September 2011 - Career Point
September 2011 - Career Point
September 2011 - Career Point
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
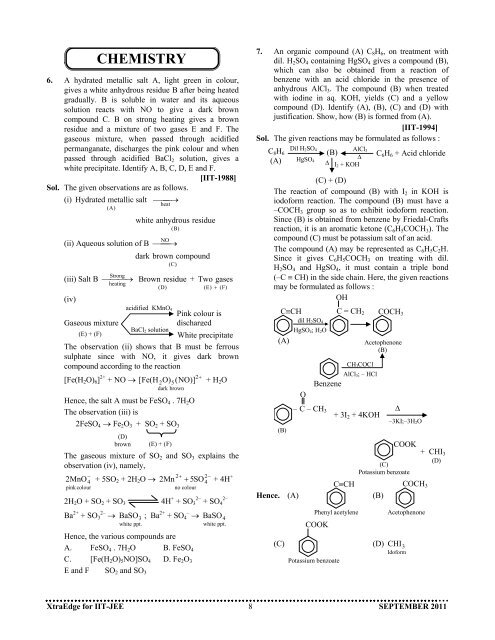
CHEMISTRY6. A hydrated metallic salt A, light green in colour,gives a white anhydrous residue B after being heatedgradually. B is soluble in water and its aqueoussolution reacts with NO to give a dark browncompound C. B on strong heating gives a brownresidue and a mixture of two gases E and F. Thegaseous mixture, when passed through acidifiedpermanganate, discharges the pink colour and whenpassed through acidified BaCl 2 solution, gives awhite precipitate. Identify A, B, C, D, E and F.[IIT-1988]Sol. The given observations are as follows.(i) Hydrated metallic salt ⎯ →(A)(ii) Aqueous solution of B(iii) Salt B(iv)⎯Strong ⎯⎯heatingGaseous mixture(E) + (F)→⎯ heat(B)white anhydrous residue⎯ NO ⎯→)dark brown compound(CBrown residue +(D)acidified KMnO 4BaCl 2 solutionTwo gases(E) + (F)Pink colour isdischargedWhite precipitateThe observation (ii) shows that B must be ferroussulphate since with NO, it gives dark browncompound according to the reaction[Fe(H 2 O) 6 ] 2+ 2+ NO → [Fe(H 2 O) 5(NO)]+ + H 2 Odark brownHence, the salt A must be FeSO 4 . 7H 2 OThe observation (iii) is2FeSO 4 → Fe 2 O 3 + SO 2 + SO 3(D)brown(E) + (F)The gaseous mixture of SO 2 and SO 3 explains theobservation (iv), namely,2MnO −4pink colour+ 5SO 2 + 2H 2 O → 2Mn2no colour2−4+ + 5SO + 4H +2H 2 O + SO 2 + SO 3 4H + + SO 2– 2–3 + SO 4Ba 2+ + SO 2– 3 → BaSO ; Ba 2+ + SO – 4 → BaSO3white ppt.Hence, the various compounds areA. FeSO 4 . 7H 2 O B. FeSO 4C. [Fe(H 2 O) 5 NO]SO 4 D. Fe 2 O 3E and F SO 2 and SO 34white ppt.7. An organic compound (A) C 8 H 6 , on treatment withdil. H 2 SO 4 containing HgSO 4 gives a compound (B),which can also be obtained from a reaction ofbenzene with an acid chloride in the presence ofanhydrous AlCl 3 . The compound (B) when treatedwith iodine in aq. KOH, yields (C) and a yellowcompound (D). Identify (A), (B), (C) and (D) withjustification. Show, how (B) is formed from (A).[IIT-1994]Sol. The given reactions may be formulated as follows :Dil HC 8 H 2SO 4AlCl 6(B)3C∆ 6 H 6 + Acid chloride(A) HgSO 4∆ I 2 + KOH(C) + (D)The reaction of compound (B) with I 2 in KOH isiodoform reaction. The compound (B) must have a–COCH 3 group so as to exhibit iodoform reaction.Since (B) is obtained from benzene by Friedal-Craftsreaction, it is an aromatic ketone (C 6 H 5 COCH 3 ). Thecompound (C) must be potassium salt of an acid.The compound (A) may be represented as C 6 H 5 C 2 H.Since it gives C 6 H 5 COCH 3 on treating with dil.H 2 SO 4 and HgSO 4 , it must contain a triple bond(–C ≡ CH) in the side chain. Here, the given reactionsmay be formulated as follows :OHC≡CHdil H 2SO 4HgSO 4; H 2O(A)(B)Hence. (A)(C)O– C – CH 3C = CH 2CH 3COClAlCl 3; – HClBenzene+ 3I 2 + 4KOHCOCH 3Acetophenone(B)∆–3KI;–3H 2OCOOK+ CHI3(D)(C)Potassium benzoateC≡CHCOCH 3(B)Phenyl acetyleneCOOKPotassium benzoate(D)AcetophenoneCHI 3IdoformXtraEdge for IIT-JEE 8 SEPTEMBER <strong>2011</strong>