 794:
tribasCall sim to simulate the netw
- Page 795 and 796:
GlossaryA
- Page 797 and 798:
ias vector - A column vector of bia
- Page 799 and 800:
Fletcher-Reeves update - A method d
- Page 801 and 802:
local minimum - The minimum of a fu
- Page 803 and 804:
perceptron learning rule - A learni
- Page 805 and 806:
symmetric hard-limit transfer funct
- Page 807 and 808:
BibliographyB
- Page 809 and 810:
discusses their current application
- Page 811 and 812:
[LiMi89] Li, J., A. N. Michel, and
- Page 813 and 814:
[RuHi86b] Rumelhart, D. E., G. E. H
- Page 815 and 816:
Demonstrations andApplicationsC
- Page 817 and 818:
Tables of Demonstrations and Applic
- Page 819 and 820:
Tables of Demonstrations and Applic
- Page 821 and 822:
DSimulinkBlock Set (p. D-2)Block Ge
- Page 823 and 824:
Block SetEach of these blocks takes
- Page 825 and 826:
Block GenerationBlock GenerationThe
- Page 827 and 828:
Block GenerationNote that the outpu
- Page 829 and 830:
ECode NotesDimensions (p. E-2)Varia
- Page 831 and 832:
VariablesVariablesThe variables a u
- Page 833 and 834:
VariablesIWZWeighted inputs.Ni-by-N
- Page 835 and 836:
FunctionsFunctionsThe following fun
- Page 837 and 838:
Argument CheckingArgument CheckingT
- Page 839 and 840:
IndexAADALINE networkdecision bound
- Page 841 and 842:
IndexManhattan 8-16tuning phase 8-1
- Page 843 and 844:
Indexlinear transfer function 2-3,
- Page 845 and 846:
IndexNNT block set D-2SimulinkNNT b