BNZ6d
BNZ6d
BNZ6d
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
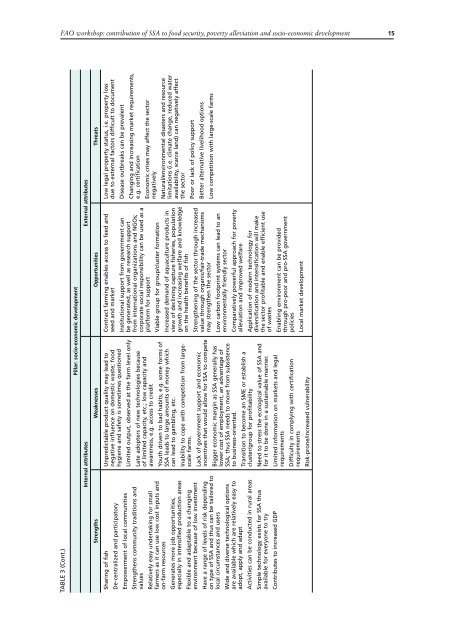
FAO workshop: contribution of SSA to food security, poverty alleviation and socio-economic development15TABLE 3 (Cont.)Pillar: socio-economic developmentInternal attributes External attributesStrengths Weaknesses Opportunities ThreatsSharing of fishDe-centralized and participatoryEmpowerment of local communitiesStrengthens community traditions andvaluesRelatively easy undertaking for smallfarmers as it can use low cost inputs andon-farm resourcesGenerates more job opportunities,especially in intensified production areasFlexible and adaptable to a changingenvironment because of low investmentHave a range of levels of risk dependingon type of SSA and thus can be tailored tolocal circumstances and usersWide and diverse technological optionsare available which are relatively easy toadopt, apply and adaptActivities can be conducted in rural areasSimple technology exists for SSA thusavailable for everyone to tryContributes to increased GDPUnpredictable product quality may lead tonegative influence on domestic waste; foodhygiene and safety is sometimes questionedLimited output, observed at the farm level onlyLate adopters of new technologies becauseof limited capacity, etc.; low capacity andawareness, e.g. access to creditYouth driven to bad habits, e.g. some forms ofSSA leads to large amounts of money whichcan lead to gambling, etc.Inability to cope with competition from largescalefarms.Lack of government support and economicincentives that would allow for SSA to competeBigger economic margin as SSA generally haslower cost of employment, an advantage ofSSA; thus SSA needs to move from subsistenceto business-oriented.Transition to become an SME or establish acluster/group for profitabilityNeed to stress the ecological value of SSA andfor it to be done in a sustainable manner.Limited information on markets and legalrequirementsDifficulty in complying with certificationrequirementsRisk-prone/increased vulnerabilityContract farming enables access to feed andseed and marketInstitutional support from government canbe generated, as well as research supportfrom international organizations and NGOs;corporate social responsibility can be used as aplatform for supportViable group for group/cluster formationIncreased demand of aquaculture products inview of declining capture fisheries, populationgrowth and increasing welfare and knowledgeon the health benefits of fishStrengthening of the sector through increasedvalue through organic/fair-trade mechanismsmay strengthen the sectorLow carbon footprint systems can lead to anenvironmentally friendly sectorComparatively powerful approach for povertyalleviation and improved welfareApplication of modern technology fordiversification and intensification will makethe sector profitable and enable efficient useof wastesEnabling environment can be providedthrough pro-poor and pro-SSA governmentpoliciesLocal market developmentLow legal property status, i.e. property lossdue to external factors difficult to documentDisease outbreaks can be prevalentChanging and increasing market requirements,e.g. certificationEconomic crises may affect the sectornegativelyNatural/environmental disasters and resourcelimitations (i.e. climate change, reduced wateravailability, scarce land) can negatively affectthe sectorPoor or lack of policy supportBetter alternative livelihood optionsLow competition with large-scale farms