Dental caries & diabetes mellitus - Pakistan Oral and Dental Journal ...
Dental caries & diabetes mellitus - Pakistan Oral and Dental Journal ...
Dental caries & diabetes mellitus - Pakistan Oral and Dental Journal ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
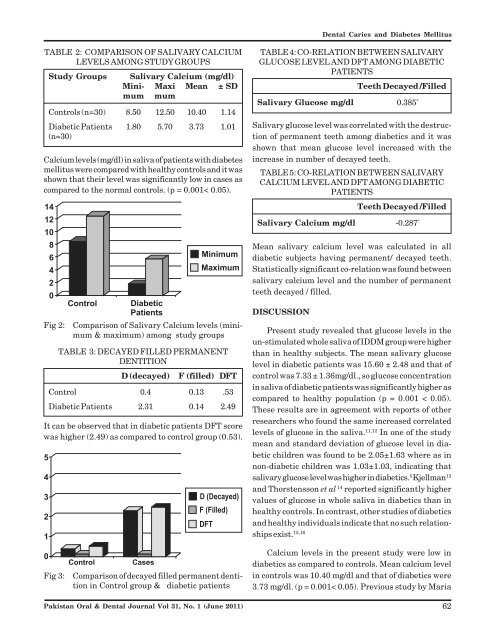
<strong>Dental</strong> Caries <strong>and</strong> Diabetes MellitusTABLE 2: COMPARISON OF SALIVARY CALCIUMLEVELS AMONG STUDY GROUPSStudy Groups Salivary Calcium (mg/dl)Mini- Maxi Mean ± SDmum mumControls (n=30) 8.50 12.50 10.40 1.14Diabetic Patients 1.80 5.70 3.73 1.01(n=30)Calcium levels (mg/dl) in saliva of patients with <strong>diabetes</strong><strong>mellitus</strong> were compared with healthy controls <strong>and</strong> it wasshown that their level was significantly low in cases ascompared to the normal controls. (p = 0.001< 0.05).TABLE 4: CO-RELATION BETWEEN SALIVARYGLUCOSE LEVEL AND DFT AMONG DIABETICPATIENTSTeeth Decayed /FilledSalivary Glucose mg/dl 0.385 *Salivary glucose level was correlated with the destructionof permanent teeth among diabetics <strong>and</strong> it wasshown that mean glucose level increased with theincrease in number of decayed teeth.TABLE 5: CO-RELATION BETWEEN SALIVARYCALCIUM LEVEL AND DFT AMONG DIABETICPATIENTSTeeth Decayed /FilledSalivary Calcium mg/dl -0.287 *Mean salivary calcium level was calculated in alldiabetic subjects having permanent/ decayed teeth.Statistically significant co-relation was found betweensalivary calcium level <strong>and</strong> the number of permanentteeth decayed / filled.Fig 2:Comparison of Salivary Calcium levels (minimum& maximum) among study groupsTABLE 3: DECAYED FILLED PERMANENTDENTITIOND (decayed)F (filled) DFTControl 0.4 0.13 .53Diabetic Patients 2.31 0.14 2.49It can be observed that in diabetic patients DFT scorewas higher (2.49) as compared to control group (0.53).DISCUSSIONPresent study revealed that glucose levels in theun-stimulated whole saliva of IDDM group were higherthan in healthy subjects. The mean salivary glucoselevel in diabetic patients was 15.60 ± 2.48 <strong>and</strong> that ofcontrol was 7.33 ± 1.36mg/dl., so glucose concentrationin saliva of diabetic patients was significantly higher ascompared to healthy population (p = 0.001 < 0.05).These results are in agreement with reports of otherresearchers who found the same increased correlatedlevels of glucose in the saliva. 11,12 In one of the studymean <strong>and</strong> st<strong>and</strong>ard deviation of glucose level in diabeticchildren was found to be 2.05±1.63 where as innon-diabetic children was 1.03±1.03, indicating thatsalivary glucose level was higher in diabetics. 5 Kjellman 13<strong>and</strong> Thorstensson et al 14 reported significantly highervalues of glucose in whole saliva in diabetics than inhealthy controls. In contrast, other studies of diabetics<strong>and</strong> healthy individuals indicate that no such relationshipsexist. 15,16Fig 3:Comparison of decayed filled permanent dentitionin Control group & diabetic patientsCalcium levels in the present study were low indiabetics as compared to controls. Mean calcium levelin controls was 10.40 mg/dl <strong>and</strong> that of diabetics were3.73 mg/dl. (p = 0.001< 0.05). Previous study by Maria<strong>Pakistan</strong> <strong>Oral</strong> & <strong>Dental</strong> <strong>Journal</strong> Vol 31, No. 1 (June 2011)62