Energy Efficiency Optimization (For Process and Power Plants)
Energy Efficiency Optimization (For Process and Power Plants)
Energy Efficiency Optimization (For Process and Power Plants)
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Energy</strong> <strong>Efficiency</strong> <strong>Optimization</strong>(<strong>For</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Power</strong> <strong>Plants</strong>)Dr.G.G.RajanCochin – IndiaPhone: 0091-484-2782158Cell: 098470 45158email: ggrajan@vsnl.comWeb: http://business.vsnl.com/ggrtech05/03/2008
05/03/2008About <strong>Energy</strong> <strong>Efficiency</strong><strong>Optimization</strong>• <strong>Energy</strong> efficiency optimization refers to theapplication of mathematical / statistical / operationsresearch techniques to minimize energyconsumption, energy cost <strong>and</strong> loss reductionwithout loss of production quantity / quality.• A basic mathematical background is desirable toknow the theoretical concepts.• It is possible to carry out energy efficiencyoptimization, by using simple tools – e.g.optimization <strong>and</strong> modeling software.
WHY ENERGY EFFICIENCYOPTIMIZATION ?<strong>Energy</strong> efficiency optimization is the best route tomeet the energy dem<strong>and</strong> at minimum cost withoutloss of production / output of the system.In conventional <strong>Energy</strong> dem<strong>and</strong> management, usersare guided by their own intuitive decisions, whichmay not be optimum.<strong>For</strong> meeting the energy dem<strong>and</strong> effectively atminimum cost <strong>and</strong> meeting all the imposedconstraints, EEO is the apt solution.05/03/2008
05/03/2008<strong>Energy</strong> efficiency optimization –Auditing approach.• To carry out <strong>Energy</strong> <strong>Efficiency</strong> <strong>Optimization</strong>users must know, which are the subsystems /equipments responsible for overall energyefficiency <strong>and</strong> what parameters need to bemonitored <strong>and</strong> controlled to achieve theobjective.• In real life situations this may include <strong>Energy</strong>Consumption / Utilization of all forms of energysuch as Fuel , Steam , Electricity , Thermal<strong>Energy</strong> etc related to the process under study
ENERGY AUDITING05/03/2008•<strong>Energy</strong> auditing of the system /subsystem helps to bring down thetotal energy consumption by losscontrol <strong>and</strong> efficiency improvement ofthe right items.•<strong>For</strong> achieving this, a systematic<strong>Energy</strong> Auditing of the total system isessential.
05/03/2008Prioritization of <strong>Energy</strong> costcentres• Prioritization of <strong>Energy</strong> cost centres is done using Pareto’stheory.• In this process , the total system is divided into a number ofsubsystems <strong>and</strong> elements <strong>and</strong> energy input / output datacollected for analysis.(design <strong>and</strong> observed energyquantities.)• <strong>Energy</strong> consumption data analysis reveals intensive energyconsumers requiring tight control <strong>and</strong> sets monitoringpriorities.• At unit level, this may cover energy consumingdevices.(e.g.boilers/heaters/turbines etc)• At macro level, analysis of total industrial sector is required.
Pareto’s Theory related to<strong>Energy</strong> <strong>Efficiency</strong> .05/03/2008• About 7 to 10% of the total equipmentconsume 70 to 75% of Total <strong>Energy</strong> Input tothe system.( Class A)• About 30% of the equipment consume 10%of Total <strong>Energy</strong> Input (class B)• The balance 60 to 70 % of equipmentconsume 6 to 7% of Total <strong>Energy</strong> Input(class C)• Same concept may be applicable for Macosystem as well.
% <strong>Energy</strong>70605040302010005/03/2008Typical Pareto’s ModelA (10%) B (20%) C(70%)% Equipments
<strong>Energy</strong> System Analysis05/03/2008• <strong>Energy</strong> System Analysis is the first activityto identify class A, Class B <strong>and</strong> class C subsystems/ equipment of the total system forPerformance Monitoring <strong>and</strong> <strong>Optimization</strong>• This concept may be applied to very largemacro systems such as national thermalpower plants, refineries, petrochemical unitsetc.• Using the data collected during the auditingprocess, it is possible to develop PerformanceModels for the sub systems ( individualplants in case of macro systems) forcorrective action.
Advantages of <strong>Energy</strong>Auditing• offers fast track solutions to <strong>Energy</strong><strong>Efficiency</strong> Management.• Monitors performance effectively• Identifies specific problem area in a veryshort time.• Offers tangible solutions.• Reduces operating cost <strong>and</strong>• Increases profit margin drastically.05/03/2008
05/03/2008Organizing Technical Audit• Technical Audit for <strong>Process</strong> & <strong>Power</strong> plants ,covers the following conventional energy centers.– Utility system (water/steam/air)– Boilers– Pumps– Compressors– Turbines ( Gas turbines & Steam turbines )– Turbo Generators– Heat Exchangers / Condensers– Miscellaneous applications– Systems analysis <strong>and</strong> MIS
Types of <strong>Energy</strong> Audit05/03/2008• Walk through energy audit• Total system analysis ( intensive )• Heater / Boiler Audit• Steam system Audit• Electrical system Audit• Loss control ( auditing process /h<strong>and</strong>ling losses )• Auditing rotating equipments• Heat exchanger system audit
05/03/2008<strong>Energy</strong> Audit findingsOffer : <strong>Energy</strong> resource break-up ( steam /power / fuel )List of class A , class B <strong>and</strong> Class CequipmentsCurrent energy efficiency of equipmentsList of equipments with lower energyefficiency<strong>Energy</strong> resource utilization <strong>and</strong> loss areas
Developing <strong>Energy</strong> <strong>Efficiency</strong> Models• <strong>Energy</strong> efficiency models may be designed toevaluate the energy efficiency of all energyintensive equipment for continuous performanceevaluation <strong>and</strong> monitoring .• This must cover all type of <strong>Energy</strong> input resourceslike Fuel , Steam , <strong>Power</strong> <strong>and</strong> Thermal <strong>Energy</strong>.• <strong>Energy</strong> efficiency Models are the key toPerformance Evaluation of the equipment ,system <strong>and</strong> sub systems for taking correctiveactions in the right direction.05/03/2008
ExampleSteam<strong>Power</strong>FuelUnit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV05/03/2008
<strong>Energy</strong> wise System Analysis Using the <strong>Energy</strong> Data, Techno Thermanalyses the entire system <strong>Energy</strong> wise <strong>and</strong>offers information such as• unit wise Steam consumption.• unit wise power consumption• unit wise fuel consumption• total energy input analysis.• <strong>Energy</strong> cost , losses etc05/03/2008
<strong>Energy</strong> type – Break-up8 %32 %60%05/03/2008 Fuel Steam <strong>Power</strong>
Unit wise <strong>Energy</strong> Consumption454035302520151050I II III IVunits%05/03/2008
Total Analysis6050403020100I II III IV05/03/2008Steam Fuel <strong>Power</strong>
Advantages of <strong>Energy</strong> <strong>Efficiency</strong>optimization05/03/2008Continuous use of <strong>Energy</strong> <strong>Efficiency</strong><strong>Optimization</strong> helps to• Identify the type of parameters to bemonitored for corrective action .• Identify the sub system performance• Identify the equipment / element responsiblefor poor performance.• identify the process parameter or othersresponsible for poor performance
An effective tool for <strong>Energy</strong> ManagementDecisions.This approach is very useful tool for taking fast<strong>Energy</strong> Management Decisions such as• Is the system performance okay ? What is theproblem ?• Which parameters are responsible ?• What is the best alternative to improveperformance05/03/2008Could also be used to identify efficiencydeterioration using various models.
Users of <strong>Energy</strong> Audit• Operating staff – process <strong>and</strong> power plants• <strong>Process</strong> Engineers / Managers• Chief Executives / Directors• <strong>Energy</strong> Management Consultants• R & D organizations• <strong>Energy</strong> Equipment manufacturers.• Thermal <strong>Power</strong> stations / power industry.05/03/2008
Cost - Benefit Analysis• Use of <strong>Energy</strong> <strong>Efficiency</strong> <strong>Optimization</strong> oncontinuous basis pays off in a few days toweeks.• Identifies equipment deterioration.• Longer run lengths / higher production /power generation of units could be achieved.• <strong>Energy</strong> costs could be minimized• Net profit could be increased.05/03/2008
Useful for MIS users• In tailored form, this could be usedto generate MIS for top executiveswho can use the information forequipment maintenance /replacement decisions at the righttime.• Substantial savings could beachieved by this.05/03/2008
POWER PLANT APPLICATIONS• This concept may be used very effectively in<strong>Power</strong> plants for evaluating <strong>and</strong> monitoring theefficiency of• <strong>Power</strong> boilers• Steam turbines• Gas Turbines• <strong>Power</strong> losses• Performance evaluation etc.05/03/2008
TYPICAL EXAMPLE• In the case of Thermal <strong>Power</strong> plants, theoverall efficiency of power generation isdetermined by• Boiler efficiency• Turbine efficiency <strong>and</strong>• Generator efficiency• Built-in modules have the capability toevaluate each parameter separately forcorrective action.05/03/2008
MIS FOR <strong>Power</strong> Plant PerformanceMonitoring <strong>and</strong> Control05/03/2008• This is a very powerful tool for Corporate / Unit level <strong>Energy</strong>Management for taking corporate <strong>and</strong> operational decisions atthe right time <strong>and</strong> cost.A typical MIS gives• <strong>Energy</strong> efficiency of individual plant vs target• Break-up of energy losses• Cost of power generation <strong>and</strong> control centres• Transmission losses unitwise vs norms• Specific power consumption etcfor corrective action at the Right time <strong>and</strong> Right Cost.
Capacity Utilization vs<strong>Efficiency</strong>Capacity utilization plays an important role onsystem efficiency.In normal case, higher the capacity utilization,higher is the efficiency. This is known as systemcharacteristics.Operational capacity must be optimized to achievehighest possible efficiency of the total system toreduce operating cost.<strong>Energy</strong> efficiency models are used to quantify thisinformation <strong>and</strong> arrive at optimal solutions.05/03/2008
Flexi target setting05/03/2008* <strong>Energy</strong> Management of a large system calls foridentifying the parameters responsible for affecting theoverall performance of the system.* This requires thorough analysis <strong>and</strong> development ofperformance models which set flexi-targets for theenergy performance under various operatingparameters.* This is achieved by customization.* This also explains the reasons for performancedeviation scientifically.
On<strong>Energy</strong> <strong>Efficiency</strong> <strong>Optimization</strong>05/03/2008
Questions on using <strong>Energy</strong><strong>Efficiency</strong> ModelsHow effectively can these models be used in theabsence of proper flow measurements for fuel <strong>and</strong>it’s properties ?05/03/2008Indirect method is used for determining theefficiency of heaters / boilers etc which does notrequire flow data . Parameters used in the programare flue gas analysis , stack temperature , ambienttemperature, Relative humidity <strong>and</strong> setting losses.This tallies very much with direct method ofefficiency determination.
Example - Equipment Maintenance /Replacement Decisions.• These models may be usedfor taking EquipmentMaintenance /Replacement Decisions tominimise the Total Cost ofOperation whichdetermines the profitability<strong>and</strong> productivity of theindustry.05/03/2008140120100806040200I II III IV Voprtg fixd total
Failure Prediction of Equipment /components These models in combinationwith Maintenance <strong>and</strong>Corrosion software may be usedeffectively to predict equipment/ component failure due tocorrosion, scaling, pitting,vibration etc using powerfulmodels.05/03/2008
Economics of InsulationRs'0000001816141210864201 2 3 4yearheat loss opr.cost savings• This approach evaluatesHeat loss from varioussections of theequipment, whichcould be used toidentify the source ofloss for takinginsulation retrofitdecisions.05/03/2008
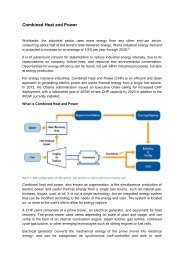
INNOVATIVE IDEAS05/03/2008CogenerationCombined heat power cycle optimizationTrigenerationOrganic rankine cycleWaste heat recoveryUsing <strong>Energy</strong> efficient equipments etc
Thank YouAny Questions ?05/03/2008