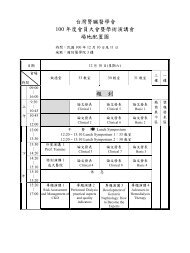
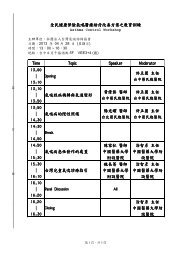
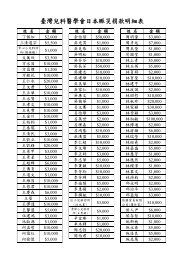
ABSTRACT OF INVITED LECTURES AND ORAL PRESENTATION
ABSTRACT OF INVITED LECTURES AND ORAL PRESENTATION
ABSTRACT OF INVITED LECTURES AND ORAL PRESENTATION
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
FP6-05ROLE <strong>OF</strong> RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN SYSTEM INA RAT MODEL <strong>OF</strong> NEONATAL CHRONICLUNG DISEASEChung-Ming Chen 1 , Yaw-Dong Lang 2 , Hsiu-ChuChou 3 , Leng-Fang Wang 4Department of Pediatrics, Taipei Medical University Hospital, Taiwan 1 ,Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Taipei Medical University, Taiwan 2 ,Department of Anatomy, Taipei Medical University, Taiwan 3 , Department ofBiochemistry, Taipei Medical University, Taiwan 4BACKGROUND: Oxygen toxicity plays animportant role in the lung injury that may lead tolung fibrosis. Angiotensin II is a profibrotic mediatorwhich induces human lung fibroblast proliferation.We investigated the effects of hyperoxia on thecomponents of renin-angiotensin system (RAS) andcollagen production and the therapeutic effect ofangiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) blocker inroom air- and hyperoxia-exposed newborn rats.METHODS: Rat pups were exposed to 1 week of >95% O 2 and a further 2 weeks of 60% O 2 . AT1Rblocker treated-rats received intraperitoneal injectionof losartan 10 mg/kg/day during the first postnatalweek and 5 mg/kg/day from postnatal 2-week to3-week old.RESULTS: Hyperoxia significantly increased totalcollagen, type I collagen, and α-smooth muscle actin(α-SMA) expression when compared to roomair-exposed rats on postnatal days 7 and 21. RAScomponents including angiotensinogen,angiotensin-converting enzyme, angiotensin II, andAT1R were significantly increased by hyperoxiawhereas AT2R was not significantly different whencompared to room air-exposed rats on postnatal days7 and 21. Hyperoxia significantly increasedextracelluar signal-regulated kinase phosphorylationbut did not affect the phosphorylation levels of p38or c-Jun N-terminal kinase on postnatal days 7 and21. Losartan significantly reduced total collagen andtype I collagen and α-SMA expression whencompared to room air-exposed rats on postnatal days7 and 21.CONCLUSIONS: Hyperoxia induces lung collagenproduction via the activation of RAS in newborn ratsand losartan reduces lung collagen production. AT1Rblocker may represent a novel therapeutic strategyfor hyperoxia-induced lung fibrosis.[Keywords]Angiotensin converting enzyme, Angiotensin,Angiotensin II types 1 and 2 receptors, CollagenFP6-06IDENTIFICATION <strong>OF</strong> ARGINASE-1 <strong>AND</strong>ADENOSINE DEAMINASE INVOLVED INIMPAIRMENT <strong>OF</strong> NEONATAL INNATE <strong>AND</strong>ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES BYPROTEOMIC DIFFERENTIAL APPROACHESHong-Ren Yu 1 , Ho-Chang Kuo 2 , Ling-Sai Chang 3 ,Chih-Chiang Wu 4 , Lin Wang 5 , Jiunn-Ming Sheen 6 ,Chia-Yu Ou 7 , Kuender D. Yang 8Department of Pediatrics, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital-Kaoshiung MedicalCenter 1 , Division of Pediatric Allergy and Immunology; Department ofPediatrics, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital-Kaohsiung Medical Center; ChangGung University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan 2 , Pediatrics, Chang Gung MemorialHospital-Kaohsiung Medical Center 3 , Division of Allergy and Immunology,Department of Pediatrics, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital-Kaohsiung MedicalCenter 4,5 , Pediatrics, Chang-Gung Memorial Hospital 6 , Obstetrics, Chang GungMemorial Hospital-Kaohsiung Medical Center, Taiwan 7 , TBC, Chang GungMemorial Hospital at Kaohsiung; and Chang Gung University 8) (Taiwan)BACKGROUND: Human newborns are knownsusceptible to microbial infection. This susceptibility isgenerally attributed to immaturity of the newbornimmune system. However, the mechanisms for impairedimmunity in newborn are still incompletely defined. Inthis study, we sought to elucidate impairment of neonatalinnate and adaptive immunity by comparing theproteomic differential approaches.METHODS: leukocytes from cord blood and adultperipheral blood were subjected to two-dimensionalpolyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (2D-PAGE) analysisfor identifying. Differential protein displays, followed byfunctional validation of neonatal innate and adaptiveimmunity.RESULTS: There were 34 differentially expressedproteins between cord blood MNC and adult MNCidentified by 2D-PAGE. The differentially displayedproteins were clustered into two major signal pathways,cellular processing and purine metabolism. Westernblots validated that abundant arginase-1 (ARG1) andRho GDP-dissociation inhibitor 2 (RhoGDI2) are mainlyfound in phagocytes: granulocytes and monocytes. Incontrast, less adenosine deaminase (ADA) and beta-actinlevels were found in monocytes. Functional validationconfirmed that modulation of arginine/ adenosine systemimproved neonatal phagocyte and T cell responses.CONCLUSION: Results from this study highlight thatimpaired innate and adaptive immunity in neonates maybe reversed by modulation of protein displays viaproteomic differential displays followed by functionalcorrection.[Keywords] neonate, immunity, proteomics, adenosine deaminase,arginase80