MANAGEMENT OF BARRETT'S ESOPHAGUS - CME Conferences
MANAGEMENT OF BARRETT'S ESOPHAGUS - CME Conferences
MANAGEMENT OF BARRETT'S ESOPHAGUS - CME Conferences
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012<strong>MANAGEMENT</strong> <strong>OF</strong> BARRETT’S<strong>ESOPHAGUS</strong>Screening, surveillance and treatmentDonald O. Castell M.D.Professor of MedicineDirector, Esophageal Disorders ProgramMedical University of South CarolinaDonald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
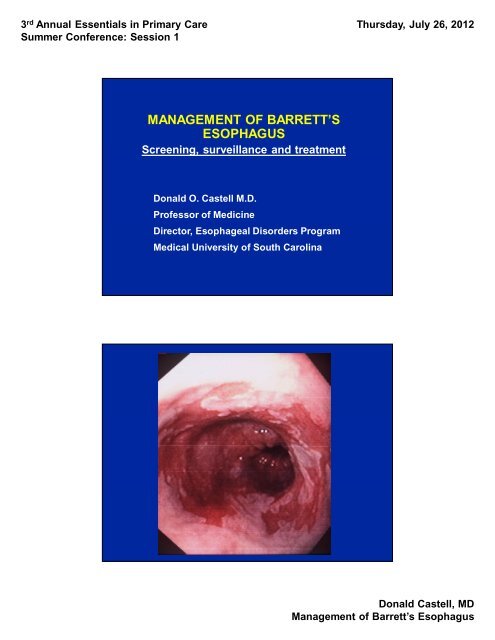
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012DIAGNOSIS <strong>OF</strong> BARRETT’S <strong>ESOPHAGUS</strong>• Suspected by endoscopy• Confirmed by biopsyBARRETT’S EPITHELIUMH&EArrows = goblet cellsMUCINDonald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012BARRETT’S <strong>ESOPHAGUS</strong>“Short segment”• Definition: Intestinal metaplasia present within 3cm or less of distal esophagus• 142 patients for elective endoscopy– Biopsies from distal 3 cm of esophagus,including squamocolumnar junction– 26 (18%) showed intestinal metaplasia(Spechler SJ, et al: Lancet 344:1533, 1994)HEARTBURN AND ESOPHAGEAL CANCERSymptomatic gastroesophageal reflux as a riskfactor for esophageal adenocarcinoma.(Lagergren J, et al: N Engl J Med 1999; 340:825)Donald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012INCIDENCE <strong>OF</strong> ESOPHAGEALCANCER IN U.S.WHITE MALESCase per 100,000 person-years5432101970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995AdenoSquamous(Devesa S, et at: Cancer 83:2049,1998)BARRETT’S <strong>ESOPHAGUS</strong> RISK FACTORS• Caucasian male• Older age: >40 yrs; >50 yrs ?• Duration of GERD: >5 yrs; >10 yrs ?• Visceral fat: waist size ?• Family history• H. pylori freeDonald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012GASTRIC ACID CONTROL IN BEIs symptom relief a reliable index?DECREASED ACID SENSITIVITY IN BARRETT’SPositive Bernstein (%)100508642Time to Sx (min)0RE BE RE BE(Johnson D, et al: J Clin Gastroenterol 9:23, 1987)Donald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012GERNABRECUMBENT REFLUX INASYMPTOMATIC BARRETT’S42 patients on lansoprazole (15-60 mg/d)403018/42 abnormal2010024/42 normal(Ouatu-Lascar, et al: Gastroenterology 117:327, 1999)Donald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012NOCTURNAL ACID BREAKTHROUGH INBARRETT’S <strong>ESOPHAGUS</strong>10080% of patients6040200NABNAB & GER(Katz PO, et al: Aliment Pharmacol Ther 12:1231, 1998)Donald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012GASTRIC ACID CONTROL IN BARRETT’SDoes acid control affect length of metaplasticepithelium?BARRETT’S <strong>ESOPHAGUS</strong>Maximal acid control (titrate with pH monitor)• 9 patients (8 male; age 44-72yrs)• Follow up 13-118 months (median 37)• Rx:PPI BID (2)PPI BID + ranitidine (7)• Linear regression: 9/9 (1-3 cm)• Squamous islands: 5/9(Srinivasan R, et al: Aliment Pharmacol Ther 15:519, 2001)Donald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012REGRESSION <strong>OF</strong> BARRETT’S WITHOMEPRAZOLE• 53 patients with BE randomized prospectively.27: ranitidine 150 mg bid26: omeprazole 40 mg bid• Symptoms controlled for 24 months• 24 hr pH at 3 months (mean and 95% CI)ranitidine: 9.4 (6.2 - 13.0)%omeprazole: 0.1 (0-1.2)%(Peters et al: Gut 45:489, 1999)RELATIVE CHANGES IN LENGTH ANDSURFACE AREA <strong>OF</strong> BARRETT’S <strong>ESOPHAGUS</strong>421-1OmeprazoleRanitidine% change (length)0-2-4% change (area)-3-5-6-7-83 9 15 24Time (months)-93 9 15 24Time (months)Peters, et al: Gut 1999;45:489-494Donald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012PRIOR ACID SUPPRESSION THERAPYRELATED TO SHORTER BARRETT’S• Retrospective analysis of 340 BE patients– Diagnosis made between 1981-2000• Mean length of BE at initial Dx: 4.4 cm (range: 0.5-16)– 201(59%) no prior Rx: 4.8 cm– 63(19%) H2RA only: 4.6 cm p=0.55– 35(10%) PPI only: 3.4 cm p=0.0013– 41(12%) both PPI & H2RA: 3.1 cm p=0.002• Conclusions:– Provides a rationale for aggressive therapy of GERD– Counters the concept that antisecretory therapyincreases risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma(El-Serag et al(Sampliner): Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004; 19: 1255)NORMALIZATION <strong>OF</strong> INTESTINALMETAPLASIA WITH ACID CONTROLN = 101; average FU = 4 yrsDysplasia or cancer: 13% LSBE; 3% SSBE; 0% EGJSIM(Horwhat et al: Am J Gastroenterol 2007; 102: 497)Donald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012MAXIMAL ACID CONTROL FORBARRETT’S <strong>ESOPHAGUS</strong>• Not achieved in prior studies• pH monitoring required (i.e. can not rely on Sx)• May produce endoscopic regression• Does it affect progression to dysplasia or cancer?PPI DELAYS DEVELOPMENT <strong>OF</strong>DYSPLASIA IN BARRETT’S• BE surveillence program from 1981-2001• PPI began in 1989• 350 patients with Barrett’s (intestinal metaplasia)– 1422 surveillance endoscopies– Median FU = 4.7 years• Delayed PPI use(>2 yrs) compared to PPI in 1 st year– 5.6X greater risk of LGD– 20.9X greater risk of HGD or adenocarcinoma• Conclusion: “PPI therapy appeared beneficial in theprevention of dysplasia & adenocarcinoma. Wesuggest that all patients with this condition, eventhose with no esophagitis or symptoms, should beencouraged to continue long term PPI therapy”.(Hillman AC et al: Med J Australia 180: 387, 2004)Donald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012HIGH GRADE DYSPLASIA IN BE• Diffuse HGD: 67 patients• Focal HGD: 33 patientsAssociated with > risk of AdenoCA Relative riskExtent of HGD 5.63Nodule on endoscopy 3.98Lack of acid suppression 2.48( Buttar et al, Gastroenterology 120:1639, 2001)PPIs REDUCE INCIDENCE <strong>OF</strong> DYSPLASIA IN BE• Retrospective review of 236 VA pts with BE over20 yrs.– 56 pts developed dysplasia (4.7%/yr)• Incidence of dysplasia lower (p
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012HOW A COMMON HEALTH PROBLEM IS QUIETLYBECOMING AN UNSUSPECTED KILLERTara Parker-PopeThe Wall Street JournalOctober 10, 2005“Chronic heartburn can turn deadly, leading to anaggressive esophageal cancer that few survive”“Use of acid-suppressing drugs may play a rolein the rise of esophageal cancer”“An alternate to drug treatment is surgery”ANTI-REFLUX SURGERY DOES NOT REMOVERISK <strong>OF</strong> ESOPHAGEAL CANCER IN GERDsurgery no surgeryMales with GERD: 6,406 35,274AdenoCa risk:* 14.1 (CI,8-23) 6.3 (CI,4.5-8.7)“The risk of developing adenocarcinoma of theesophagus remains increased after antirefluxsurgery”* Excluded 1 st year FU(Ye, Chow, Lagergren et al: Gastroenterology 121:1296, 2001)Donald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012FUNDOPLICATION DOES NOT DECREASE THERISK <strong>OF</strong> ESOPHAGEAL CANCER IN GERD• Review of VA data base from 1986-199097.5% men; mean age 55 yrsFollow-up > 10 yrs for all• GERD with fundo: 946 (8 cancer) (risk ratio=1.9)• GERD without fundo: 1,892 (8 cancer)• No GERD: 5,676 (0 cancer)• Conclusion: “GERD is a risk factor foresophageal cancer, but there is insufficientevidence that fundoplication reduces that risk”(Tran et al: Am J Gastro 2005; 100: 1002)MEDICAL VS SURGICALTREATMENT?“When you come to a fork in the road,TAKE IT”Yogi BerraDonald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012BARRETT’S SURVEILLANCE GUIDELINESACG 2008–The grade of dysplasia determines thesurveillance interval– No dysplasia in 2 consecutive samples: every 3 years– LGD: every year until no dysplasia– HGD: intensive surveillance (q 3 months) orintervention; particularly for mucosal irregularity ormulti-focal (>5 crypts)<strong>MANAGEMENT</strong> <strong>OF</strong> HGD IN BARRETT’S• Intensive surveillance• Surgery• Endoscopic–Ablation–Mucosectomy/dissectionDonald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012<strong>MANAGEMENT</strong> <strong>OF</strong> HGD IN BE• Intensive surveillance (flat mucosa)–Repeat biopsies q3months for 1 year(i.e. “the hunt”)–Then, yearly if no cancer–Intervene when adenocarcinoma arises»Incidence @ 16% at 10 years(Sontag et al: Loyola)<strong>MANAGEMENT</strong> <strong>OF</strong> HGD IN BE• Esophagectomy–Operative mortality varies by center»8.1% if high volume (>19/year)»23% if low volume (50%Birkmeye. N Engl J Med 2002;346:1128-37Donald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012GERD TREATMENTGod put the esophagus in theback of the chest to keep itaway from surgeons.<strong>MANAGEMENT</strong> <strong>OF</strong> HGD IN BEEndoscopic Ablation of Barrett’s epitheliumSuppress Acid reflux (medical or surgical)Healing with squamous epitheliumDonald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012ENDOSCOPIC ABLATION <strong>OF</strong> BE: PDTPDT + OM(n=138)OM alone(n=70)HGD eliminated(p < .0001)Progression tocancer(p = .027)77% 39%15% 29%(Overholt et al: GIE 2007; 66: 460ENDOSCOPIC ABLATION <strong>OF</strong> BE: PDT• Complications:–Stricture 39%»up to 50% in other reports–Sunburn 46%–Nausea 33%–Chest pain 32%–Fever 21%Donald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012RFA: COMPLETE DYSPLASIA RESPONSEOne year follow-up% of patients1009080706050403020100N=37N=22RFAShamN=17N=17HGDLGDAll patients on esomeprazole 40mg bid(Shaheen et al:DDW, 2008)ENDOSCOPIC ABLATION <strong>OF</strong> BE: RFA• Complication:–Stricture (rare)–Throat pain–Odynphagia–DysphagiaSelf limited(Ganz, et al: GIE, 2007; 65: AB147)Donald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus
3 rd Annual Essentials in Primary CareSummer Conference: Session 1Thursday, July 26, 2012THE BEST TREATMENT FOR BARRETT’SALTERNATIVES TO EVIDENCEBASED MEDICINEEminence-based medicineVehemence-based medicineEloquence-based medicineProvidence-based medicineConfidence-based medicineExperience; white hairEmphasis; volumeVerbal; sartorial“God only knows”Restricted to surgeons(Isaacs D, Fitzgerald D: The Oncologist 2001; 6: 390)Donald Castell, MDManagement of Barrett’s Esophagus