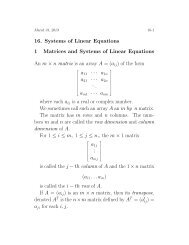
16. Systems of Linear Equations 1 Matrices and Systems of Linear ...
16. Systems of Linear Equations 1 Matrices and Systems of Linear ...
16. Systems of Linear Equations 1 Matrices and Systems of Linear ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
March 31, 2013 16-18Try a few more examples yourself to get comfortable with this.Now, notice that each <strong>of</strong> the matrices P ij , E c,i , E ci+j is invertible. Indeed,Eij−1 = E ij , Ec,i−1 = E 1/c,i , <strong>and</strong> Eci+j −1 = E −ci+j .It follows that if we do a sequence <strong>of</strong> k row modifications to a matrix Athis amounts to successively multiplying it on the left by k matrices obtainedfrom one <strong>of</strong> the three types P ij , E c,i , E ci+j .This means that after k such modifications, the matrix A is replaced byD 1 D 2 . . . D k Awhere each D k is one <strong>of</strong> the P ij , E c,i or E ci+j we just discussed.If we had an augmented matrixA | I<strong>and</strong> we do the same row modifications on it, then, <strong>and</strong> the end, we getD 1 D 2 . . . D k A | D 1 D 2 . . . D k IIf we end up with I on the left, then D 1 D 2 . . . D k = A −1 . On the rightwe end up with D 1 D 2 . . . D k I = D 1 D 2 . . . D k . So we have written down A −1 .5.1 A simple method to compute the inverse <strong>of</strong> a 3 × 3matrixLet A = (a ij ) be an invertible n × n matrix. We can use determinants <strong>and</strong>Cramer’s rule to get a simple way to compute A −1 using Cramer’s rule.We first observe that Cramer’s rule holds for every invertible square matrix:The i−th coordinate <strong>of</strong> the solution to A · x = b has the formx i = det(A i)det(A)where A i is the matrix obtained by replacing the i−th column <strong>of</strong> A bythe i−th unit column vector e T i .Since A −1 is the solution X <strong>of</strong> the matrix equation A · X = I, the i − thcolumn <strong>of</strong> A −1 is the solution to the matrix equation A · x = e T i .We apply Cramer’s rule to the case <strong>of</strong> a 3 × 3 invertible matrix