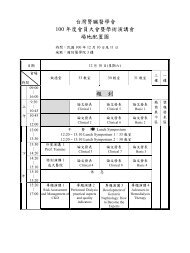
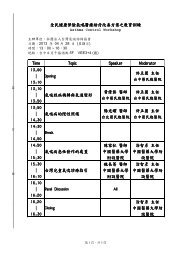
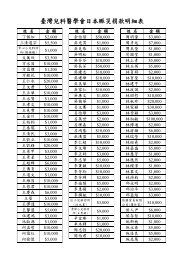
ABSTRACT OF INVITED LECTURES AND ORAL PRESENTATION
ABSTRACT OF INVITED LECTURES AND ORAL PRESENTATION
ABSTRACT OF INVITED LECTURES AND ORAL PRESENTATION
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
FP2-01A LONGITUDINAL MOLECULARSURVEILLANCE <strong>OF</strong> CLINICALMETHICILLIN-RESISTANTSTAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS ISOLATES INNEONATAL INTENSIVE CARE UNITS,1998-2007Yhu-Chering Huang, Lin-Hui Su, Tzou-Yien LinDepartments of Pediatrics and Laboratory Medicine, Chang GungMemorial Hospital, and Chang Gung University College of Medicine,TaiwanFP2-02CHARACTERIZATION <strong>OF</strong> VARIANTS IN THEPROMOTER <strong>OF</strong> BZLF1 GENE <strong>OF</strong> EBV INNONMALIGNANT EBV-ASSOCIATED DISEASESIN CHINESE CHILDRENZheng-De XIE, Ying-Kang JIN, Li-Wei GAO, Kun-LingSHENBeijing Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing,ChinaBACKGROUND:Methicillin-resistantStaphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has been animportant nosocomial pathogen in our neonatalintensive care units (NICUs) since 1990s. To assessthe molecular characteristics of these MRSA strains,we conducted this study.MATERIALS: We collected MRSA clinical isolatesfrom the infants hospitalized at our NICUs from1998 to 2007, except 2002. A total of 429 clinicalisolates were selected for molecular analysis,including 10 isolates in 1998, 56 in 1999, 56 in 2000,40 in 2001, 93 in 2003, 69 in 2004, 46 in 2005, 21 in2006 and 38 in 2007.RESULTS: A total of 7 pulsotypes were identified.There were two major clones and characterized assequence type (ST) 239 (or its single locus variant)/pulsotype A (Hungary clone)/ staphylococcalchromosomal cassette (SCC) mec III orIIIA/Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL)-negative,accounting for 62% of the isolates, andST59/pulsotype C/SCCmec IV/PVL-negative,accounting for 26%. The former clone was dominant(> 50% of the isolates) from 1998 to 2004, becameweakened (39% of the isolates) in 2005, reached zeroin 2006, and then resurged in 2007 (18% of theisolates). The latter clone remained steady (around30%) during the study period, except in 1998, 2001and 2003 (no more than 10%). Two communityclones, characterized as ST 59/pulsotype D/SCCmecV T /PLV-positive and ST 59/pulsotype AN/SCCmecIV/PVL-negative, emerged and increased markedlyin 2007.CONCLUSION: There were two dominant MRSAclones prevailing in our NICUs between 1998 and2007. The epidemic as well as endemic clone, ST239, dominated before 2005 and was replaced by thecommunity clones, ST 59, thereafter.[Keywords]Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus,neonatal intensive care units, molecular analysisOBJECTIVES: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) associateddiseases, such as infectious mononucleosis (IM),EBV-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis(EBV-HLH) and chronic active EBV infection (CAEBV)are four main clinical phenotype of nonmalignant EBVassociated diseases in children. The aim of this study is toexplore the polymorphic variants of EBV BamHIfragment Z (BZLF1) promoter zone Zp in thesenonmalignant EBV associated diseases in Chinesechildren..METHODS: The Zp region was directly sequenced in206 EBV-positive DNA samples: 40 from healthcontroled cases, 88 from IM, 46 from EBV-HLH and 32from CAEBV. Type 1 or type 2 EBV was examined byPCR for EBNA2 and EBNA3C subtyping. Thechi-square test was used to assess for statisticallysignificant differences among proportions, and atwo-tailed P-value ≤0.05 was chosen as statisticallysignificant.MAIN RESULTS: Type 1 EBV was predominant in allgroups (81.3~96.7%) and there was no significantdifference in the frequency of the EBV type 1 and type 2among different group (P>0.05). Four polymorphic Zpvariants were detected, including Zp-P, Zp-V3, Zp-P4and Zp-V1. Zp-P variant was dominant in all groupsinvolved. Zp-V3 variant was more frequent in CAEBVand EBV-HLH, statistically significantly associated withCAEBV (P ≤0.01). Frequency of co-infection varants(mainly Zp-P+V3) were higer in CAEBV and EBV-HLH,compared with IM and controls.CONCLUSION: Type 1 EBV and BZLF1 Zp-P variantare predominant variants in nonmalignant EBVassociated diseases in Chinese children. Zp-V3 variantmay correlates with the developing of sever EBVinfection diseases, such as CAEBV and EBV-HLH.[Keywords]Epstein-Barr virus, infectious mononucleosis, HLH,CAEBV66