Relative Bactericidal Effectiveness of Hypochlorous Acid and ...
Relative Bactericidal Effectiveness of Hypochlorous Acid and ...
Relative Bactericidal Effectiveness of Hypochlorous Acid and ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
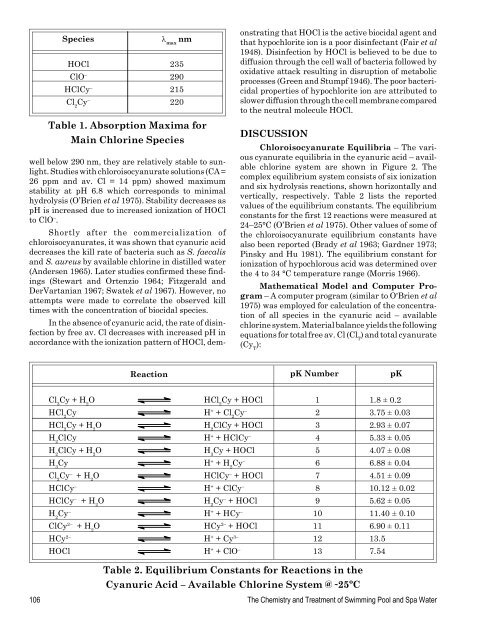
SpeciesHOClClO –HClCy –Cl 2Cy –l maxnm235290215220Table 1. Absorption Maxima forMain Chlorine Specieswell below 290 nm, they are relatively stable to sunlight.Studies with chloroisocyanurate solutions (CA =26 ppm <strong>and</strong> av. Cl = 14 ppm) showed maximumstability at pH 6.8 which corresponds to minimalhydrolysis (O’Brien et al 1975). Stability decreases aspH is increased due to increased ionization <strong>of</strong> HOClto ClO – .Shortly after the commercialization <strong>of</strong>chloroisocyanurates, it was shown that cyanuric aciddecreases the kill rate <strong>of</strong> bacteria such as S. faecalis<strong>and</strong> S. aureus by available chlorine in distilled water(Andersen 1965). Later studies confirmed these findings(Stewart <strong>and</strong> Ortenzio 1964; Fitzgerald <strong>and</strong>DerVartanian 1967; Swatek et al 1967). However, noattempts were made to correlate the observed killtimes with the concentration <strong>of</strong> biocidal species.In the absence <strong>of</strong> cyanuric acid, the rate <strong>of</strong> disinfectionby free av. Cl decreases with increased pH inaccordance with the ionization pattern <strong>of</strong> HOCl, demonstratingthat HOCl is the active biocidal agent <strong>and</strong>that hypochlorite ion is a poor disinfectant (Fair et al1948). Disinfection by HOCl is believed to be due todiffusion through the cell wall <strong>of</strong> bacteria followed byoxidative attack resulting in disruption <strong>of</strong> metabolicprocesses (Green <strong>and</strong> Stumpf 1946). The poor bactericidalproperties <strong>of</strong> hypochlorite ion are attributed toslower diffusion through the cell membrane comparedto the neutral molecule HOCl.DISCUSSIONChloroisocyanurate Equilibria – The variouscyanurate equilibria in the cyanuric acid – availablechlorine system are shown in Figure 2. Thecomplex equilibrium system consists <strong>of</strong> six ionization<strong>and</strong> six hydrolysis reactions, shown horizontally <strong>and</strong>vertically, respectively. Table 2 lists the reportedvalues <strong>of</strong> the equilibrium constants. The equilibriumconstants for the first 12 reactions were measured at24–25°C (O’Brien et al 1975). Other values <strong>of</strong> some <strong>of</strong>the chloroisocyanurate equilibrium constants havealso been reported (Brady et al 1963; Gardner 1973;Pinsky <strong>and</strong> Hu 1981). The equilibrium constant forionization <strong>of</strong> hypochlorous acid was determined overthe 4 to 34 °C temperature range (Morris 1966).Mathematical Model <strong>and</strong> Computer Program– A computer program (similar to O'Brien et al1975) was employed for calculation <strong>of</strong> the concentration<strong>of</strong> all species in the cyanuric acid – availablechlorine system. Material balance yields the followingequations for total free av. Cl (Cl T) <strong>and</strong> total cyanurate(Cy T):ReactionpK NumberpKCl 3Cy + H 2O HCl 2Cy + HOCl 1 1.8 ± 0.2HCl 2Cy H + + Cl 2Cy – 2 3.75 ± 0.03HCl 2Cy + H 2O H 2ClCy + HOCl 3 2.93 ± 0.07H 2ClCy H + + HClCy – 4 5.33 ± 0.05H 2ClCy + H 2O H 3Cy + HOCl 5 4.07 ± 0.08H 3Cy H + + H 2Cy – 6 6.88 ± 0.04Cl 2Cy – + H 2O HClCy – + HOCl 7 4.51 ± 0.09HClCy – H + + ClCy – 8 10.12 ± 0.02HClCy – + H 2O H 2Cy – + HOCl 9 5.62 ± 0.05H 2Cy – H + + HCy – 10 11.40 ± 0.10ClCy 2– + H 2O HCy 2– + HOCl 11 6.90 ± 0.11HCy 2– H + + Cy 3– 12 13.5HOCl H + + ClO – 13 7.54Table 2. Equilibrium Constants for Reactions in theCyanuric <strong>Acid</strong> – Available Chlorine System @ ˜25ºC106 The Chemistry <strong>and</strong> Treatment <strong>of</strong> Swimming Pool <strong>and</strong> Spa Water