Download - IFTM University
Download - IFTM University
Download - IFTM University
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
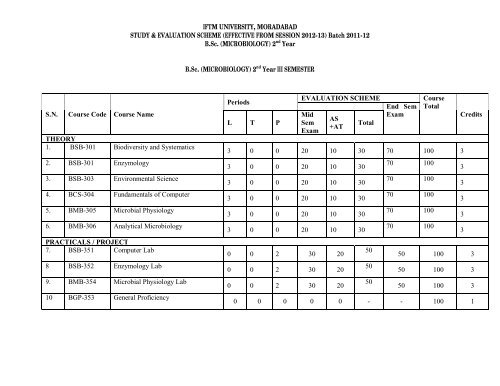
<strong>IFTM</strong> UNIVERSITY, MORADABADSTUDY & EVALUATION SCHEME (EFFECTIVE FROM SESSION 2012-13) Batch 2011-12B.Sc. (MICROBIOLOGY) 2 nd YearB.Sc. (MICROBIOLOGY) 2 nd Year III SEMESTERS.N. Course Code Course NameTHEORY1. BSB-301 Biodiversity and Systematics2. BSB-301 Enzymology3. BSB-303 Environmental Science4. BCS-304 Fundamentals of Computer5. BMB-305 Microbial Physiology6. BMB-306 Analytical MicrobiologyPRACTICALS / PROJECT7. BSB-351 Computer Lab8 BSB-352 Enzymology Lab9. BMB-354 Microbial Physiology Lab10 BGP-353 General ProficiencyPeriodsL T PEVALUATION SCHEMEMidSemExamAS+ATTotalEnd SemExamCourseTotal3 0 0 20 10 30 70 100 33 0 0 20 10 303 0 0 20 10 303 0 0 20 10 303 0 0 20 10 303 0 0 20 10 300 0 2 30 200 0 2 30 200 0 2 30 2050505070 10070 10070 10070 10070 100Credits50 100 350 100 350 100 30 0 0 0 0 - - 100 133333
<strong>IFTM</strong> UNIVERSITY, MORADABADSTUDY & EVALUATION SCHEME (EFFECTIVE FROM SESSION 2012-13) Batch 2011-12B.Sc. (MICROBIOLOGY) 2 nd YearB.Sc. (MICROBIOLOGY) 2 nd Year IV SEMESTERS.N. Course Code Course NameTHEORY1. BMA-409 Introductory Biostatistics2. BSB-401 Introductory Bioinformatics3. BSB-402 Recombinant DNA TechnologyPeriodsL T PEVALUATION SCHEMEMidSemExamAS+ATTotalEnd SemExamCourseTotal3 0 0 20 10 30 70 100 33 0 0 20 10 303 0 0 20 10 304. BSB-403 Metabolism of Carbohydrates andNucleic acid 3 0 0 20 10 3070 10070 10070 100Credits3335. BMB-404 Industrial Microbiology6. BMB-405 Medical MicrobiologyPRACTICALS / PROJECT7. BSB-451 Bioinformatics8 BSB-452 R-DNA technology9. BMB-453 Seminar10 BGP-454 General Proficiency3 0 0 20 10 3070 10033 0 0 20 10 3070 10030 0 2 30 205050 100 30 0 2 30 205050 100 30 0 2 30 205050 100 30 0 0 0 0 - - 100 1
<strong>IFTM</strong> UNIVERSITY, MORADABADSTUDY & EVALUATION SCHEME (EFFECTIVE FROM SESSION 2012-13) Batch 2011-12B.Sc. (MICROBIOLOGY) 2 nd YearBSB-301 Biodiversity and SystematicsUnit 1: Biodiversity & Population Dynamics: Biodiversity – Concept, definition, species,diversity, ecosystem diversity, genetic diversity, Magnitude of biodiversity, distribution ofbiodiversity, assessment of biodiversity, utilization of biodiversity, conservation of biodiversity;Population Dynamics- Population density & relative abundance, Population age distribution,Growth forms & carrying capacity, Population structure : isolation &territoriality, Interactions.Unit 2: Ecosystem, Biodiversity & Biogeography: The species & individual in the ecosystem-Habitat & niche, Ecological equivalence, Biological clock, Basic behavioral patterns;Biodiversity & major biomes of world; Biogeography- Specific flora and fauna: Comprehensiveaccount.Unit 3: Conservation of Biodiversity- Importance, Conservation strategies – in situ and ex situmethods: advantages, limitations and applications; Conservation laws, policies andorganizations.Unit 4: Bioprospecting of microbes, plants and animals; Biological systematics – principles andpractices; Tools & techniques of biological systematics of: microbes, plants and animalswithreference to the sources of data as applicable for group such as: Morphology, Anatomy,Histology, Chemistry, Cytology, Molecular biology, Micromorphology, Palenology andEmbryology.Unit 5: Biosystematics; Analysis of Biodiversity- Biodiversity indices, Mathematical modelingfor analysis of population variationRecommended Text/Reference Books1. Ecology :Begon&Hareper2. The biology of biodiversity :M.Kato3. Biodiversity : E.O. Willson4. Evolution : Stearns & Hoekstra5. Animal behaviour :Alcock6. Ecological analysis : Freeman & Herron7. Elements of taxonomy : E. Mayor8. Plant Taxonomy &Biodiversity :Stace9. Fundamentals of Plant Systematics : Radford10. Taxonomy of Angiosperms: Naik, V.N.
<strong>IFTM</strong> UNIVERSITY, MORADABADSTUDY & EVALUATION SCHEME (EFFECTIVE FROM SESSION 2012-13) Batch 2011-12B.Sc. (MICROBIOLOGY) 2 nd YearBSB-302 EnzymologyUnit 1: Enzymes As Catalysts: Overview--Proteins as catalysts (historical background); Enzymecharacteristics and properties; Enzyme nomenclature & classification; Enzyme Isolation,Purification and Assay.Unit 2: Enzyme Kinetics: Kinetics of single substrate reactions; Enzyme inhibition; Multisubstratereactions.Unit 3: Mechanism of Enzyme Catalysis: Kinetics of single substrate reactions; Enzymeinhibition; Multi-substrate reactions.Unit 4: Enzyme Regulation: Partial Proteolysis; Phosphorylation, Adenylylation, Disulphidereduction; Allosteric regulation.Unit 5: Industrial, Agricultural and Clinical Applications of Enzymes: Comprehensive Account.Recommended Text/Reference Books1. Alan Fersht: Structure and Mechanism in Protein Science, 2nd ed. W.H. Freeman &Co.2. Nicolas Price & Lewis Stevens: Fundamentals of Enymology, 2nd edition, OxfordUniv. Press, New York, NY.3.Trevor Palmer: Understanding Enzymes, Second Edition, J. Wiley & Sons, NewYork.4. Donald Voet& Judith Voet: Biochemistry, J. Wiley & Sons, New York5. Geoffrey Zubay (1993): Biochemistry, 3rd edition, Wm. C. Brown, Oxford6. Berg, Tymoczo and Stryer: Biochemist
<strong>IFTM</strong> UNIVERSITY, MORADABADSTUDY & EVALUATION SCHEME (EFFECTIVE FROM SESSION 2012-13) Batch 2011-12B.Sc. (MICROBIOLOGY) 2 nd YearBSB-303 Environmental SciencesUnit –1: Environmental Sciences: Introduction, definition, Scope, Importance, Need forPublic Awareness Natural Resources: Renewable and non Renewable recourses,Biogeochemical Cycles Ecological Succession, Ecological pyramidsUnit –2: Concept of an Ecosystem: Structure and function of an ecosystem Producers,consumers and decomposers, Energy flow in the ecosystem ,Ecological succession, Foodchains, food webs and ecological , pyramids , Introduction, types, characteristic features,structure and function of the following ecosystem Forest ecosystem, Grassland ecosystem,Desert ecosystem, Aquatic ecosystems (ponds, streams, lakes, rivers, ocean)Unit –3: Environmental pollution and pollutants, Causes, effects and control measures of:Air pollution, Water pollution, Soil pollution, Marine pollution, Noise pollution, Thermalpollution, Nuclear pollution, Solid waste management: Causes, effects and control measuresof urban and industrial wastes.Unit –4: Introduction – Definition: genetic, species and ecosystem diversityBiogeographical classification of India,Value of biodiversity: consumptive use, productiveuses, social, ethical aesthetic and option values ,Biodiversity at global, national and locallevels ,India as a mega-diversity nation ,Hot-spots of biodiversity,Threats to biodiversity:habitat loss, poaching of wildlife, man wildlife conflicts ,Endangered and endemic speciesof India,Conservation of biodiversity: In-situ and Ex-situ conservation ofbiodiversity,Biodiversity and its conservation: introduction value of biodiversity,biodiversity at global, national and local level, hotspots of biodiversity, and its conservationUnit –5: Global warming, acid rains, depletion of ozone layer population growth thepopulation explosion, family welfare |Program, human rights, Biofertilizers , Biopesticidesvermicomposting.Recommended Text/Reference Books1. Environmental studies By Dr. S.K. Dhameja2. Environmental & Ecology P.K.Agrawal3. Environmental & Ecology Deswal & Deswal4. Basic concepts and applications in environment Indusekher Thakur
<strong>IFTM</strong> UNIVERSITY, MORADABADSTUDY & EVALUATION SCHEME (EFFECTIVE FROM SESSION 2012-13) Batch 2011-12B.Sc. (MICROBIOLOGY) 2 nd YearBCS-304 Fundamentals of ComputersUnit-1: Introduction to Computer:-Definition, Characteristics. Generation of Computers,Capabilities and Limitations. Introduction to Operating System. Concept of Bios, BootingFiles.Basic Components of a Computer System-Control Unit, ALU, Input/output functions andcharacteristics. Memory Introduction, Classifications- Volatile Memory and Non- Volatile ,Flash Memory, ROM, RAM, EPROM, PROM, EEPROM other types of memory.Unit-2: Input, Output and storage Units:-Computer Keyboard, Pointing Devices: Mouse,Trackball, Touch Panel, and Joystick, Light Pen, Scanners, Various types of Monitors, Touchsensitivescreens, Optical Recognition System, Pen based systems, Digitizers, MICR, OCR,OMR, Bar-code Reader, digital camera. Hard Copy Devices:- Impact and Non- Impact Printers-Daisy Wheel, Dot Matrix, Line Printer, Chain Printer, Comb Printers, Non Impact Printers-DeskJet, Laser Printer, Thermal Transfer Printer, Barcode Printers, Electro static printers andplotters. High Level Language and Low Level Language, Firmware, Compiler, Interpreter andAssembler.Unit-3: Introduction and Features of “C” language, Structure of “C” program , Identifiers andKeywords, Constants, Variables, Scope of variables, Typedef, Type Conversion, ArithmeticOperators, Library Functions, Input/output Statements, getchar(), Putchar(), scanf, printf,Compound statements and block. Relational Operators, Logical Operators, Bitwise Operators,Unary Operators, If—Else Statement, Operators, Switch statement, goto statement and Label.Iteration statements: For Loop, While Loop, Do While Loop, Nested Loop, Continue and Breakstatements.Unit-4: Array and Structures: Declaration, Concept of One Dimensional and Multi Dimensionalarrays, Defining Structure, Declaration of Structure Variable, Accessing Structure members,nesting of structures, Array of structures.Unit-5: Difference between Union and Structure. Functions: Need of “C” function, User Definedand Library Functions, Prototype of Function, Call by Value, Call by Reference, Nesting ofFunctions, Recursion, Array as Function Argument, Structure as Function Argument.Recommended Text/Reference Books1. Computer Fundamentals B.Ram2. Computer fundamentals P.K Sinha (BPB Publications)3. Programming in Ansi C E.balagurusamy (3rd edition McGraw Hill)
<strong>IFTM</strong> UNIVERSITY, MORADABADSTUDY & EVALUATION SCHEME (EFFECTIVE FROM SESSION 2012-13) Batch 2011-12B.Sc. (MICROBIOLOGY) 2 nd YearBMB-305 Microbial PhysiologyUnit 1: Definition and Scope of Microbiology: History and recent developments; Spontaneousgeneration - Biogenesis-contributions of Louis Pasteur, Leewenboek, Lazaro Spallanzani, JohnTyndall, Joseh Lister & Robert Koch. Microscopy: simple, compound, light microscopy - Darkground, Phase contrast, Fluorescence and Electron Microscopy.Unit 2: Microbial Kingdoms: Five kingdoms; Cell theory; Binomial nomenclature of microbes;Species concept - Description of organisms &Classical approach with examples.Unit 3: Structural aspects of Prokaryotes: Structure and function of cell wall, cilia, flagella,slime layer, capsule, pili, cytoplamic membrane and cytoplasmic inclusions, and sporulation;Kingdom of prokaryotes; Classical techniques of microbial identification - morphological,physiological and biochemical properties.Unit 4: Structural and functional aspects of bacteria: Structure of a typical bacterial cell;Structures and functions of intracellular organelles of bacteria; Comprehensive physiological,biochemical and molecular level mechanism of host-parasite interaction and pathogenicity.Unit 5: Sterilization Principles: Dry heat, moist heat, filtration, Tyndallization, Pasteurization;Radiation & disinfection; Antimicrobial chemotherapy; Antibiotics – source, classification,mode of action; Antimicrobial resistance; Tests for sensitivity to antimicrobial agents and itsquality control.Recommended Text/Reference Books1.Brock, TD. Smith D.W. and madigan M.T. 1984.Biology of Microorganisms.4 th edition.Englewood, cliffs. N.J. Prentice Hall2. Development Biology - S.F. Gillbert3. Developmental Biology - K.V. Rao4. Developmental Biology - S.C. Goel5. Developmental Biology – Wolpert6. Embryology of Angiosperms – S.S. Bhojwani and S.P. Bhatnagar7. An Introduction to Plant Cell Development – J. Burgess
<strong>IFTM</strong> UNIVERSITY, MORADABADSTUDY & EVALUATION SCHEME (EFFECTIVE FROM SESSION 2012-13) Batch 2011-12B.Sc. (MICROBIOLOGY) 2 nd YearBMB-306 Analytical MicrobiologyUnit 1: Introduction to analytical microbiology. Significance of analytical techniques inlaboratory.Physical and chemical sciences versus analytical microbiology.Unit 2: Microscopy:Microscopic identification of various microorganisms; phase contrast andconfocal microscopy; SEM-TEM microscopy.Unit 3: Methods of biochemical analysis: Glucose, sugars, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins andnucleotides;enzymatic assays of various metabolites.Unit 4: Electrophoretic Techniques: Electrophoresis of proteins and nucleic acids; ID & 2DGels; pulsed field electrophoresis; capillary electrophoresis; western southern and northernblotting; dot and slot, gel documentation. Nucleotide and DNA Analysis: DNA purification,PCR-based analysis; DNA fingerprinting; DN Asequencing.Unit 5: Immuno-Techniques: Antiserum production, immunofluroscence, immunohistocompatibility ELISA;localization of cells in tissues immunoblotting; monoclonal antibodies.Recommended Text/Reference Books1. Introduction to Biophysics: Pranab Kumar Banerjee; S.Chand Publications; 20082. Instrumental Methods of Analysis:Ewing; 1992.3. Instrumental Methods of Analysis: Hobert, Willard, Merritt & Dean; CBS Publishers andDistributers; 19924. Instrumental Methods of Chemical Analysis: Gurdeep R. Chatwal; 7 Sham K. Anand;Himalaya Publishing House.
<strong>IFTM</strong> UNIVERSITY, MORADABADSTUDY & EVALUATION SCHEME (EFFECTIVE FROM SESSION 2012-13) Batch 2011-12B.Sc. (MICROBIOLOGY) 2 nd YearBMA-409 Introductory BiostatisticsUnit I: Introduction to Biostatistics: definition, statistical method, Biological measurement,kinds of Biological data, function of Statistics and limitation of Statistics. Application ofBiostatistics, Role of Biostatistics in modern research, parametric and nonparametric methods(Tests).Unit II: Collection of data, Presentation of Data, classification and tabulation, types ofrepresentation (graphic-bar diagram, pie diagram and curves and basic concept of calculus).Sampling and sampling design.Unit-III: Measure of central tendency, mean, Median, Mode, Geometric Mean, Measure ofdispersion, Variability and changes, Deviations-quartile deviation, mean deviation, standarddeviation, standard, Error, coefficient of variations.Unit-IV: Test of Hypothesis, Test of significance, chi-square test, t-test, F-test and ANOVA(Analysis of variance) One way and two way classification.Unit-V: Probability Theory of random experiment and associated sample space, events,definition of probability, algebra of events, addition and multiplication Theorems on Probability(Without Proof) Probability Distribution. Binomial Distribution, Poisson distribution and NormalDistribution and their Applications in Biostatistics.Recommended Text/Reference Books1. Georgr W and Willian G., Statistical Methods, IBH Publication2. R. Rangaswami, A Text Book of Agricultural Statistics, New Age International Publication3. Zar, J., Biostatistics, Prenticw Hall, London
<strong>IFTM</strong> UNIVERSITY, MORADABADSTUDY & EVALUATION SCHEME (EFFECTIVE FROM SESSION 2012-13) Batch 2011-12B.Sc. (MICROBIOLOGY) 2 nd YearBMB-401 Introductory BioinformaticsUNIT-I: Introduction of Bioinformatics, Biological Dataqbases. Primary and secondarydatabase. Specialized sequence databases of EST, TFB Sites, SNP’s, gene expression.Pfam, PROSITE, BLOCK (Secondary databases). Data retrieval with ENTREZ, SRS,DBGETUNIT-II: Principles of DNA sequencing (chemical chain termination, Dideoxy chaintermination method, Automatic sequencer). RNA sequencing. Protein sequencing (Edmand degradation method)UNIT-III: Sequence alignment (pairwise and multiple, global and local). Sequencealignment algorithm (FAST, BLAST, Needleman and Wunsch, Smith Waterman).Database similarity searches (BLAST, FASTA and PSI BLAST). Amino acidsubstitution matrices (PAM BLOSUM)UNIT-IV: Protein structure prediction ( Chou Fasman method) : Secondary and tertiarystructures. Homology Modelling, ORF prediction, Gene prediction, Micro array dataanalysis. Profiles and motifs.UNIT-V: Structure visualization methods (RASMOL, CHIME etc.). Protein Structurealignment and analysis. Application of Bioinformatics in drug discovery and drugdesigning.Recommended Text/Reference Books1. Bioinformatics: Principles and applications by Ghosh and Mallick (oxford)university press)2. Bioinformatics by Andreas D Boxevanis (Wiley Interscience)3. Fundamental concept of bioinformatics by Dan e. krane4. Introduction to bioinformatics by Attwood and Parry Smith (Pierson educationPublication)5. Instant notes in Bioinformatics by Westhead, parish and Tweman (Bios scientificpublishers)
<strong>IFTM</strong> UNIVERSITY, MORADABADSTUDY & EVALUATION SCHEME (EFFECTIVE FROM SESSION 2012-13) Batch 2011-12B.Sc. (MICROBIOLOGY) 2 nd YearBMB-402 Recombinant DNA TechnologyUnit I: General introduction to the concepts of recombinant DNA technology, Tools of r-DNAtechnology, Adopters and Linkers, Topoisomerases, DNA ligase. Restriction enzyme.Unit II: Vectors in gene cloning-plasmids, bacteria phages, shuttle vectors, Ti plasmid,expression vectors, shotgun cloning and cDNA cloning techniques. General idea of PCRtechnology.Unit III: General idea about regulation of gene expression, Post translational modificationsGene organization, expression in Mitochondria and Chloroplast.Unit IV: In-vitro construction of recombinant DNA molecule. Screening and selection ofrecombinant host cells. Gene libraries: Genomic DNA and cDNA Cloning techniques. Blottingtechniques: Southern, western and northern blot.Unit V: Techniques for recombinant DNA technology, Electrophoratic techniques, Polymerasechain reaction, Site directed mutagenesis, nucleic acid sequencing, Sanger’s method, Applicationof r-DNA technology.Textbooks and references:1. G.R. Glick & J.J. Pasternak: Molecular Biotechnology2. Watson, Hopkin, Roberts et al.: Molecular Biology of the Gene, 4 th ed.3. T.A. Brown – Gene Cloning.4. Microbial Genetics – D. Frifielder.5. Baltimore- Molecular Biology of the Cell.6. Benjamin Levin – Genes VIII, 8 th ed.7. R.Williamson – Genetic Engineering.
<strong>IFTM</strong> UNIVERSITY, MORADABADSTUDY & EVALUATION SCHEME (EFFECTIVE FROM SESSION 2012-13) Batch 2011-12B.Sc. (MICROBIOLOGY) 2 nd YearBMB 403 – Metabolism of Carbohydrate and Nucleic acidUnit-I: Carbohydrates: its nomenclature, classification with examples chemical structures ofmonosaccharides and disaccharides in pyranose and furanose form. Isomerism: stereoisomers,optical isomers, epimers, anomers. Mutarotation, specific rotation.Unit-II: Metabolism of Carbohydrates: Digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, glycogenesisand glycogenolysis, Conversion of Pyruvate to Acetyl CoA. Tricarboxilic acid cycle: Chemicalstructure of intermediates sites of ATP production, regulatory mechanism.Unit-III: Gluconeogenesis: From Lactate, Glycerol and Glucogenic amino acids Control of keygluconeogenetic enzymes. Pentose phosphate pathway: Importance of generation of NADPHUnit-IV: Nucleic acids: Structure of purines, pyrimidines, nucleosides and nucleotides. Structuretypes and biological role of RNA and DNA.Unit-V: Metabolism of Nucleic acids: Source of carbon and nitrogen in the synthesis of purineand pyrimidine. Catabolism of purine and pyrimidine. Disorders of purine and pyrimidinemetabolism.RECOMMENDED BOOKS –1. Biochemistry – J. L. Jain2. Biochemistry - Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet3. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, Fourth Edition by David L. Nelson,4. Michael M. Cox, Hardcover: 1100 pages, Publisher: W. H. Freeman5. Lubert Stryer's Biochemistry, published by W. H. Freeman and Company6. Harper’s biochemistry
<strong>IFTM</strong> UNIVERSITY, MORADABADSTUDY & EVALUATION SCHEME (EFFECTIVE FROM SESSION 2012-13) Batch 2011-12B.Sc. (MICROBIOLOGY) 2 nd YearBMB-404 Industrial MicrobiologyUnit-I: Introduction to Industrial Biotechnology/Microbiology: Brief History and Developmentsin Industrial Biotechnology/Microbiology, techniques of microbial culture, growth media,sources of nutrition, maintenance of microbial culture and strain preservation.Unit-II: Improvement of Industrial Strains: mutation, genetic engineering techniques,preservation of cultures-storage on agar slants, soil culture, lyophilization, storage in liquidnitrogen.Unit-III: Fermentation: Brief introduction, Fermentors: basic function of Baffle, Impeller andSparger. Types of fermenter-aerated and agitated fermenter.Unit-VI: General concept of recovery: inoculum and culture media in fermentation. Recoveryprocess-biomass separation, centrifugation, liquid- liquid extraction, cell disruption.Unit-V: Microbial production of industrial products: Production of Organic Acids (Citric andlactic acid), Amino Acids (Lysine), Alcohols and Penicillin.RECOMMENDED BOOKS –1. Murray Moo -Young, Comprehensive Biotechnology, Vol. 1 & III-latest ed. 452. Microbes & Fermentation, A. Lel and Kotlers Richard J. Mickey, Oriffin Publication3. Industrial Fermentations- Leland, N. Y. Chemical Publishers.4. Prescott and Dunn’s- Industrial Microbiology, 4 th , ed.
<strong>IFTM</strong> UNIVERSITY, MORADABADSTUDY & EVALUATION SCHEME (EFFECTIVE FROM SESSION 2012-13) Batch 2011-12B.Sc. (MICROBIOLOGY) 2 nd YearBMB-405 Medical MicrobiologyUnit 1: Normal microflora of the human body ( Skin, throat, gastrointestinal tract, urogenitaltract , Host-pathogen interaction .Definitions of invasion, pathogen, parasite, pathogenicity,toxigenicity, virulence, carriers and their types, nosocomial infections, opportunistic infections,septicemia, septic shock, transmission and spread of infection.Unit 2: Sample collection, transport and diagnosis. Collection, transport and culturing ofclinical samples, principles of different diagnostic tests (ELISA, Immunofluorescence,Agglutination based tests, Complement fixation, PCR, DNA probes).Unit 3: Bacterial diseases (with reference to symptoms, pathogenesis, transmission, prophylaxisand Control. Bacillus anthracis, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Streptococcus pyogenes,Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhi and paratyphi,Unit 4: Bacterial diseases (with reference to symptoms, pathogenesis, transmission, prophylaxisand Control. Shigella dysenteriae, Helicobacter pylori, Vibrio cholerae, Haemophilus influenza,Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Treponema pallidum.Unit 5: Viral diseases (with reference to symptoms, pathogenesis, transmission, prophylaxis andcontrol) Polio, Chicken pox, Herpes, Hepatitis, Rabies, Influenza with brief description of birdand swine flu, Dengue,Reference Books:1) Textbook of Microbiology : R Ananthanarayan and CKJ Paniker2) Sherris Medical Microbiology ( Kenneth Ryan, C George Ray, Naffis Ahmad)