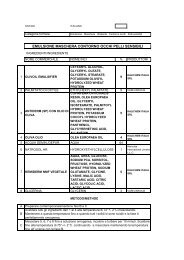
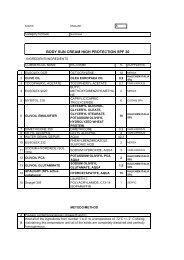
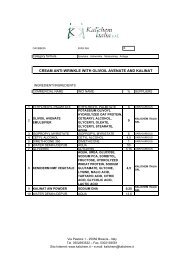
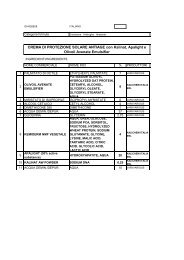
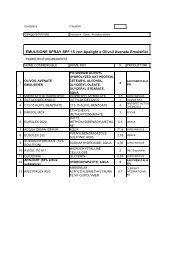
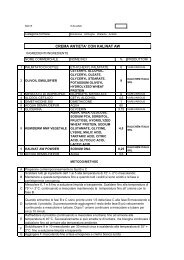
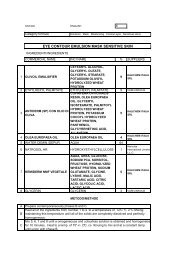
KALIDENT-Idorssiapatite di Calcio -STDE - Kalichem.it
KALIDENT-Idorssiapatite di Calcio -STDE - Kalichem.it
KALIDENT-Idorssiapatite di Calcio -STDE - Kalichem.it
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
3. Remineralisation of Subsurface<strong>KALIDENT</strong>-Calcium Hydroxyapat<strong>it</strong>e, having almost the same compos<strong>it</strong>ion as our teeth, <strong>di</strong>rectlyprovides mineral to demineralised subsurface areas of the tooth (incipient caries), restoring theenamel to <strong>it</strong>s near-natural state, w<strong>it</strong>hout changing the compos<strong>it</strong>ion of the enamel. This is in contrastto fluorides, which are not true remineralising substances by themselves, but promote teethremineralisation by salivary calcium phosphate, by creating a new substance, fluorapat<strong>it</strong>e, on thetooth surface. Fluorides tend to form a coating on the surface of the enamel, in contrast tohydroxyapat<strong>it</strong>e, which tends to restore subsurface lesions from the deeper part of the lesion first.This deep restorative effect has been enhanced by the reduction of the hydroxyapat<strong>it</strong>e particle sizeto two-figure nanometer size, facil<strong>it</strong>ating their deeper penetration into the enamel.FUNCTIONAL CLAIMSFeatures-Dental sens<strong>it</strong>iv<strong>it</strong>y-Remineralization and filling of surface lesions-Plaque clinical-physical removal-Acid antierosion-Bio-available calcium and phosphate ions-Boosts natural abil<strong>it</strong>y of saliva to remineralise tooth structureAlleviates:-Teeth Erosion-Dental Wh<strong>it</strong>e lesions-Rampant caries-Dental effects of aci<strong>di</strong>c mouth-Enamel problems in newly-erupted teethBibliographyThe Journal of Cosmetic Wh<strong>it</strong>ening Vol.3 2005Interaction of Small Crystal Form of Hydroxyapat<strong>it</strong>e w<strong>it</strong>h Mutans StreptococciT. ARAKAWA, T. ISHIZAKI, R.E. HAYMAN, N. HANADA, and H. SENPUKUJournal of Dental Research Vol. 83, 2036, Honolulu Abstracts. Special Issue A. 2004Sede legale: Via San Bartolomeo 9- 25128 BRESCIASede operativa: Via Pastore 1 - 25082 Botticino Sera (Brescia) ItaliaTel. 0302693532 – Fax. 0302193581S<strong>it</strong>o Internet: www.kalichem.<strong>it</strong> – e.mail: kalichem@kalichem.<strong>it</strong>
A New Enamel Restoring Agent for Use after PMTCM. NISHIO, H. KAWMATA, K. FUJITA, T. ISHIZAKI, R. HAYMAN, and T. IKEMIJournal of Dental Research Vol. 83, 1920, Honolulu Abstracts. Special Issue A. 2004A New Enamel Restoring Agent for Use after BleachingH. KAWAMATA, K. FUJITA, T. ISHIZAKI, R. HAYMAN, and T. IKEMIJournal of Dental Research Vol. 83, 1919, Honolulu Abstracts. Special Issue A 2004Interaction of Small Crystal Form of Hydroxyapat<strong>it</strong>e w<strong>it</strong>h Mutans StreptococciJournal of Dental Research Vol.82, B81-0548, Goteborg Abstracts, 2003Two New Methods for Evaluation of Subsurface Enamel LesionsK. FUJITA, H. KAWAMATA, T. ISHIZAKI, R.E. HAYMAN, T. UCHIYAMA, M.KIMURA, H.KIBA, and T. IKEMI,Journal of Dental Research Vol.82, B78-0521, Goteborg Abstracts, 2003Microhardness Testing to Evaluate Remineralization of Tooth EnamelT. FUJIMARU, T. ISHIZAKI, R.E. HAYMAN, and K. NEMOTO,Journal of Dental Research Vol.82, B77-0519, Goteborg Abstracts, 2003Effect of hydroxyapat<strong>it</strong>e toothpaste on v<strong>it</strong>al tooth colorC.GUO, H.LIU, and l. KATAYAMAJuan of Dental Research Vol.81, A254-1964, San Diego Abstracts, 2002Adsorption Effect of Hydroxyapat<strong>it</strong>e to Oral StreptococciT.ARAKAWA, T.ISHIZAKI, R.E.HAYMAN, N . HANADA,and H. SENPUKUJournal of Dental Research Vol.81, A200-1478, San Diego Abstracts, 2002Remineralization Effects of Nanohydroxyapat<strong>it</strong>e-Containing Dentifrice: a pH-Cycling Study UsingSupernatantRemineralization by Nanohydroxyapat<strong>it</strong>e-Containing Dentifrice: a pH-Cycling Study Using SlurryPost-Bleach Stain Inhib<strong>it</strong>ion by Nano-Hydroxyapat<strong>it</strong>e: a Cyclical Staining TestRestoration of Post-Bleach Enamel Gloss Using a Non-Abrasive, Nano-Hydroxyapat<strong>it</strong>e Con<strong>di</strong>tionerRevolutionary Biomaterial for Improving Oral Health – Australian MadeTERRY SLOUGHAuxiliary, May/June 2000Sede legale: Via San Bartolomeo 9- 25128 BRESCIASede operativa: Via Pastore 1 - 25082 Botticino Sera (Brescia) ItaliaTel. 0302693532 – Fax. 0302193581S<strong>it</strong>o Internet: www.kalichem.<strong>it</strong> – e.mail: kalichem@kalichem.<strong>it</strong>
Bin<strong>di</strong>ng Characteristics of Streptococcus mutans for Calcium and Casein PhosphopeptideR.K. ROSE, Division of Restorative Dentistry, The Dental School, Bristol, UKCaries Research 34:5:2000, 427-431A clinical trial of the anticaries efficacy of casein derivatives complexed w<strong>it</strong>h calcium phosphate inpatients w<strong>it</strong>h salivary gland dysfunctionK. DAVID HAY, W. URRAY THOMSON, Green Lane Hosp<strong>it</strong>al and Univers<strong>it</strong>y of OntagoOral Surgery Oral Me<strong>di</strong>cine Oral Pathology, March 2002Xerostomia and youK DAVID HAY, KIM J GEARNew Zealand Journal 98: 46-51; 2002Saliva and Oral HealthEDGAR WM, O’MULLANE DMLondon: Br<strong>it</strong>ish Dental Association, second e<strong>di</strong>tion, London 1996Circa<strong>di</strong>an rhythms in flow rate and compos<strong>it</strong>ion of human stimulated subma<strong>di</strong>bular salivaFERGUSON DB, BOTCHWAY CAArchives of Oral Biology 24: 433-437, 1979The Xerostomia Inventory: a multi-<strong>it</strong>em approach to measuring dry mouthTHOMSON WM, CHALMERS JM, SPENCER AJ, WILLIAM SMCommun<strong>it</strong>y Dental Health 16: 12-17, 1998Further testing of the xerostomia inventoryTHOMSON WM, WILLIAM SMOral Surgery Oral Me<strong>di</strong>cine Oral Pathology Oral Ra<strong>di</strong>ology and EndodonticsPilocarpine and other cholinergic drugs in the management of salivary gland dysfunctionFERGUSON MMOral Surgery Oral Me<strong>di</strong>cine and Oral PathologyAnticariogenic complexes of amorphous calcium phosphate stabilized by casein phosphopeptides: AreviewREYNOLDS ECSede legale: Via San Bartolomeo 9- 25128 BRESCIASede operativa: Via Pastore 1 - 25082 Botticino Sera (Brescia) ItaliaTel. 0302693532 – Fax. 0302193581S<strong>it</strong>o Internet: www.kalichem.<strong>it</strong> – e.mail: kalichem@kalichem.<strong>it</strong>
Special Care in Dentistry 18: 8-16, 1998Qual<strong>it</strong>y of life and nutr<strong>it</strong>ional stu<strong>di</strong>es in patients w<strong>it</strong>h xerostomiaHAY KD, MORTON RP, WALL CRNew Zealand Journal 97: 128-137, 2001The association of xerostomia and inadequate intake in older adultsRHODUS NL, BROWN J.Journal of the American Dietetic Association 90: 1688-1692, 1990Qual<strong>it</strong>ative nutr<strong>it</strong>ional intake analysis of older adults w<strong>it</strong>h Sjogren’s SyndromeRHODUS NLGerodontology 7: 61-69, 1998The information on product specifications provided herein is only bin<strong>di</strong>ng to the extent confirmed by<strong>Kalichem</strong> in a wr<strong>it</strong>ten Sales Agreement. KALICHEM EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ANYRESPONSIBILITY FOR THE SUITABILITY OF THE PRODUCTS FOR ANYSPECIFIC OR PARTICULAR PURPOSES INTENDED BY THE USER. Suggestions for the useand application of the products and guide formulations are given for information purposes only andw<strong>it</strong>hout comm<strong>it</strong>ment. Such suggestions do not release <strong>Kalichem</strong>´customers from testing the productsas to their su<strong>it</strong>abil<strong>it</strong>y for the customer’s intended processes and purposes. <strong>Kalichem</strong> does not assumeany liabil<strong>it</strong>y or risk involved in the use of <strong>it</strong>s products as the con<strong>di</strong>tions of use are beyond <strong>it</strong>s control.The user of the products is solely responsible for compliance w<strong>it</strong>h all laws and regulations applyingto the use of the products, inclu<strong>di</strong>ng intellectual property rights of third parties.Sede legale: Via San Bartolomeo 9- 25128 BRESCIASede operativa: Via Pastore 1 - 25082 Botticino Sera (Brescia) ItaliaTel. 0302693532 – Fax. 0302193581S<strong>it</strong>o Internet: www.kalichem.<strong>it</strong> – e.mail: kalichem@kalichem.<strong>it</strong>