Case Studies of Families Involved with Welfare and Child Welfare
Case Studies of Families Involved with Welfare and Child Welfare
Case Studies of Families Involved with Welfare and Child Welfare
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
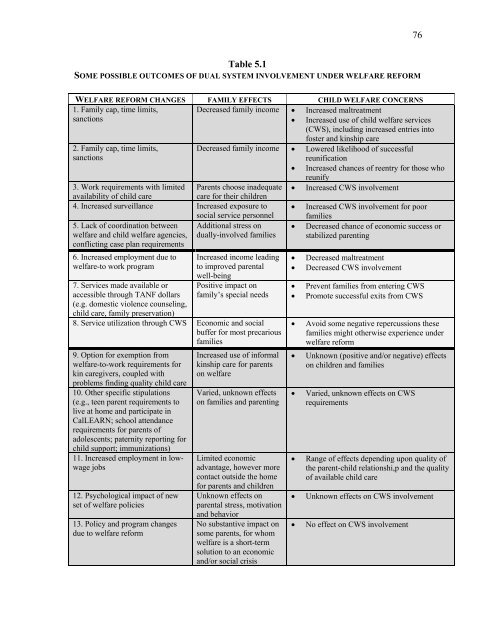
76Table 5.1SOME POSSIBLE OUTCOMES OF DUAL SYSTEM INVOLVEMENT UNDER WELFARE REFORMWELFARE REFORM CHANGES FAMILY EFFECTS CHILD WELFARE CONCERNS1. Family cap, time limits, Decreased family income • Increased maltreatmentsanctions• Increased use <strong>of</strong> child welfare services(CWS), including increased entries into2. Family cap, time limits,sanctions3. Work requirements <strong>with</strong> limited Parents choose inadequateavailability <strong>of</strong> child carecare for their children4. Increased surveillance Increased exposure tosocial service personnel5. Lack <strong>of</strong> coordination between Additional stress onwelfare <strong>and</strong> child welfare agencies, dually-involved familiesconflicting case plan requirements6. Increased employment due towelfare-to work program7. Services made available oraccessible through TANF dollars(e.g. domestic violence counseling,child care, family preservation)foster <strong>and</strong> kinship careDecreased family income • Lowered likelihood <strong>of</strong> successfulreunification• Increased chances <strong>of</strong> reentry for those whoreunifyIncreased income leadingto improved parentalwell-beingPositive impact onfamily’s special needs8. Service utilization through CWS Economic <strong>and</strong> socialbuffer for most precariousfamilies9. Option for exemption fromwelfare-to-work requirements forkin caregivers, coupled <strong>with</strong>problems finding quality child care10. Other specific stipulations(e.g., teen parent requirements tolive at home <strong>and</strong> participate inCalLEARN; school attendancerequirements for parents <strong>of</strong>adolescents; paternity reporting forchild support; immunizations)11. Increased employment in lowwagejobs12. Psychological impact <strong>of</strong> newset <strong>of</strong> welfare policies13. Policy <strong>and</strong> program changesdue to welfare reformIncreased use <strong>of</strong> informalkinship care for parentson welfareVaried, unknown effectson families <strong>and</strong> parentingLimited economicadvantage, however morecontact outside the homefor parents <strong>and</strong> childrenUnknown effects onparental stress, motivation<strong>and</strong> behaviorNo substantive impact onsome parents, for whomwelfare is a short-termsolution to an economic<strong>and</strong>/or social crisis• Increased CWS involvement• Increased CWS involvement for poorfamilies• Decreased chance <strong>of</strong> economic success orstabilized parenting• Decreased maltreatment• Decreased CWS involvement• Prevent families from entering CWS• Promote successful exits from CWS• Avoid some negative repercussions thesefamilies might otherwise experience underwelfare reform• Unknown (positive <strong>and</strong>/or negative) effectson children <strong>and</strong> families• Varied, unknown effects on CWSrequirements• Range <strong>of</strong> effects depending upon quality <strong>of</strong>the parent-child relationshi,p <strong>and</strong> the quality<strong>of</strong> available child care• Unknown effects on CWS involvement• No effect on CWS involvement