Modes of fossil preservation
Modes of fossil preservation
Modes of fossil preservation
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
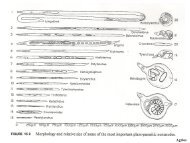
Types <strong>of</strong> Fossil Preservation1. Impression2. Compression3. Mold4. Cast5. Permineralization (petrifaction)6. Unaltered plant remains7. Chemical <strong>fossil</strong>s
PermineralizationMost informationMost infrequentWaters highly charged with mineral material fillcell lumens and intercellular spaces, gelphase solidifies, prevents crushing and cellwalls are unaltered or changed little.Replacement-when cell walls later replacedwith mineral material
Carboniferous coal ball
Need to be examined using adissecting microscopePeels
Fossil sperm in a gymnosperm seedsperm
Fossil egg inside an archegoniumArchegonium in megaspore <strong>of</strong> heterosporous lycopod
Mitosis in the <strong>fossil</strong> record-LycosporaInterphaseMetaphaseAnaphasePhotos byS.D. Brack
Unaltered plant parts
AmberFossil resin
Chemical <strong>fossil</strong>sCalcium carbonate – stromatolite- formed by certain blue green or green algae
Reading• Chapter 1 – Introduction: what is a <strong>fossil</strong>and how are <strong>fossil</strong>s used? (pp. 1-6,Stewart & Rothwell text) GWR will talkabout some <strong>of</strong> this next week.• Chapter 2 – Plant <strong>fossil</strong>s: <strong>preservation</strong>,preparation and age determination (pp. 7-23).• Chapter 3 – Fossil record, systematics andnomenclature (pp. 24-31)
Nomenclature and Classification <strong>of</strong>Fossil PlantsNames for <strong>fossil</strong> plants start withSternberg 1820International Code <strong>of</strong> Botanical Nomenclature –the rulesClassification=grouping <strong>of</strong> organisms based onsimilarities and differencesTaxon=any taxonomic unit (each category orgroup)Taxonomic hierarchy <strong>of</strong> classes-Linnaeanhierarchy
Linnaeus-Linnean hierarchyKingdomPhylum (Division)ClassOrderFamilyGenus (genera)Species (species)These are nested classesNow Domain is a group <strong>of</strong> Kingdoms
Domain: Prokaryota (prokaryotes)Kingdom: EubacteriaKingdom: ArchaebacteriaDomain: Eukaryota (eukaryotes)Kingdom: ProtistaKingdom: FungiKingdom: AnimaliaKingdom: Plantae
DivisionSubdivisionClassOrderFamilyGenusSpecies-phyta-phytina-opsida-ales-aceaeendings follow therules for Latin grammar
Linnaeus 1st to use binomial nomenclatureBasic unit is the speciesPlatanus occidentalis L.Generic name + specific epithet = species nameCommon name: plane tree or sycamoreL. = Linnaeus, the authority
Names for <strong>fossil</strong> plantsOrgansOrgan genera-plant organ assignable to a familyForm genera-plant organ not assignable to afamilyMorphotaxon=<strong>fossil</strong> taxa based onmorphology, an organ or part <strong>of</strong> a plant atany level <strong>of</strong> classification.-ites ending used many times for <strong>fossil</strong> taxa
1 st <strong>fossil</strong>s
Oldest <strong>fossil</strong> organisms-Towers Fm. - NW Australia11 taxa<strong>of</strong>filamentousblue greenalgaedescribed3.465 billionyrs. b.p.Schopf, 19921993
Thin Section Technique