Polynomials: Factoring - XYZ Custom Plus
Polynomials: Factoring - XYZ Custom Plus
Polynomials: Factoring - XYZ Custom Plus
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
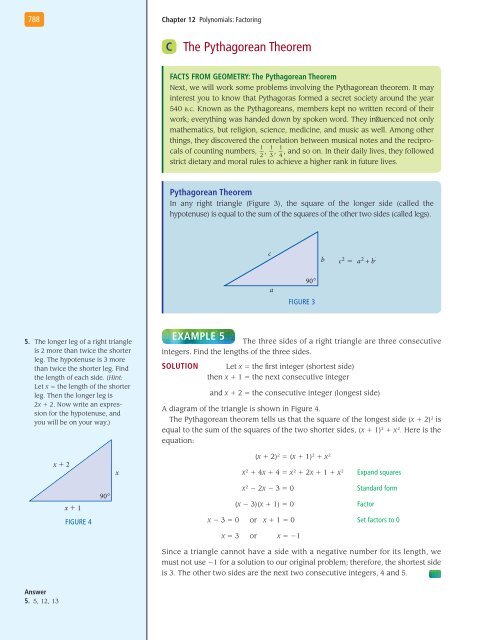
788Chapter 12 <strong>Polynomials</strong>: <strong>Factoring</strong>CThe Pythagorean TheoremFACTS FROM GEOMETRY: The Pythagorean TheoremNext, we will work some problems involving the Pythagorean theorem. It mayinterest you to know that Pythagoras formed a secret society around the year540 b.c. Known as the Pythagoreans, members kept no written record of theirwork; everything was handed down by spoken word. They influenced not onlymathematics, but religion, science, medicine, and music as well. Among otherthings, they discovered the correlation between musical notes and the reciprocalsof counting numbers, _ 1 2 , 1 _3 , 1 _, and so on. In their daily lives, they followed4strict dietary and moral rules to achieve a higher rank in future lives.Pythagorean TheoremIn any right triangle (Figure 3), the square of the longer side (called thehypotenuse) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides (called legs).cb c 2 = a 2 + b 2a90Figure 35. The longer leg of a right triangleis 2 more than twice the shorterleg. The hypotenuse is 3 morethan twice the shorter leg. Findthe length of each side. (Hint:Let x = the length of the shorterleg. Then the longer leg is2x + 2. Now write an expressionfor the hypotenuse, andyou will be on your way.)Example 5The three sides of a right triangle are three consecutiveintegers. Find the lengths of the three sides.Solution Let x = the first integer (shortest side)then x + 1 = the next consecutive integerand x + 2 = the consecutive integer (longest side)A diagram of the triangle is shown in Figure 4.The Pythagorean theorem tells us that the square of the longest side (x + 2) 2 isequal to the sum of the squares of the two shorter sides, (x + 1) 2 + x 2 . Here is theequation:x + 2x(x + 2) 2 = (x + 1) 2 + x 2x 2 + 4x + 4 = x 2 + 2x + 1 + x 2Expand squaresx + 1Figure 490x 2 − 2x − 3 = 0Standard form(x − 3)(x + 1) = 0 Factorx − 3 = 0 or x + 1 = 0 Set factors to 0x = 3 or x = −1Since a triangle cannot have a side with a negative number for its length, wemust not use −1 for a solution to our original problem; therefore, the shortest sideis 3. The other two sides are the next two consecutive integers, 4 and 5.Answer5. 5, 12, 13