A fuzzy inference system with application to player selection and ...
A fuzzy inference system with application to player selection and ...
A fuzzy inference system with application to player selection and ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
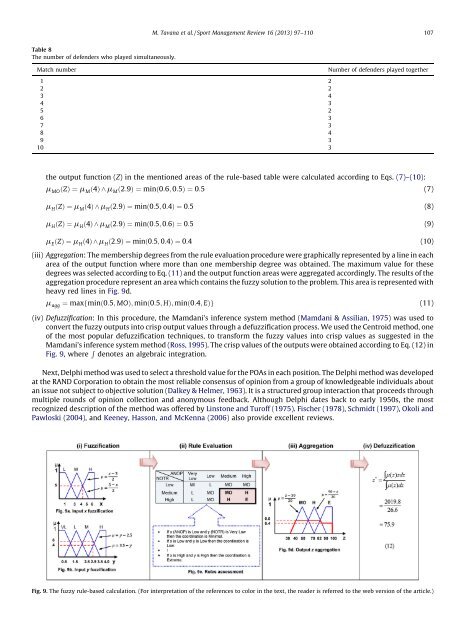
M. Tavana et al. / Sport Management Review 16 (2013) 97–110 107Table 8The number of defenders who played simultaneously.Match number Number of defenders played <strong>to</strong>gether1 22 23 44 35 26 37 38 49 310 3the output function (Z) in the mentioned areas of the rule-based table were calculated according <strong>to</strong> Eqs. (7)–(10):m MO ðZÞ ¼ m M ð4Þ ^ m M ð2:9Þ ¼ minð0:6; 0:5Þ ¼ 0:5 (7)m H ðZÞ ¼ m M ð4Þ ^ m H ð2:9Þ ¼ minð0:5; 0:4Þ ¼ 0:5 (8)m H ðZÞ ¼ m H ð4Þ ^ m M ð2:9Þ ¼ minð0:5; 0:6Þ ¼ 0:5 (9)m E ðZÞ ¼ m H ð4Þ ^ m H ð2:9Þ ¼ minð0:5; 0:4Þ ¼ 0:4 (10)(iii) Aggregation: The membership degrees from the rule evaluation procedure were graphically represented by a line in eacharea of the output function where more than one membership degree was obtained. The maximum value for thesedegrees was selected according <strong>to</strong> Eq. (11) <strong>and</strong> the output function areas were aggregated accordingly. The results of theaggregation procedure represent an area which contains the <strong>fuzzy</strong> solution <strong>to</strong> the problem. This area is represented <strong>with</strong>heavy red lines in Fig. 9d.m agg ¼ maxfminð0:5; MOÞ; minð0:5; HÞ; minð0:4; EÞg (11)(iv) Defuzzification: In this procedure, the Mamdani’s <strong>inference</strong> <strong>system</strong> method (Mamdani & Assilian, 1975) was used <strong>to</strong>convert the <strong>fuzzy</strong> outputs in<strong>to</strong> crisp output values through a defuzzification process. We used the Centroid method, oneof the most popular defuzzification techniques, <strong>to</strong> transform the <strong>fuzzy</strong> values in<strong>to</strong> crisp values as suggested in theMamdani’s <strong>inference</strong> <strong>system</strong> method (Ross, 1995). The crisp values of the outputs were obtained according <strong>to</strong> Eq. (12) inFig. 9, where R denotes an algebraic integration.Next, Delphi method was used <strong>to</strong> select a threshold value for the POAs in each position. The Delphi method was developedat the RAND Corporation <strong>to</strong> obtain the most reliable consensus of opinion from a group of knowledgeable individuals aboutan issue not subject <strong>to</strong> objective solution (Dalkey & Helmer, 1963). It is a structured group interaction that proceeds throughmultiple rounds of opinion collection <strong>and</strong> anonymous feedback. Although Delphi dates back <strong>to</strong> early 1950s, the mostrecognized description of the method was offered by Lins<strong>to</strong>ne <strong>and</strong> Turoff (1975). Fischer (1978), Schmidt (1997), Okoli <strong>and</strong>Pawloski (2004), <strong>and</strong> Keeney, Hasson, <strong>and</strong> McKenna (2006) also provide excellent reviews.Fig. 9. The <strong>fuzzy</strong> rule-based calculation. (For interpretation of the references <strong>to</strong> color in the text, the reader is referred <strong>to</strong> the web version of the article.)