SNDT Women's University SNDT Women's University 1, Nathibai ...
SNDT Women's University SNDT Women's University 1, Nathibai ...
SNDT Women's University SNDT Women's University 1, Nathibai ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>SNDT</strong> Women’s <strong>University</strong>(Sndt.digitaluniversity.ac)Premlila Vithaldas PolytechnicSyllabusDiploma in Medical Laboratory Technology<strong>SNDT</strong> Women’s <strong>University</strong>1, <strong>Nathibai</strong> Thackersey Road,Mumbai 400 020Revised – 20081
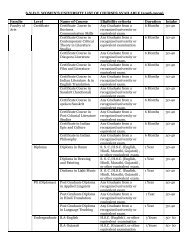
SYLLABUS FORMATDIPLOMA I MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHOLOGYSCHEME: SEMESTER IPaperPRSubject L P/T D TP TWCodeEXAMT Credits1001 General*P-4Chemistry42 1/2 75 25+25 25 150 61002 Physics 3 P-2 2 50 25+25 25 125 41003 Anatomy-Physiology3 P-2 2 50 25+25 25 125 41004 Biology 3 P-2 2 50 25+25 25 125 41005 SLC 2 - 2 25 25 - 50 2Total 15 10 575 20• PRACTICAL IS OF THREE HOURSSCHEME: SEMESTER IIPaperPRSubject L P/T D TP TWCodeEXAMT Credits2001 Organic Chemistry 4 P-4 2 1/2 75 25+25 25 150 62002 Physics 3 P-2 2 50 25+25 25 125 42003 Anatomy- 3 P-2 2 50 25+25 50 125 4Physiology2004 Biology 3 P-2 2 50 25+25 25 125 42005 SLC 2 - 2 25 25 - 50 22006 PersonalityDevelopment2 - - 25 25 - - 2Total 17 10 575 22SCHEME: SEMESTER IIIPaperPRSubject L P/T D TP TWCodeEXAMT Credits3001 Biochemistry 2 P-2 2 25 25+25 25 100 43002 Microbiology 3 P-4 2 50 25+25 25 125 53003 Hematology 1 P- 2 25 25+25 25 100 223004 SLC 2 - 2 25 25 - 50 23005 Computer- P-4 2 - 25 25 50 2Applications3006 Book Keeping 2 - 2 25 25 - 50 2-- Phlebotomy - P-4 - - - - - 2Total 10 16 475 192
SCHEME: SEMESTER IVPaperPRSubject L P/T D TP TWCodeEXAMT Credits4001 Biochemistry 3 P-6 2 50 25+25 50 150 64002 Microbiology 3 P-6 2 50 25+25 50 150 64003 Hematology 2 T-2 P- 2 25 25+25 25 100 424004 Clinical 2 P-4 2 25 25+25 25 100 4Pathology4005 SLC 2 - - 25 25 - 50 2-- Phlebotomy - P-4 - - - - - 2Total 12 24 550 24SCHEME: SEMESTER V (UIVERISTY EXAMIATIO)PaperPRSubject L P/T D TP TWCodeEXAMT Credits5001 Biochemistry 3 P-4 2 25 25+25 25 150 55002 Microbiology 3 P-6 2 25 25+25 50 150 65003 Hematology 2 P-2 2 25 25+25 25 100 35004 Clinical 2 P-4 2 25 25+25 25 100 4Pathology5005 Histopathology 2 T-2 P-22 25 25+25 25 100 412 20 600 22Total3
SCHEME: SEMESTER VI- ITERSHIP CREDITS: 20The students are rotated in following sections for three and half weeks in thelaboratories of hospitals.o. Subject Credits Marks1 Biochemistry 3 752 Microbiology & Serology 5 1253 Hematology & Blood Banking 6 1504 Clinical pathology 3 755 Histopathology & Cytology 3 75Total 20 500SCHEME: SEMESTER IPaperPRSubject L P/T D TP TWCodeEXAMT Credits1001 General*P-4Chemistry42 1/2 75 25+25 25 150 61002 Physics 3 P-2 2 50 25+25 25 125 41003 Anatomy-Physiology3 P-2 2 50 25+25 25 125 41004 Biology 3 P-2 2 50 25+25 25 125 41005 SLC 2 - 2 25 25 - 50 2Total 15 10 575 20• PRACTICAL IS OF THREE HOURS4
Semester – IGeneral Chemistry (Theory)Credits: 4 ( 4 Hrs./ Week)Sr.o. Topic Sub-topics1 Structure of Atom2 Chemical Periodicity3 Radioactivity4Chemical Bondingand Molecular Shape5 Ionic Equilibrium6 Acids and BasesSubatomic particles, At no.,At mass no., At mass,Electronic theory of valency,Electrovalency, simplecovalency, co-ordinatecovalency, Electronicconfiguration and its pictorialrepresentation.Periodic law, Periodic Table,Inert gases, Normal elements,Transition elements, Periodicproperties, Characteristics ofs, p, d & f block elements.Isotopes & Isobars, NuclearStability, Radioactivity andproperties of radiations,Radioactive series, Half lifeperiod, Nuclear fission,Nuclear fusion, Atomictransmutation and artificialradioactivity, Radioactiveisotopes – preparation anduses.Orbital develop in bondformation, Sigma and Pibonds, Hydrogen bond, Coordinationand Complexation,Chelation.Arrhenius theory ofelectrolytic dissociation,degree of dissociation andfactors affecting it, Solubilityproduct, Common-ion effect.Definitions, properties &Equivalent weights of acidsand bases, Neutralization,Titration, Normality,Molarity, Preparation ofStandard solutions, pH-Definition, Calculation ando.ofHrs.WeightageofMarks(%)6 97 98 123 84 87 95
significance, Buffer solutions.7 Chemical Kinetics8Oxidation andReduction9 Electrochemistry10 States of matter11Adsorption andColloidsLaw of mass action, Chemicalequilibrium, Equilibriumconstant, Le Chateliar’sprinciple, Factors affectingchemical equilibrium andrates of the reactions, workingof acid-base indicators, Order4 9and Molecularity of thereaction, 1 st , 2 nd and Zeroorderreactions,Pseudomonomolecularreactions.Electronic concept ofOxidation & Reduction, Halfcell & Half cellpotential, Standard Half cell,Std. Hydrogen electrode,5 9E.M.F. of a half and of acomplete cell and itscalculation, Redox titrations.Conductors, Electrolytes,Electrolysis, Specificelectrolysis mechanisms,Faraday’s laws of5 9electrolysis, specific, Molar &Equivalent conductances.Definition & composition ofmatter, Intermolecular spaceand Intermolecular Force,Various states of matter –distinction, Solids – Allotropy& sublimation, Liquids – 6 9surface tension and viscosity,Gases – Kinetic theory ofgases and Criticaltemperature, Critical pressureand Critical volume.Adsorption – Definition,Characteristic features andapplications, Distinctionbetween true solution colloid,5 9Preparation, properties andapplications of colloids.Total: 60 Hrs.6
Semester – IGeneral Chemistry (Practical)Credits: 2 ( 4 Hrs. / Week )Use of valency in writing Molecular Formulae of compounds. (2Hrs.)Study of Bunsen Burner, Parts & Flames of the burner. (2Hrs.)Qualitative Analysis of the water soluble and insoluble salts containingPb 2+ , Cu 2+ , Cd 2+ , Sn 2+ , Bi 3+ , Al 3+ , Cr 3+ , Fe 2+ , Fe 3+ , Ni 2+ , Co 2+ , Zn 2+ , Mn 2+ , Ba 2+ , Ca 2+ ,NH 4 1+ , K 1+ , Na 1+ , Cl 1- , I 1- , NO 3 1- , SO 4 2- , CO 3 2- , S 2- , PO 4 3- .(40 Hrs.)Volumetric AnalysisPreparation & Standardization of 0.1 N (approx) HCl solution with std. 0.1 N Na 2CO 3 solution.(2Hrs.)Preparation & Standardization of 0.1N (approx) NaOH solution with std. 0.1NSuccinic acid solution, Preparation & Standardization of 0.1N (approx) H 2 SO 4solution with Std. NaOH solution.(4 Hrs.)Preparation & Standardization of 0.1N KMnO4 solution (approx) with std. 0.1N 0.1NNa 2 C 2 O 4 solution Preparation & Standardization of 0.1N (approx) FeSO 4 .7H 2 Osolution with Std. KMnO 4 solution.(4 Hrs.)Preparation & standardization of 0.1N (approx) Na 2 S 2 O 3 .5H 2 O solution with std 0.1NK 2 Cr 2 O 7 solution.(4 Hrs.)Purification TechniquesSublimation, Crystallization, Distillation.(2 Hrs.)Practicals)Total: 60 Hrs. (307
Semester – IPhysics (Theory)Credits: 3 (3 Hrs / Week)Sr. o. Topic o.of Hrs.Weightage ofMarks(%)1 Units and dimensions 7 162 Graph 2 63 Rate of variation 5 124 Viscosity 5 125 Concept of pressure 4 86 Work, Power & Energy 4 87 Rotational motion 4 88 Vibration of bodies 3 69 Surface tension 4 810 Temperature and its measurement 3 611 Heat 4 10TOTAL 45Semester – IPhysics (Practical)Credits: 1 (2 Hrs / Week)Sr. o. Topic o.of Hrs.1 To study the use of Vernier caliper. 42 To study the use of screw gauge 23 To study the use of Analytical balance. 44 To study the use of traveling microscope 25 To verify the Boyle’s law – using the U-tube manometer 46 To study the use of thermometer. 47To determine the specific heat of the solid by the method ofmixture.48To study the use of instruments- magnetic stirrer, centrifuge,Balance, hot air oven, constant temperature water bath. 6TOTAL 308
Semester - IAnatomy – Physiology (Theory)Credits: 3 (3 Hrs. / Week)Sr. o.Topico. ofHrs.WeightageofMarks(%)1 Scope of Anotomy & Physiology 2 22 Introduction to the Body as a Whole 3 63 A General Review of Diseases 2 64 Elementary tissues of the body 4 85 Digestive system 5 106 Study of Diseases related to Digestive System 1 67 Respiratory System 4 88Study of Diseases related to RespiratorySystem with special reference to Tuberculosis1 49 Excretory System 5 1210Study of Diseases related to Kidney withSpecial reference to Renal Function Tests andDialysis Techniques2 411 Reproductive system 4 1012 A Review of Sexually Transmitted Diseases 2 413 A General Review of HIV/ AIDS 2 414 Skeletal System 4 1015 Central Nervous System 3 616 Study of Diseases Related to Nervous System 1 2TOTAL:45 Hours9
Semester - IAnatomy – Physiology (Practical)Credits: 1 (2 Hrs. / Week)Sr. o. Topic o. of Hrs.1 Introduction to Body as a Whole 42 Fundamental Tissues of the Body 43 Digestive system 24 Skeletal System 45 Central Nervous System 46 Respiratory System 27 Excretory System 28 Urine Examination 29 Reproductive System 410 Family Planning Procedures 2TOTAL:30 Hours10
Semester - IBiology (Theory)Credits: 3 (3 Hrs. / Week)Sr. o. Topic o. of Hrs.WeightageofMarks(%)1Introduction and Relation of Biology toD.M.L.T.1 ---2 Structure of Animal and Plant Cell 7 63 Cell Division 4 64 Basic Tissues 2 65 External Features of Frog and Rabbit 3 86 Digestive System of Frog and Rabbit 4 107 Respiratory System of Frog and Rabbit 3 108 Circulatory System of Frog and Rabbit 5 109 Excretory System of Frog and Rabbit 4 1010 Nervous System of Frog and Rabbit 5 1011 Reproductive System of Frog 3 1012 Development of Frog 2 813 Introduction to Microbiology and Pathology 2 6Total 4511
Semester - IBiology (Practical)Credits: 1 (2 Hrs. / Week)Sr. o. Topic o. of Hrs.1 Introduction and Relation of Biology to D.M.L.T. 22 External features of frog 23 Digestive system 24 Arterial system 25 Venous system 26 Urino-genital system 47 Animal classification- Invertibrates 108 Animal classification- Vertibrates 6Total 3012
Semester: ISkills in Language CommunicationCredits: 2 (2 Hrs. / Week)Sr.o. Topic Sub-Topics Hrs. WeightageofMarks(%)1. GrammarParts of speech, tense, voice,medical words and terms,direct n indirect8 282.ComprehensionpassagesListening/reading 10 603. Vocabulary Enhancing Synonyms/antonyms 2 44. Oral CommunicationTalking about day to dayactivities, viva preparation andpresentation of viva8 ----5. Phonetics Vowels & diphthongs 2 8Total30 Hrs.13
SCHEME: SEMESTER IIPaperPRSubject L P/T D TP TWCodeEXAMT Credits2001 Organic Chemistry 4 P-4 2 1/2 75 25+25 25 150 62002 Physics 3 P-2 2 50 25+25 25 125 42003 Anatomy- 3 P-2 2 50 25+25 50 125 4Physiology2004 Biology 3 P-2 2 50 25+25 25 125 42005 SLC 2 - 2 25 25 - 50 22006 PersonalityDevelopment2 - - 25 25 - - 2Total 17 10 575 22Semester – IIOrganic Chemistry (Theory)Credits: 4 (4 Hrs / Week)Sr.o.123TopicClassification ofOrganicCompounds andtheir omenclatureSaturatedHydrocarbonsUnsaturatedHydrocarbons4 Alcohols5 EthersSub-topicsClassification of OrganicCompounds andHydrocarbons, Functionalgroups, Isomerism,Homologous series,Empirical, Molecular andstructural formulae, OrganicNomenclature.Sp 3 hybridization, Preparation& properties of Alkenes,Methane, Ethane,Cycloalkanes.Sp 2 hybridization, Preparation& properties of Alkenes,Ethene, Dienes, Cis-Transisomerism. Sp hybridization,Preparation, properties & usesof Acetylene.Classification, preparation,properties & uses of alcohol,Methods of manufacture ofEthyl alcohol, RectifiedSpirit, Absolute alcohol &Denatured alcohol.Preparation, properties & usesof Diethyl ether, Anesthetico.ofHrs.WeightageofMarks(%)5 75 75 83 72 414
6 Halohydrocarbons7Aldehydes andKetones8 Carboxylic acids9Derivatives ofCarboxylic acids10 Aliphatic Amines11 Fats and Oils12 Carbohydrates13Benzene and otherAromaticCompoundsether, Vinyl ether, thioethers.Preparation & properties ofAlkyl halides, Grignard’sreagent, preparation,properties and uses ofHaloforms – Chloroform &Iodoform.Preparation & properties ofAldehydes & Ketones,Formaldehyde, Acetaldehyde,Acetone, Paraldehyde &Chloral hydrate.Classification, nomenclature,preparation and properties ofCarboxylic acids, Formicacid, Acetic acid, Oxalic acid,Succinic acid, Tartaric acid,Lactic acid, Citric acid.Optical isomerism.Nomenclature, preparation &properties of Acid halides,Acid amides, Acid anhydrides& Esters.Classification, Nomenclature,preparation & properties ofAliphatic amines, QuaternaryAmmonium Salts.Nomenclature, preparation, ofFats & Oils, Analysis –Saponification value, Acidvalue, Iodine value, Fixed oils– Arachis oil, Castor oil,Linseed oil, Sesame oil &Ethyl Oleate.Classification & Qualitativetests of Carbohydrates,Glycosides, Structures ofGlucose, Fructose, Sucrose,Lactose, Starch & cellulose.Benzene – Structure,Molecular orbital diagram,preparation and properties,Substitution in Benzene, usesof Benzene, Aromaticcompounds – Preparation,properties & uses ofNitrobenzene, BenzeneSulfonic acid, Chlorobenzene,4 84 75 82 52 55 93 913 1215
Toluene, Aniline,Benzaldehyde, Phenol,Acetophenone, Benzoic acid,Salicylic acid, Derivatives ofSalicylic acid, Cinnamic acid.Nomenclature & properties of14Fused RingHydrocarbonsNaphthalene, Anthracene &Phenanthrene, steroidal2 4skeleton.Total:60 Hrs.16
Semester – IIOrganic Chemistry (Practical)Credits: 2 ( 4 Hrs. / Week )General Organic SpottingOxalic acid, Acetone, Acetic acid, Ethyl alcohol, Chloroform, Citric acid, Glycerol,Benzoic acid, Benzaldehyde, Aniline, Nitrobenzene, Phenol, Salicylic acid.(30 Hrs.)Carbohydrate spottingGlucose, Fructose, Lactose, Sucrose, Starch.(14 Hrs.)Determination of the melting point of given Organic Solid(8 Hrs.)Determination of the boiling point of given Organic Liquid(8 Hrs.)Practicals)Total: 60 Hrs. (3017
Semester – IIPhysics (Theory)Credits: 3 (3 Hrs / Week)Sr. o. Topic o.of Hrs.Weightage ofMarks(%)1 Current electricity 6 162 D.C.circuts 5 103 Circuit elements 4 84 Reflection of light 5 125 Refraction of light 5 126 Dispersion of light 4 87 Diffraction of light 2 48 Polarization of light 3 89 Mechanical waves 3 610 Electromagnetic waves 3 611 Optical instruments 5 10TOTAL 45Semester – IIPhysics (Practical)Credits: 1 (2 Hrs / Week)Sr. No. Topic No.of Hrs.1To determine the value of unknown resistance using Ohm’slaw42 To verify the law of series combination of resistors 23 To verify the law of parallel combination of resistors 44 To verify the laws of reflection 25To determine the refractive index if the material of the glassslab.46To study the variation in the angle of deviation with theangle of incidence.478To determine the refractive index of the liquid usingconcave mirror.To study the instruments - Compound microscope,Photometer and spectrophotometer,P H meter, Distillationapparatus,De-ioniser.46TOTAL 3018
Semester - IIAnatomy – Physiology (Theory)Credits: 3 (3 Hrs. / Week)Sr. o.Topico. ofHrs.WeightageofMarks(%)1 Circulatory System 6 122Study of Diseases Related to Cardio-vascularSystem with Special Reference to MyocadialInfraction and High Blood Presure2 63 Blood 4 104Study of Diseases Related to Blood with SpecialReference to Anemias2 65 Lymphatic System 2 46 Study of Cancer and Related Disorders 2 67 Endocrine system 4 88Study of Diseases Related to Metabolism &Endocrinal Disorders with Special Reference toDiabetes Mellitus4 109 Sensory organs 5 1010 Accessory organs -Liver & Salivary Glands 4 811 Study of Hepatitis and Related Conditions 2 612 Nutrition 2 41314Study Deficiency Diseases with Emphasis onmalnutritionStudy of Allergic Conditions and It’sManifestations15 Health Education 22 4224TOTAL:45 Hours19
Semester - IIAnatomy – Physiology (Practical)Credits: 1 (2 Hrs. / Week)Sr. o. Topic o. of Hrs.1 Blood 42 Basic Hematology 83 Lymphatic System 44 Endocrine System 25 Special Senses 26 Nutrition 27 Identification of Surgical Instruments 28 Recording Blood Pressure 49 Workshop on How to take ECG. 2TOTAL:30 Hours20
Semester - IIBiology (Theory)Credits: 3 (3 Hrs. / Week)Sr. o. Topic o. of Hrs.WeightageofMarks(%)1 Introduction to Botany 1 -----2 Morphology – Seed and seed germination 2 63 The Root 5 84 The Stem 7 85 The Leaf 4 86 Inflorescence 2 67 Flower 2 68 Pollination 1 69 Fertilization 2 610 Fruit and seed dispersal 2 611 Microbiology 5 812 Parasitism - adaptations 1 413 Life cycles of Parasites 5 2014 Sterilization Methods 3 415 Staining techniques 3 4Total 4521
Semester - IIBiology (Practical)Credits: 1 (2 Hrs. / Week)Sr. o. Topic o. of Hrs.1 Plant classification 22 Seed and seed germination 23 Roots 24 Stem 25 Leaf 26 Inflorescence 27 Flower 28 Fruit 29 Microbiology 610 Parasitology 8Total 3022
Semester: IISkills in Language CommunicationCredits: 2 (2 Hrs. / Week)Sr.o. Topic Sub-Topics Hrs. Marks1. GrammarSimple, compound, complex,punctuation, tense.6 162.ComprehensionpassagesListening/Reading 8 403. Vocabulary enhancing Prefixes/suffixes 1 44. Phonetics Vowels & diphthongs 3 125. Written communicationParts & layouts, styles ofletters, enquiry, reply to8 28enquiry, making paragraph.6. Oral communicationPreparation and presentationof viva4Total 30 Hrs.23
SCHEME: SEMESTER IIIo. Subject L P/T D TP TWPREXAMTCredits3001 Biochemistry 2 P-2 2 25 25+25 25 100 43002 Microbiology 3 P-4 2 50 25+25 25 125 53003 Hematology 1 P-2 2 25 0+25 25 100 23004 SLC 2 - 2 25 25 - 50 23005ComputerApplications- P-4 2 - 25 25 50 23006 Book Keeping 2 - 2 25 25 - 50 2-- Phlebotomy - P-4 - - - - - 2Total 10 16 475 19SEMESTER IIIBIOCHEMISTRY - THEORYCREDITS: TWO (2 Hrs/Week)Sr.No. Topics Sub- Topic Hrs1BiochemistryLaboratoryPrinciples &Procedures2 Glassware3 Solutions &Reagents4Equipments &InstrumentsIntroductionVarious types of Laboratories,Lab safety, Lab. First Aid,Responsibilities of technicians &studentsComposition, General types,Standardization of Glassware,Selection of Glassware,Care & MaintenanceIntroduction and GeneralConsideration,Preparation of Normal, Molar,Percent solutions, BufferSolutions, Buffered Substrates,Indicators, Primary Standards,Other Complex ReagentsBalances, Hot air ovenCentrifuge, IncubatorsWaterbath, Photometer,Colorimeter, Nephelometer,Spectrophotometer, pH meter,Distillation Plant, Deionizers,Weightage ofMarks (%)5 104 84 1011 4424
56Chemistry ofCarbohydratesTraining theTechnicianAutomatic Dispensers andDilutors, Principles, Care,Maintenance & specificationsDefinition, Important functions,Classification, Monosaccharides,Oligosaccharides,Polysaccharides, Properties,Digestion, Absorption, BriefMetabolism, Glycolysis,Gluconeogenesis, HexoseMonophosphate ShuntClinical SignificanceBlood Glucose DeterminationBasic RequirementsVacutainers, Collection, Testing,Specimen Stability4 202 8TOTAL: 30 Hours25
SEMESTER IIIBIOCHEMISTRY - PRACTICALCREDITS: OE (2 Hrs/Week)SrNo.1TopicsIntroduction to Biochemistry LaboratoryGlassware, Safety measures, MaintenanceHrs22 Standardisation of 1ml. Volumetric pipette 23 Preparation of Normal solutions of Acids & AlkaliesDetermination ofNormality of 10 gm% NaOH24 Preparation of 1N HCl from Conc.HCl 25 Preparation of 1N NaOH 26 Preparation of 2/3N H 2 SO 4 from conc.H 2 SO 4 47Preparation of protein-free filtratePreparation of anti-coagulated bulbsSterilization of syringes & needles28910Preparation of 200 ml phosphate buffer & determination of pH byusing pH meterWorking of photometer, Standardization of photometerWorking of spectrophotometerDetermination of unknown concentration of colored solution Byphotometer46211 Determination of CSF proteins by turbidimetric method 2TOTAL: 30 Hours26
SEMESTER IIIMICROBIOLOGY - THEORYCREDITS: THREE (3 Hrs/Week)o. TOPIC Hrs. WeightageofMarks(%)1 Orientation to Diagnostic Microbiology 12 History of Microbiology 1 23 Microscopy- Structure of compound microscope. Imageformation, resolution, Definition, Chromatic and sphericalaberrations. Care of microscope.6 16Dark ground illumination.Fluorescent MicroscopyPhase contrast microscope and electron microscope4 Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.Bacterial Anatomy.Cell wall, Cell membrane, Capsule, 6 16Flagellum, Pili, Fimbriae. Function, demonstration.5 Endospore – chemical composition, staining properties, 1 46 Differential Staining ProceduresMaking and staining of films. Preparing grease free slidesand cover- slips. Preparation of smear.Gram staining, Acid fast staining, India InkPreparation,Albert’s Staining - Principle, Clinicalsignificance, mechanism and QC7 167 Classification of medically important bacteria 2 68 Sterilization and disinfection. – Definition. Classes ofdisinfectants and it’s properties, Dry heat. Use of hot airoven. Moist heat. Use of Inspissator & Arnold steamsterilizer. Use of autoclave.Use of ionizing & non ionizing radiations9 Growth and nutrition of bacteriaPhysical and chemical requirements. Growth curve.10 Classification of media – general purpose, enriched,enrichment, selective and transport11 Biochemical media – Use of MR-VP broth, Tryptonewater, Simmon’s citrate agar. Use of TSI agar andChristen’s urea broth. Use of Nitrate broth, Nutrientgelatine and PPA agar, – Use of Oxidase and Catalasetest.8 182 21 46 1012 Antimicrobial susceptibility Testing.Kirby Baur Method.3 413 Universal Safety Precautions 1 2TOTAL 4527
SEMESTER IIIMICROBIOLOGY - PRACTICALCREDITS: TWO (4 Hrs. /Week)O. TOPIC Hrs.1 Use of Compound Light Microscope2Low, High And Oil- immersion lenses2 Hanging Drop Preparation 23 Monochrome Staining 24 Gram Staining 45 Ziehl-Neelson Staining 46 India Ink Preparation 27 Albert’s Staining 48 Fontana’s Staining Method 29 Kirk-Patrik’s Staining Method 210 Schaffer- Fulton Staining Method 211 Introduction and Use of Glassware 212 Use of Hot Air Oven, Arnold Steam Sterilizer, Inspissator 213 Use of Filters 214 Adjustment of pH 215 Preparation and Use of General Purpose MediaPeptone Water, Nutrient Broth, Nutrient Agar Plate and Slant 6,MacConkey Agar,Mulller Hinton Agar16 Preparation and use of Biochemical MediaMR-VP Broth,Tryptone Broth,Simmon’s Citrate Agar617 Preparation and use of Biochemical MediaNitrate Broth, Nutrient Gelatin,Triple Sugar Iron Agar,Phenylalanine Pyruvic Agar,8Sugar Medium,Motility Agar18 Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testingby Kirby Baur MethodPreparing McFarland Standard,6Standardization of InoculumPerforming the Test.Interpretation and Reporting.19 Universal Safety Precautions 2TOTAL 6028
SEMESTER IIIHAEMATOLOGY - THEORYCREDITS: OE (1 Hr./Week)o. TOPIC Hrs.1 Introduction & Importance of Hematology inDiagnosis of diseases, Components of blood& their functions, Different Blood collectiontechnique, Use of various anticoagulants,Effects of anticoagulant on cell morphology2 Hemopoietic system of the body, Generalconsiderations, Normal sites for poiesisErythropoeisis, Stages of RBC developmentinfluencing factors, Normal RBC morphology3 Hemoglobin synthesis & Iron metabolism,Normal & Abnormal Hb with emphasis onclinical significance, Different methods todetermine Hb & its important4 Leucopoiesis, Factors influencingleucopoiesis, White blood cell morphologyWeightageofMarks(%)1 32 41 22 25 Thrombopoisis, Morphology of platelets 1 16 Total WBC, RBC & Platelets count byhaemocytometry & their clinical significance2 27Hematocrit Determination by differentmethods & clinical significance, Bloodindices, Calculations & Clinical significance1 18 Blood smearsStudy of normal - abnormal erythrocytes & 1 3leucocytes with their clinical significance9 Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate PrincipleDifferent methods, Clinical significance1 210 Reticulocyte count & Absolute eosinophilcount with their clinical significance1 211 Automation in HematologyIntroduction & Basic Principle, Cell countingby impendence method & Advantages1 2Coulter Counter12 Study of complete Histogram & Laboratorydiagnosis of Diseases 1 1Total 15 2529
SEMESTER IIIHAEMATOLOGY - PRACTICALCREDITS: TWO (4 Hrs./Week)o. TOPIC Hrs.1Blood Collection by different methodsPreparation of different reagent stain and anticoagulant2 Estimation of Hb by different methods 2345Total WBC countTotal RBC countPreparation and staining of Blood SmearDifferent WBC countIdentification of abnormal WBC and RBCEstimation of PCV by different methods & Calculationof blood indices6 Estimation of E.S.R. by different methods 4789Reticulocyte count / Ab Eosinophil CountPlatelet count / Arenth count4Screening of Anameia SmearScreening of Leukemia Smear4AutomationStudy of Haemogram2Total 30244430
Semester: IIISkills in Language CommunicationCredits: 2 (2 Hrs. / Week)Sr.o.Topic Sub-Topics Hrs. WeightageofMarks(%)1. Grammar Preposition/conjunction/tense/direct nindirect2 Comprehensionpassage3. Vocabularyenhancing4. Writtencommunication5. Oralcommunication4 04Listening/reading 8 10Synonyms/antonyms/homonyms 4 04Developing paragraph, letterwriting(formal n informal), essaywriting, note-making.Description of an incident, dialogue,preparation and presentation of viva.Total10 076 --------30Hrs.31
Semester: IIIComputer ApplicationsCredits: 2 (4 Hrs. / Week)O. TOPIC Hrs.1234Introduction to computersDefinition, FunctionAreas of ApplicationParts of ComputerClassification of computer hardwareClassification of ComputersDefinition and description of Operating SystemIntroduction to DOSIntroduction to Windows XPFeatures of Windows XP5 Introduction to MS – Word and its use 166 Introduction to PowerPoint and its use 167 Introduction to MS – Excel and its use 108 Application of Computer in Medical Laboratory 6TOTAL 60242432
Semester: IIIBook- keepingCredits: 2 (2 Hrs. / Week)Sr.o.Topico. ofHrs.WeightageofMarks (%)1Introduction To Book- KeepingDefinition and ConceptNature and Importance4 4Accounting TermsPrinciples of Double Entry2JOURNALClassification of AccountsRules for Accounting, Journalizing4 4Exercises3LEDGERIntroduction- Sub-division Of LedgerMechanics of Posting, Balancing of Accounts,5 32Exercises4Subsidiary BooksTypes and Recording Of Entries2 8Posting to the Ledger5Subsidiary books CASH BOOKExercises, Kinds of CashbooksRecording of Entries, Bank Transaction, Bank 6 20ReconciliationAnd Contra entry6PETTY CASH BOOKTypes of Petty Cash Book2 8Simple, Analytical Balancing7 Trial Balance – Method, Preparation 2 88Final AccountsPreparation of Trading & Profit and LossAccounts, Balance SheetAdjustment Entries5 16TOTAL 3033
SCHEME: SEMESTER IVo. Subject L P/T D TP TWPREXAMTCredits4001 Biochemistry 3 P-6 2 50 25+25 50 150 64002 Microbiology 3 P-6 2 50 25+25 50 150 64003 Hematology 24004ClinicalPathologyT-2 P-22 25 25+25 25 100 42 P-4 2 25 25+25 25 100 44005 SLC 2 - - 25 25 - 50 2Phlebotomy - P-4 - - - - - 2Total 12 24 550 2434
SEMESTER IVBIOCHEMISTRY: THEORYCREDITS: THREE (3 HOURS/WEEK)Sr. o. Topic o. of Hrs.1234Chemistry of CarbohydratesDefinition, Important Functions,Classification, Monosaccharides,Oligosaccharides, Polysaccharides,Properties, Absorption & Metabolism ofCarbohydrates.Regulation of Blood SugarDiabetes Mellitus, Urine & Blood GlucoseDetermination , GTT, GlycosylatedhemoglobinChemical Tests in Kidney DiseaseGeneral Consideration, Determination ofBlod Urea Nitrogen, urea Metabolism,Determination of Serum Creatinine,Creatinine Metabolism, Determination ofUric Acid and Uric Acid MetabolismChemistry of ProteinsDefinition, Functions, Structures &Classification of Proteins, Properties ofProteins & Amino Acids, Summary ofProtein Digestion, Amino Acid Metabolism,Determination of Serum ProteinsEnzymesIntroduction, Enzymes as Catalysts, EnzymeSpecificity, Enzyme Catalysis, FactorsAffecting Enzyme Activity, InorganicPositive and Negative Modifiers,Coenzymes, Isoenzymes,EnzymeClassification, Enzymes in ClinicalDiagnosis, Uses of Enzymes, LaboratoryDeterminationsTOTAL: 45WeightageofMarks(%)10 2411 2612 2412 2635
SEMESTER IVBIOCHEMISTRY: PRACTICALSCREDITS: THREE (6 HOURS/WEEK)Sr.No.123456TopicsUrinary Sugar DeterminationQuantitative Estimation of urinary sugarQualitative estimation of urinary sugarIdentification of reducing sugars in urineSerum Glucose estimation by GOD-POD methodFolin-Wu method for sugar determinationUrea Nitrogen Estimation , Blood Urea Nitrogen EstimationUrine Urea Nitrogen EstimationCreatinine Estimation, Serum Creatinine EstimationUrine Creatinine EstimationUric acid Estimation, Serum Uric acid EstimationUrine Uric acid EstimationProteins Estimation, Serum Total Proteins, Serum AlbuminSerum A/G ratio7 Proteins Estimation, CSF & Urine ProteinsHrs.610886868 Enzyme Estimations, SGPT – StandardizationSGPT- Determination9 SGOT – StandardisationSGOT – Determination1011Serum Alkaline phosphatase- StandardisationSerum Alkaline phosphatase – DeterminationSerum Acid phosphatase – StandardisationSerum Acid phosphatase- Determination12 Serum Amylase Estimation 613Serum LDH StandardisationSerum LDH - Determination14 Amino Acid Separation by Chromatography 2TOTAL 906666636
SEMESTER IVMICROBIOLOGY - THEORYCREDITS: THREE (3 Hrs/Week)o. TOPIC Hrs. WeightageofMarks(%)1 General considerations & philosophy of specimen 1 4collection, transportation & processing2 Processing Urine for cultue2 8Anatomy of urinary tract & noncultural techniquesused for the screening of significant bacteruria.Collection, Transport and culture.3 Processing Stool for Culture.Anatomy of G_I tract & factors affecting colonisationof pathogens. Attributes of pathogens. LaboratoryDiagnosis of Enteric fever,Bacillary Dysentry,4 8Cholera.Other Agents involved with G-I tract Infections4 Processing Throat SwabCollection,Transport and Culture for LaboratoryDiagnosis of Sore throat, Diphtheria, Vincent’s Angina2 8and Pertusis5 Processing Sputum for CultureCollection,Transport and Culture for Laboratory 2 8Diagnosis of Pnuemonia and Tuberculosis6 Processing Blood for CultureGeneral considerations. Choosing properanticoagulant. Non-cultural techniques for bloodculture. Routine Blood Culture. Laboratory diagnosis4 8of Tularemia,Plague,Brucellosis, Recurrent fever,Weil’s disease, Rat-bite fever, Sodoku7 Processing Cerebrospinal Fluid for CultureNon cultural techniques for C.S.F. Microscopy,Limulus lysate test, CIEP, Latex agglutination tests. 5 8Biochemistry.Cultural Techniques for CSF.8 Processing Genital Tract MaterialLaboratory Diagnosis of Gonorrhoea, Syphilis, 5 8Chancroid, Granuloma inguinale, LGV.Genital herpes9 Processing Ear SwabLaboratory Diagnosis of Inclusion and Purulent1 637
Conjuctivitis10 Processing Eye SwabLaboratory Diagnosis of Otitis Media11 Processing Wound Swab for Culture12 Lumen Dwelling Protozoa and Helminths13 Tissue Dwelling Protozoa & Helminths14 Mycobacteria & Actinomycetes15 Enteric Gram -ve rods16 Other Gram –ve rods1 61 44 63 45 62 42 4TOTAL4538
SEMESTER IVMICROBIOLOGY - PRACTICALCREDITS: THREE (6 Hrs./Week)O. TOPIC Hrs.1 Study of Lactose fermenters - E.coli, Klebsiella spp. & Enterobacterspp62Study of Proteus mirabilis and vulgaris 63Study of Salmonella typhi, paratyphi A and paratyphi B 64Study of Shigella shiga, flexneri, boydii and sonnie 125Study of Serratia marcescens 66Study of Vibrio cholarae 67Study of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 68Processing urine specimen69Processing an ear swab610Processing blood for culture611Processing stool specimen612Processing wound swab613Processing rectal swab614Processing sputum sample6TOTAL9039
No ofWeekSEMESTER IVHAEMATOLOGY - THEORYCREDITS: TWO (2 Hrs./Week)TopicsHrs.WeightageofMarks (%)1Introduction to coagulase study,Haemostasis & Coagulation factor2 42Mechanism of coagulation. Intrinsic &ExtrinsicPathway. Fibrinolytic System2 83Laboratory Investigation in CoagulationClinical significance & Interpretation. Platelet count 4 8Bleeding time & Clotting time4Clot retraction and clot lysis time, Prothrombin time,Plasma recalcification time2 8Partial thromboplastin time5Activated partial thromboplastin timeThrombin time Identification of FDP.2 46Fibrinogen estimation and titrePlatelet aggregation time4 8Thromboplastin generation time7Different lab investigation in bleeding disorderAutomation in coagulase studiesBasic Principles & working of different types of2 12coagulometer8Immuno Haematology – Introduction.Red cell antigen -antibody2 89 ABORh blood - Laboratory investigation, DU test 2 1210Compatibility test, Coomb’s test, Antibody titre testAntibody screening test2 811Blood banking - Blood donor selection and bleedingtechnique, Significance of investigation of bloodbags, Importance of different blood components, itsuses and preservation2 412 Blood transfusion technique, reactions &investigations.13Introduction to the HDN diseases & diagnosis.Automation in Blood Banking, Waste Managementin Blood Bank2 828TOTAL 3040
Sr.No TopicsSEMESTER IVHAEMATOLOGY - PRACTICALCREDITS: TWO (4 Hrs./Week)1 Laboratory safety & Introduction to coagulase study 22 Laboratory reagent preparation for coagulation studies 23 Coagulase Investigation - Platelet count, Bleeding time- Clotting time 44 Clot retraction and clot lyses time, Prothrombin time 45 Plasma recalcification time & Partial thromboplastin time 2678Activated partial thromboplastin time ,Thrombin time,Identification of FDPFibrinogens estimation and titer. Platelet aggregation timeThromboplastin generation timeDifferent laboratory investigation in bleeding disorderAutomation in coagulase studies.Basic principle, Function, Advantages9 Immuno Haematology. Introduction. Laboratory reagent preparation 210 ABO -Rh blood group by different methods. Du test 411 Compatibility test & Coomb’s test 412 Antibody titre test &Antibody screening test 413Blood banking - Selection and Preparation of Donor, Bleedingtechnique, Transportation, storage& preservation of blood bags.14 Preparation of different blood components, its uses and preservation 415 Blood transfusion technique 216 Lab investigation for blood transfusion reaction test 417 Lab. Diagnosis test for HDN disease 418Function maintaining of blood bank equipmentAutomation in Blood BankingWaste management in blood bankingHrs.44424TOTAL 6041
Semester - IVClinical Pathology (Theory)Credits: 2 (2 Hrs. / Week)Sr. o. Topic o. of Hrs.WeightageofMarks(%)1 Orientation to Clinical Pathology 12URINE EXAMINATIONIntroduction & clinical significance,Different Types of samplesCollection & preservation1 83 Physical Examination of urine 2 84Chemical Examination of urineClinical Significance of proteins & sugarsClinical Significance of Occult blood test &Ketone bodiesClinical Significance of Test for bilepigmentsTest for bile salts, Test for urobilinogen8 205 Microscopic Examination of urine 3 126 Study of urinary calculi 1 47 Pregnancy Tests 2 889101112STOOLS EXAMINATIONClinical significanceCollection & TransportationPreservativesPhysical Examination of stoolsNormal samples, Abnormal samplesChemical ExaminationOccult blood test, Bile pigments,StercobilinogenMicroscopic ExaminationSlide preparation, Saline, Iodine, Methyleneblue, Concentration methods,Sedimentation & floatation methodsParasitologyProtozoa, Helminths1 41 41 43 86 2042
TOTAL:30 HoursSemester - IVClinical Pathology (Practical)Credits: 2 (4 Hrs. / Week)Sr. o. Topic o. of Hrs.1 Orientation to Clinical Pathology 22URINE EXAMINATIONIntroduction & clinical significance,Different Types of samplesCollection & preservation3 Physical Examination of urine 44Chemical Examination of urineClinical Significance of proteins & sugarsClinical Significance of Occult blood test & KetonebodiesClinical Significance of Test for bile pigmentsTest for bile salts, Test for urobilinogen5 Microscopic Examination of urine 66 Study of urinary calculi 27 Pregnancy Tests 489101112STOOLS EXAMINATIONClinical significanceCollection & TransportationPreservativesPhysical Examination of stoolsNormal samples, Abnormal samplesChemical ExaminationOccult blood test,Bile pigments, StercobilinogenMicroscopic ExaminationSlide preparation,Saline,Iodine,Methylene blueConcentration methods,Sedimentation & floatation methodsParasitologyProtozoa, Helminths216222612TOTAL:60 Hrs.43
Semester: IVSub: Skills in Language CommunicationCredits: 2 (2 Hrs. / Week)Sr.o. Topic Sub-Topics Hrs.1. Grammar2.3.4.5.ComprehensionpassagesVocabularyenhancingWrittencommunicationOralcommunicationPreposition, tense, voice, direct nindirect, auxiliariesWeightageofMarks(%)6 20Listening/reading 8 40Medical words & terms/ homonyms. 3 12Letter writing (formal) : applicationfor a job, resume, a letter ofpermission, enquiry n reply toenquiry, orderEnquiry, complaint, interaction withpatient, preparation n presentation ofvivaTotal309 284 --------------44
SCHEME: SEMESTER V (UIVERISTY EXAMIATIO)o. Subject L P/T D TP TWPREXAMTCredits5001 Biochemistry 3 P-4 2 25 25+25 25 150 55002 Microbiology 3 P-6 2 25 25+25 50 150 65003 Hematology 2 P-2 2 25 25+25 25 100 35004ClinicalPathology5005 Histopathology 22 P-4 2 25 25+25 25 100 4T-2 P-22 25 25+25 25 100 4Total 12 20 600 2245
SEMESTER: VSUBJECT: BIOCHEMISTRY (THEORY)CREDITS: THREE (3 Hours/Week)Sr.o.123456TopicsKIDNEY FUNCTION TEST-General consideration, Thekidneys,Formation of urine, Kidney function, Role ofnephrons, Hormonal regulation, Laboratory tests aiding inthe evaluation of kidney function test,Clinical significanceLIVER FUNCTION TEST- Introduction, The liver, Liverfunction. Bile pigment metabolism. Disordered bilepigment metabolism, Pre-hepatic jaundice, Hepaticjaundice, Post- hepatic jaundice, routinely performed liverfunction testsClinical significanceCHEMISTRY OF LIPIDS- Definition, Importance,Classification & Properties. Digestion and absorption oflipids & Lipoprotein metabolism. Fredrickson’sclassification of lipoprotein. Lipid profile tests & ClinicalsignificanceCARDIAC PROFILE TESTS - Cardiac profile tests,General consideration, Ischemic heart diseases,Artherosclerosis, Risk factor & Related laboratory testsWATER AND MINERAL METABOLISM-Generalconsideration, Body fluid distribution, Factors whichinfluences distribution of body water,Mineral metabolism,Calcium and phosphorus metabolism, Laboratory tests –electrolytes( sodium, potassium, chloride) determination,Flame photometry, Iron selective electrode technology,Clinical significanceACID BASE BALANCE- Diffusion of gases in the lungs,Action of buffer systems, Disturbances in acid – basebalance, Laboratory determinationHrs.WeightageofMarks(%)7 127 127 145 126 124 1246
7CHEMISTRY OF HORMONES- Introduction, regulationof action of hormones, General mechanism of actions,Classification of hormones, Hormones of thyroid gland ,Hormones of the gonads, Hormones of anterior andposterior pituitary gland ,RIA and ELISA techniques6 168 AUTOMATION- Historical aspects, Various types, 3 10Batch and random access analysesTOTAL 4547
SEMESTER: VSUBJECT: BIOCHEMISTRY (PRACTICAL)CREDITS: TWO (4 Hours/Week)Sr.o Topics Hours1 Determination of creatinine clearance 42 Determination of urea clearance 434567Liver function testss. bilirubin (Malloy evelyn’s , Jendrassic – Grof’s method) ,SGPT, SGOT , Alkaline phoshatade ( Rate of reaction methods) ,Thymol turbidity tests ,Serum proteins ( end point reaction method) ,Gamma Gt ( rate of reaction method ) : DemonstrationLipid profile testsDetermination of s. total cholesterol ( end point , enzymatic method),HDC cholesterol ( end point , enzymatic method) ,S. triglycerides ( end point , enzymatic method) ,LDC – C,VLDL – C,Ratio of T. chol / HDL -CCardiac injury panel testsCPK ( rate of reaction method ) : DemonstrationLDH ( rate of reaction method ), SGOT ( rate of reaction method )SHBD ( rate of reaction method )Determination of electrolytes in serum / urine/ CSFCalcium - ( Cresolphalein complexone method), Inorganicposphorus( Fiske- Subbarow’s method or Uv linetic method),Sodium,Potassium & Chloride - Flame photometryHormonal studies :demonstration of- determination of T3, T4, TSH,LH, FSH, by RIA and ELISA methodTOTAL161610826048
SEMESTER VMICROBIOLOGY - THEORYCREDITS: THREE (3 Hrs/Week)o. TOPIC Hrs. Marks1 Staphylococci 1 22 Streptococci 1 43 Neisseriae1 24 Facultative & Aerobic Gram Positive Rods 1 45 Clostridia and Other Anaerobic RodsAnaerobic Cultivation3 86 Spirochetes 1 27 Mycoplasma 1 28 Chlamydiae 1 29 Rickettsiae10 Fungi & Laboratory Diagnosis of Mycoses11 ImmunologyThe Innate Immune SystemT- Cells & Cell Mediated ImmunityB Cells & Humoral ImmunityAntigen Antibody Reactions12 VirologyIntroduction to VirusesClassification of VirusesCultivation of VirusesReplication of VirusesHepatitis VirusesRetroviruses & AIDSPrions13 Automation in Microbiology14 Quality Control & Quality Assurance inMicrobiology Laboratory1 22 810 2415 302 25 84549
SEMESTER VMICROBIOLOGY - PRACTICALCREDITS: THREE (6 Hrs/Week)o. TOPIC Hrs.1 Study of Staphylococci 62 Study of Streptococci 63 Study of Corynebacterium diphtheriae 64 Processing throat swab 65 Introduction to serology. Equipments and glassware used in serology 46 Antigen Antibody Reactions 47 Widal test 68 V.D.R.L. Test 49 RPR Test 410 RA Test 411 CRP Test 412 ASO Test 413 Tests for Hepatitis 614 Tests for HIV/AIDS 615 TORCH Test 216 Isolation and Identification of Fungi 6Study of Candida albicans 6Quality Control in Microbiology Laboratory 6TOTAL 9050
SEMESTER VHEMATOLOGY- THEORYCREDITS: TWO (2 Hrs/Week)Sr.No. Topic Hrs.WeightageOfMarks (%)1 Introduction to the Advanced Hematology 123Clinical Significance, Interpretation and diagnosis ofSickle cell detection by different methodsHeinz body, G 6 PD testClinical Significance, Interpretation and diagnosis of,LE cell test, Serum iron/TIBC test1 81 124 Importance of normal & abnormal Hb in the diagnosis. 1 85 Hb electrophoresis, Osmotic fragility test 1 86 Laboratory diagnosis of Blood parasitic infections 1 87 Importance of bone marrow screening. 1 48 Classification & laboratory diagnosis of anemias 1 89 Classification & laboratory diagnosis of leukemia 2 810 Diagnosis of bleeding disorders by different methods 1 811 Profile- Immunohematology 1 812Blood transfusion technique & management oftransfusion reaction1 813 Automation in Hematology 1 814 QC & Waste Management in Hematology 1 4TOTAL 3051
Sr.No1SEMESTER VHEMATOLOGY - PRACTICALCREDITS: OE (2 Hrs/Week)TopicsSickling test, Solubility test, Heinz body preparation, G.P.D.estimation2 Osmotic fragility, Nestroft test, L.E. cell Phenomena 23 Laboratory diagnosis of blood parasite 24 Fetal HB estimation 25 Serum iron and TIBC estimation 26Bone marrow collection and smear preparation attainingtechnique7 Cytochemical test 28 HB electrophoresis 29 Screening of anemia slide 210 Screening of leukemia slide 211 Absolute Eosinophil, Reticulocyte, Platelet & Arneth count 212 Complete Hemogram report 213 Complete coagulase study 214 Complete immuno hematological test 215 Automation in Hematology 2No ofHrs.22TOTAL 3052
SEMESTER VHISTOPATHOLOGY- THEORYCREDITS: TWO (2 Hrs/Week)Sr.No. Topic Hrs.123Introduction & orientation to Histopathology andcytological techniques. Cell division.Basic steps in tissue processing.Basic Histopathology techniques.Methods of examination of tissues & cells.Dissociation. Smear technique. Vital stainingMethods of tissue preparation.Preparation of paraffin sections. Celloidinembedding. Preparation of frozen section.Weightage ofMarks (%)2 42 42 84 Fixation2 8Reagents employed. Decalcification5Gross examination and fixation of tissue.Requirements and procedures.2 46Tissue processing. Manual Methods and use ofautomatic tissue processor. Types of cryostats.2 87 Paraffin section cutting. 2 88Theory of staining. Staining techniques.. Basicstaining. Mountants. Mounting procedures2 89Frozen section techniques. Celloidin SectionCutting Technique2 810 Special staining techniques. 2 811Exfoliative cytology techniques.Clinical significance. Specimen collectionPreparation of smear & fixation. Various stainingtechniques & Papanicolaou method2 1212Museum techniques.Preparation of specimen. Storage of specimenMounting of museum specimen2 413ImmunohistochemistryIntroduction. Electron microscopic techniques 2 8Recent advances Flow Cytometry. EnzymeHistochemistry.14 Automation in Histopathology 2 415Organization of Histopathology Laboratory &Waste Management2 4TOTAL 3053
SEMESTER VHISTOPATHOLOGY- PRACTICALCREDITS: TWO (4 Hrs/Week)Sr.No. Topics Hrs.1 Use and care of equipment and glassware 42 Gross Examination of fresh-fixed specimens 43 Fixation Technique, Preparation of fixative 44 Different methods to be followed after fixatives 45Decalcification techniquePreparation of Decalcifying Reagents6 Processing & Paraffin wax embedding Technique 47 Vacuum Impregnating Technique 48 Casting—Block making Technique 4910Manual Processing TechniqueHitokinet- Auto –Tissue processing TechniqueDifferent types of Microtome, Microtome knivesHoning -Stropping11 Section cutting Technique 412 H & E Staining Technique 413 Special Staining Technique 414 Cytology- Smear preparation and Staining Technique 415Museum Technique 4TOTAL 6044454
Semester - VClinical Pathology (Theory)Credits: 2 (2 Hrs. / Week)Sr. o. Topic o. of Hrs. Marks123456Seminal Fluid ExaminationAnatomy of male reproductive systemClinical significanceCollection & transportSeminal Fluid ExaminationPhysical ExaminationNormal & abnormal samplesChemical Examination – Routine chemicaltests alongwith special tests like eosin test &glucose ringer testSeminal Fluid ExaminationMicroscopic ExaminationWet mount preparationSmear preparation for morphologicalstudiesSpermatozoa countAnatomy & physiology of CSFClinical significance of CSF collectionPhysical Examination of CSFChemical Examination of CSFMicroscopic Examination of CSFExamination of Body FluidsPhysiology of body fluid formationPhysical, Chemical, microscopicexamination, Examination of pleural fluid,peritoneal fluidpericardial & synovial fluidSPUTUM EXAMINATION-Introduction &clinical significance, Collection of samples,Physical examination, Microscopicexaminations4 23 25 44 55 46 57 Waste Management 1 18 Profile Studies - Urine 1 19 Profile Studies - Stool 1 1TOTAL:30 Hours55
Semester - VClinical Pathology (Practical)Credits: 2 (4 Hrs. / Week)Sr. o. Topic o. of Hrs.123456Seminal Fluid ExaminationAnatomy of male reproductive systemClinical significanceCollection & transportSeminal Fluid ExaminationPhysical ExaminationNormal & abnormal samplesChemical Examination – Routine chemical testsalongwith special tests like eosin test & glucoseringer testSeminal Fluid ExaminationMicroscopic ExaminationWet mount preparationSmear preparation for morphologicalstudiesSpermatozoa countAnatomy & physiology of CSFClinical significance of CSF collectionPhysical Examination of CSFChemical Examination of CSFMicroscopic Examination of CSFExamination of Body FluidsPhysiology of body fluid formationPhysical, Chemical, microscopicexaminationExamination of pleural fluid, peritonealfluidpericardial & synovial fluidSPUTUM EXAMINATIONIntroduction & clinical significanceCollection of samplesPhysical examinationMicroscopic examinations7 Waste Management 28 Profile Studies - Urine 29 Profile Studies - Stool 2861081012TOTAL:60 Hours56
SCHEME: SEMESTER VI- ITERSHIP CREDITS :20The students are rotated in following sections for three and half weeks in thelaboratories of hospitals.o. Subject Credits Marks1 Biochemistry 3 752 Microbiology & Serology 5 1253 Hematology & Blood Banking 6 1504 Clinical pathology 3 755 Histopathology & Cytology 3 7557
SYLLABUS FORMATDIPLOMA I MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHOLOGYSCHEME: SEMESTER IPaperPRSubject L P/T D TP TWCodeEXAMT Credits1001 General*P-4Chemistry42 1/2 75 25+25 25 150 61002 Physics 3 P-2 2 50 25+25 25 125 41003 Anatomy-Physiology3 P-2 2 50 25+25 25 125 41004 Biology 3 P-2 2 50 25+25 25 125 41005 SLC 2 - 2 25 25 - 50 2Total 15 10 575 20• PRACTICAL IS OF THREE HOURSSCHEME: SEMESTER IIPaperPRSubject L P/T D TP TWCodeEXAMT Credits2001 Organic Chemistry 4 P-4 2 1/2 75 25+25 25 150 62002 Physics 3 P-2 2 50 25+25 25 125 42003 Anatomy- 3 P-2 2 50 25+25 50 125 4Physiology2004 Biology 3 P-2 2 50 25+25 25 125 42005 SLC 2 - 2 25 25 - 50 22006 PersonalityDevelopment2 - - 25 25 - - 2Total 17 10 575 22SCHEME: SEMESTER IIIPaperPRSubject L P/T D TP TWCodeEXAMT Credits3001 Biochemistry 2 P-2 2 25 25+25 25 100 43002 Microbiology 3 P-4 2 50 25+25 25 125 53003 Hematology 1 P- 2 25 25+25 25 100 223004 SLC 2 - 2 25 25 - 50 23005 Computer- P-4 2 - 25 25 50 2Applications3006 Book Keeping 2 - 2 25 25 - 50 2-- Phlebotomy - P-4 - - - - - 2Total 10 16 475 1958