Start a pig farm (Part 3) - Ubisi Mail Magazine
Start a pig farm (Part 3) - Ubisi Mail Magazine
Start a pig farm (Part 3) - Ubisi Mail Magazine
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
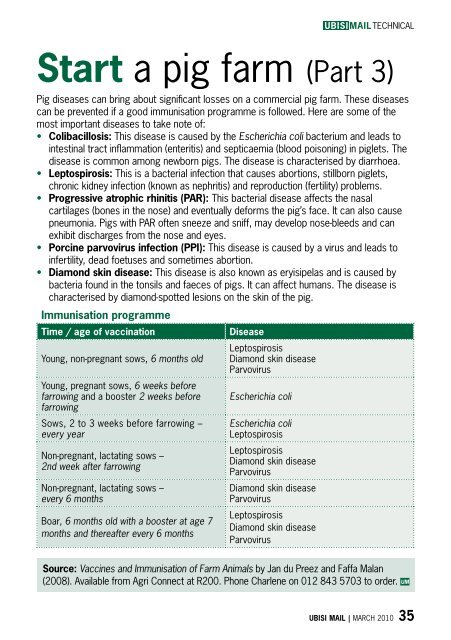
TECHNICAL<strong>Start</strong> a <strong>pig</strong> <strong>farm</strong> (<strong>Part</strong> 3)Pig diseases can bring about significant losses on a commercial <strong>pig</strong> <strong>farm</strong>. These diseasescan be prevented if a good immunisation programme is followed. Here are some of themost important diseases to take note of:• Colibacillosis: This disease is caused by the Escherichia coli bacterium and leads tointestinal tract inflammation (enteritis) and septicaemia (blood poisoning) in <strong>pig</strong>lets. Thedisease is common among newborn <strong>pig</strong>s. The disease is characterised by diarrhoea.• Leptospirosis: This is a bacterial infection that causes abortions, stillborn <strong>pig</strong>lets,chronic kidney infection (known as nephritis) and reproduction (fertility) problems.• Progressive atrophic rhinitis (PAR): This bacterial disease affects the nasalcartilages (bones in the nose) and eventually deforms the <strong>pig</strong>’s face. It can also causepneumonia. Pigs with PAR often sneeze and sniff, may develop nose-bleeds and canexhibit discharges from the nose and eyes.• Porcine parvovirus infection (PPI): This disease is caused by a virus and leads toinfertility, dead foetuses and sometimes abortion.• Diamond skin disease: This disease is also known as eryisipelas and is caused bybacteria found in the tonsils and faeces of <strong>pig</strong>s. It can affect humans. The disease ischaracterised by diamond-spotted lesions on the skin of the <strong>pig</strong>.Immunisation programmeTime / age of vaccinationYoung, non-pregnant sows, 6 months oldYoung, pregnant sows, 6 weeks beforefarrowing and a booster 2 weeks beforefarrowingSows, 2 to 3 weeks before farrowing –every yearNon-pregnant, lactating sows –2nd week after farrowingNon-pregnant, lactating sows –every 6 monthsBoar, 6 months old with a booster at age 7months and thereafter every 6 monthsDiseaseLeptospirosisDiamond skin diseaseParvovirusEscherichia coliEscherichia coliLeptospirosisLeptospirosisDiamond skin diseaseParvovirusDiamond skin diseaseParvovirusLeptospirosisDiamond skin diseaseParvovirusSource: Vaccines and Immunisation of Farm Animals by Jan du Preez and Faffa Malan(2008). Available from Agri Connect at R200. Phone Charlene on 012 843 5703 to order. UMUBISI MAIL | MARCH 2010 35
TECHNICALMafu a dikolobe• Lefu la letshollo la dikolobe(colibacillosis): Lefu lena le baka letshollodikolojaneng tse sa tswa tswalwa.• Lefu la leptospirosis: Lefu lena le bakaho folotsa, le dikolojana tse hlahang dikgathetse, tshwaetso diphiyong, mathata aho tswala madinyana.• Lefu la progressive atrophic rhinitis:Lefu lena le baka nyumonia le diphasefahlehong sa dikolobe. Ho thimola, hotswa madi dinkong, ho tswa lero dinkongle melaka mahlong.• Lefu la tshwaetso le bitswang porcineparvovirus infection: Ho nyopa,madinyana a tswalwang a shwele, hofolotsa.• Lefu la letlalo le bitswang diamondskin disease: Diso tse matheba akang taemane letlalong. Diso tsena ditshwaetsa lesapo la mokokotlo, pelo,manonyeletso, feberu.Izifo zeehagu• I-Colibacillosis: Idala urhudokwiihagu ezisandula kuzalwa.• I-Leptospirosis: Idala iimekozokuqhomfa, iihagwanaezizalwa zifile, usulelolwezintso, iingxaki zenzala.• I-atrophic rhinitiseqhubekayo: Idalainyumoniya yaye yonakalisaubuso behagu. Ukuthimla,ukumongoza, ubhobhozooluphuma kwimpumlo nasemehlweni.• Usulelo lwe-Porcine parvovirus: Ukungazali, izinto engekazalwa ezifileyo,ukuqhomfeka.• Isifo solusu sedayimani: Izilonda ezidala amachokoza afana nedayimani kulusu.Sichaphazela umnqonqo, intliziyo, amalungu, ifiva. UMUBISI MAIL | MARCH 2010 37