Scheme and Syllabus of B. Tech. Aeronautical Engineering - Ptu.ac.in
Scheme and Syllabus of B. Tech. Aeronautical Engineering - Ptu.ac.in
Scheme and Syllabus of B. Tech. Aeronautical Engineering - Ptu.ac.in
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Punjab <strong>Tech</strong>nical University PTU/DA/6 th August 2011B.<strong>Tech</strong> <strong>Aeronautical</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong><strong>Scheme</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Syllabus</strong><strong>of</strong>B. <strong>Tech</strong>. <strong>Aeronautical</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>(3 rd to 8 th Semester)Batch 2010ByDepartment <strong>of</strong> AcademicsPunjab <strong>Tech</strong>nical University1
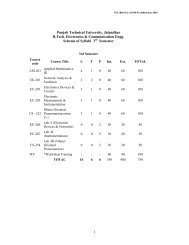
Punjab <strong>Tech</strong>nical University PTU/DA/6 th August 2011B.<strong>Tech</strong> <strong>Aeronautical</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>Third SemesterCont<strong>ac</strong>t Hours: 32 Hrs.Load Allocation MarksCourse Course NameDistribution TotalCodeL T P Int. Ext. MarksME 206 Fluid Mechanics 3 1 0 40 60 100AM 201 Mathematics - III 3 1 0 40 60 100AE 201 Introduction To Aeronautics 3 1 0 40 60 100AE 203 Aerodynamics - I 4 1 0 40 60 100ME 201 Strength Of Materials - I 3 1 0 40 60 100ME 207 M<strong>ac</strong>h<strong>in</strong>e Draw<strong>in</strong>g 1 0 6 40 60 100AE 205Workshop Tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g Of 4 WeeksDuration After 2nd semester 60 40100ME 211 Strength <strong>of</strong> Materials Lab 0 0 2 30 20 50ME 214 Fluid Mechanics Lab 0 0 2 30 20 50Total 17 5 10 360 440 8002
Punjab <strong>Tech</strong>nical University PTU/DA/6 th August 2011B.<strong>Tech</strong> <strong>Aeronautical</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>ME 206 Fluid Mechanics-IPART-A1. Fluid <strong>and</strong> their properties: Concept <strong>of</strong> fluid, difference between solids, liquids <strong>and</strong> gases; ideal <strong>and</strong>real fluids; capillarity, vapour pressure, compressibility <strong>and</strong> bulk modulus; Newtonian <strong>and</strong> non-Newtonian fluids.2. Fluid Statics: Concept <strong>of</strong> pressure, Pascal’s law <strong>and</strong> its eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g applications, Hydrostatic paradox.Action <strong>of</strong> fluid pressure on a plane (horizontal, vertical <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>cl<strong>in</strong>ed) submergedsurf<strong>ac</strong>e, resultant force <strong>and</strong> center <strong>of</strong> pressure, force on a curved surf<strong>ac</strong>e due to hydrostatic pressure.Buoyancy <strong>and</strong> flotation, stability <strong>of</strong> float<strong>in</strong>g <strong>and</strong> submerged bodies, met<strong>ac</strong>entre height <strong>and</strong> itsdeterm<strong>in</strong>ation, periodic time <strong>of</strong> oscillation, pressure distribution <strong>in</strong> a liquid subjected to constanthorizontal/ vertical <strong>ac</strong>celeration, rotation <strong>of</strong> liquid <strong>in</strong> a cyl<strong>in</strong>drical conta<strong>in</strong>er.3. Fluid K<strong>in</strong>ematics : Classification <strong>of</strong> fluid flows, velocity <strong>and</strong> <strong>ac</strong>celeration <strong>of</strong> fluid particle, local <strong>and</strong>convective <strong>ac</strong>celeration, normal <strong>and</strong> tangential <strong>ac</strong>celeration, streaml<strong>in</strong>e, path l<strong>in</strong>e <strong>and</strong> streak l<strong>in</strong>e, flowrate <strong>and</strong> discharge mean velocity, cont<strong>in</strong>uity equation <strong>in</strong> Cartesian <strong>and</strong> cyl<strong>in</strong>drical, polar coord<strong>in</strong>ates.Rotational flows, rotation velocity <strong>and</strong> circulation, stream <strong>and</strong> velocity potentialfunctions, flow net.PART-B4. Fluid Dynamics : Euler’s equation, Bernoulli’s equation <strong>and</strong> steady flow energy equation;representation <strong>of</strong> energy changes <strong>in</strong> fluid system, impulse momentum equation, k<strong>in</strong>etic energy <strong>and</strong>momentum correction f<strong>ac</strong>tors, flow along a curved streaml<strong>in</strong>e, free <strong>and</strong> forced vortex motions.5. Dimensional Analysis <strong>and</strong> Similitude: Fundamental <strong>and</strong> derived units <strong>and</strong> dimensions, dimensionalhomogeneity. Rayleigh’s <strong>and</strong> Buck<strong>in</strong>gham’s Pi method for dimensional analysis. Dimensionlessnumbers <strong>and</strong> their significance, geometric, k<strong>in</strong>ematic <strong>and</strong> dynamic similarity, model studies. Lam<strong>in</strong>ar<strong>and</strong> Turbulent Flows: Flow regimes <strong>and</strong> Reylods number, critical velocity <strong>and</strong> critical Reynoldsnumber, lam<strong>in</strong>ar flow <strong>in</strong> circular cross- section pipes. Turbulent flows <strong>and</strong> flow losses <strong>in</strong> pipes, Darcyequation, m<strong>in</strong>or head losses <strong>in</strong> pipes <strong>and</strong> pipe fitt<strong>in</strong>gs, hydraulic <strong>and</strong> energy gradient l<strong>in</strong>es.6. Flow Measurement: Manometers, pitot tubes, venturi meter <strong>and</strong> orifice meters, orifice, mouthpieces,notches <strong>and</strong> weirs, rotameter.Suggested Read<strong>in</strong>gs / Books:1. Fluid Mechanics <strong>and</strong> Fluid Power <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> by D.S. Kumar : S.K. Kataria <strong>and</strong> SonsPublishers.2. Mechanics <strong>of</strong> Fluids by Massey BS; Van Nostr<strong>and</strong> Re<strong>in</strong>hold Co.3. Fluid Mechanics by Douglas JF, Gasiorek JM, Swaffield JP; Poitman3
Punjab <strong>Tech</strong>nical University PTU/DA/6 th August 2011B.<strong>Tech</strong> <strong>Aeronautical</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>4. Fluid Mechanics by Streetes VL <strong>and</strong> Wylie EB; Mcgraw Hill Book Co._________________________________________________________________________________AM-201 MATHEMATICS-IIIPART-A1. Fourier Series Periodic functions, Euler's formula. Even <strong>and</strong> odd functions, half range expansions,Fourier series <strong>of</strong> different wave forms.2. Lapl<strong>ac</strong>e Transforms Lapl<strong>ac</strong>e transforms <strong>of</strong> various st<strong>and</strong>ard functions, properties <strong>of</strong> Lapl<strong>ac</strong>etransforms, <strong>in</strong>verse Lapl<strong>ac</strong>e transforms, transform <strong>of</strong> derivatives <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>tegrals, Lapl<strong>ac</strong>e transform <strong>of</strong> unitstep function, impulse function, periodic functions, applications to solution <strong>of</strong> ord<strong>in</strong>ary l<strong>in</strong>ear differentialequations with constant coefficients, <strong>and</strong> simultaneous differential equations.3. Special Functions Power series solution <strong>of</strong> differential equations, Frobenius method, Legendre'equation, Legendre polynomial, Bessel's equation, Bessel functions <strong>of</strong> the first <strong>and</strong> second k<strong>in</strong>d.Recurrence relations, equations reducible to Bessel's equation, Error function <strong>and</strong> its properties.PART-B4. Partial Differential Equations Formation <strong>of</strong> partial differential equations, L<strong>in</strong>ear partial differentialequations, homogeneous partial differential equations with constant coefficient Applications: Waveequation <strong>and</strong> Heat conduction equation <strong>in</strong> one dimension. Two dimensional Lapl<strong>ac</strong>e equation, solutionby the method <strong>of</strong> separation <strong>of</strong> variables. Lapl<strong>ac</strong>ian <strong>in</strong> polar coord<strong>in</strong>ates.5. Functions <strong>of</strong> Complex Variable Limits, cont<strong>in</strong>uity, derivative <strong>of</strong> complex functions, analyticfunction, Cauchy-Riemann equation, conjugate functions, harmonic functions; Conformal Mapp<strong>in</strong>g:Mapp<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> a complex function, conformal mapp<strong>in</strong>g, st<strong>and</strong>ard transforms, mapp<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> st<strong>and</strong>ardelementary transformations, complex potential, applications to fluid flow problems; ComplexIntegration : L<strong>in</strong>e <strong>in</strong>tegrals <strong>in</strong> the complex plane, Cauchy's theorem, Cauchy's <strong>in</strong>tegral formula <strong>and</strong>derivatives <strong>of</strong> analytic function. Taylor's <strong>and</strong> Laurent's expansions, s<strong>in</strong>gular po<strong>in</strong>ts, poles, residue,complex <strong>in</strong>tegration us<strong>in</strong>g the method <strong>of</strong> residues, evaluation <strong>of</strong> real <strong>in</strong>tegrals by contour <strong>in</strong>tegration.Suggested Read<strong>in</strong>gs / Books1. Advanced <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Mathematics by Kreysz<strong>in</strong>g Erw<strong>in</strong> ; Wiley Eastern, New Delhi2. Higher <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong> Mathematics by BS Grewal : Khanna Publishers, New Delhi.3. Numerical Solutions <strong>of</strong> Differential Equations by NK Ja<strong>in</strong> ; Prentice Hall, Delhi.4. Differential Equations by Sharma <strong>and</strong> Gupta ; Krishna Prakashan Media (P) Ltd., Meerut.4
Punjab <strong>Tech</strong>nical University PTU/DA/6 th August 2011B.<strong>Tech</strong> <strong>Aeronautical</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>AE 201 Introduction to AeronauticsPART-A1. IntroductionHistory <strong>of</strong> aviation, History <strong>of</strong> sp<strong>ac</strong>e flight, History <strong>of</strong> Indian sp<strong>ac</strong>e experience, Pre Wright Brothers era,Wright Flyer, Conventional airplane, progress <strong>in</strong> airplane design <strong>and</strong> applications, Current status. Otherk<strong>in</strong>ds <strong>of</strong> heavier than air vehicles, helicopter, VSTOL m<strong>ac</strong>h<strong>in</strong>es.Symbology <strong>of</strong> aerosp<strong>ac</strong>e : US Deptt <strong>of</strong> defence Aerosp<strong>ac</strong>e Vehicle Designation,Vehicle Type Symbol : G-H-Q-S-V-Z; Basic Mission Symbols : A-B-C-E-F-AL-O-P-Q-S-T-U-X;Modified Mission Symbols : A-C,D,E,F,H,K,L,M,O,P,Q,R,S,T,U,V,W; Rocket Symbols : B,M,N,R,S;Manuf<strong>ac</strong>turers <strong>of</strong> Aerosp<strong>ac</strong>e Vehicle <strong>in</strong> India-Aircraft, Sp<strong>ac</strong>e Vehicles, Ma<strong>in</strong> Aircraft operators <strong>in</strong> India;Aircraft Certification : Type certification, Airworth<strong>in</strong>ess, CAA, FAA, DGCA, ICAO, Aircraft registration& mark<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> aircraft registered <strong>in</strong> India VT-AAA-ZZZ,VT HAA-HZZ, Introduction to Aircraft Communication System : Air B<strong>and</strong> Frequencies, Navigation-GPS, Instruments, Aircraft Flight Control System, Manual, Assisted, Stability Augmentation System,Autopilot, Fly by wire.Classification with examples : By flights regime; sub-Sonic, Supersonic, Hypersonic FlightsBy w<strong>in</strong>g pl<strong>ac</strong>ement; High W<strong>in</strong>g, Low W<strong>in</strong>g, Mid W<strong>in</strong>g, Cruciform (X) W<strong>in</strong>g;By Type : Aerostatic, Aerodynamic, FW, RW, Variable sweep, Mixed fixed-Rotary, surf<strong>ac</strong>e effectvehiclesBy Planforms : Rectangular, Elliptical, Delta, Double Delta, Ogive,By stall speed & w<strong>in</strong>g span : (I-VI) comb<strong>in</strong>ation (A-III).System <strong>of</strong> Axes – Motion longitud<strong>in</strong>al (Roll axis), lateral (Pitch axis), vertical (Yaw axis) (x,y,z), velocity(u, v, w) <strong>and</strong> <strong>ac</strong>celeration. Angles <strong>of</strong> rotation – Roll, Pitch, Yaw, Airfoil Nomenclature, Symmetric &Cambered Airfoil, Angle <strong>of</strong> Att<strong>ac</strong>k.Types <strong>of</strong> Missions ; Fly by, orbiter, atmospheric, l<strong>and</strong>er, penetrator, observatory, Communicator,Aerosp<strong>ac</strong>e mission <strong>of</strong> future.Cockpit def<strong>in</strong>ition parts, seats, flight deck central column rudder pedal <strong>in</strong>strument panel, pedestal panel,side console, overhead panel, glass cockpit, joystick.2. Sp<strong>ac</strong>e VehiclesMissile <strong>and</strong> its types, sp<strong>ac</strong>e vehicles <strong>and</strong> its types, reusable sp<strong>ac</strong>e vehicles, sp<strong>ac</strong>e shuttle ,satellites, types<strong>of</strong> satellites <strong>and</strong> their functions5
3. Airplane PropulsionPunjab <strong>Tech</strong>nical University PTU/DA/6 th August 2011B.<strong>Tech</strong> <strong>Aeronautical</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>PART-BRequirement <strong>of</strong> power to fly, balance <strong>of</strong> forces, various means <strong>of</strong> produc<strong>in</strong>g power for forward flight.,piston eng<strong>in</strong>es ,jet propulsion-thrust equation, turbojet, turb<strong>of</strong>an, ramjet eng<strong>in</strong>es. Locations <strong>of</strong> sucheng<strong>in</strong>es, Propellor <strong>and</strong> its use. Rocket eng<strong>in</strong>es.4. Airplane Structures & MaterialsStructural arrangement <strong>of</strong> the Wright Flyer,. Structural details <strong>of</strong> l<strong>and</strong><strong>in</strong>g gear, w<strong>in</strong>g, fuselage <strong>and</strong> tailplanes, functions <strong>of</strong> ribs, sk<strong>in</strong>, spars, str<strong>in</strong>gers, longerons. Monocoque <strong>and</strong> semi-monocoquestructures,materials for ma<strong>in</strong> components5. Control Systems & LEVEL FLIGHTVarious types <strong>of</strong> flaps, function <strong>of</strong> rudder, elevator, ailerons, flaprons, elevons, types <strong>of</strong> tailplanes,condition for straight & level flight, flight path angleSuggested Read<strong>in</strong>gs/ Books:1 Fundamentals <strong>of</strong> Flight Richard S. Shevel , Prentice Hall2 Introduction to flight- John D. Anderson3 Mechanics <strong>of</strong> flight by A.C. Kermode4 Aircraft Basic Science :Ralph D. Bent & James L. M<strong>ac</strong>k<strong>in</strong>ley5 Jet Aircraft Power Sysytem : J<strong>ac</strong>k V.Casamassa & Ralph D.Bent_________________________________________________________________________________________AE 202 AERODYNAMICS- IPART-A1. IntroductionFluid statics, pascal’s law,Cont<strong>in</strong>uum <strong>and</strong> free molecular flows, <strong>in</strong>visid <strong>and</strong> viscous flows,<strong>in</strong>compressible <strong>and</strong> compressible flows. Newtonian <strong>and</strong> Non-Newtonian flows. Pitot static tube,measurement <strong>of</strong> air-speed, pressure coefficient. Aerodynamic force <strong>and</strong> moments. Dimensionalanalysis, non-dimensional parameters, M, Re, Fr etc., flow similarity.2. Description <strong>of</strong> Fluid MotionLagrangian <strong>and</strong> Eulerian methods, Description <strong>of</strong> properties <strong>in</strong> a mov<strong>in</strong>g fluid, local <strong>and</strong> material rate<strong>of</strong> change. Streaml<strong>in</strong>es, Pathl<strong>in</strong>es, Streakl<strong>in</strong>es, Reynolds Transport theorem, Vorticity <strong>and</strong>circulation. Laws <strong>of</strong> vortex motion. Translation, rotation <strong>and</strong> rate <strong>of</strong> deformation <strong>of</strong> fluid particles.6
3. Equations <strong>of</strong> Fluid MotionPunjab <strong>Tech</strong>nical University PTU/DA/6 th August 2011B.<strong>Tech</strong> <strong>Aeronautical</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>Equation <strong>of</strong> conservation <strong>of</strong> mass for control volume, special form <strong>of</strong> equation <strong>of</strong> conservation <strong>of</strong>mass, differential form <strong>of</strong> equation <strong>of</strong> conservation <strong>of</strong> mass Euler's <strong>and</strong> Navier-Stoke equations.Derivation <strong>of</strong> Bernaulli's equation for <strong>in</strong>visid <strong>and</strong> viscous flow fields. Momentum equation <strong>and</strong>angular momentum equation <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>tegral form.4. Invisid-Incompressible FlowPART-BCondition on velocity for <strong>in</strong>compressible flow. Lapl<strong>ac</strong>e's equations. Potential function, streamfunction. Basic elementary flows: Uniform flows, source flow, Doublet flow <strong>and</strong> Vortex flow.Superimposition <strong>of</strong> elementary flows. Non lift<strong>in</strong>g <strong>and</strong> lift<strong>in</strong>g flow over a circular cyl<strong>in</strong>der,comparison with real flow over circular cyl<strong>in</strong>der. Kutta-Jaukowski theorem, generation <strong>of</strong> lift.5. Introduction To Viscous FlowQualitative aspects <strong>of</strong> viscous flows, viscosity <strong>and</strong> thermal conductivity. Phenomenon <strong>of</strong> separation.Navier-Stokes equation; Viscous flow energy equation. Some ex<strong>ac</strong>t solutions <strong>of</strong> Navier-Stokesequations: plane Poiseuille flow , Couette flow, Hagen-Poiseuille flow <strong>and</strong> Hele-Shaw flow6. Introduction To Incompressible Boundary LayerBL concept, BL properties, derivation <strong>of</strong> Pr<strong>and</strong>tl's BL equations, Blasius solution, Karman's Integralequation. Turbulent BL over a plate, sk<strong>in</strong> friction drag, BL control.Suggested Read<strong>in</strong>gs / Books:1. Fundamentals <strong>of</strong> Aerodynamics: John D.Anderson(Jr.) 2 nd Ed.McGraw Hill2. Fluid Mechanics <strong>and</strong> its Applications: Gupta <strong>and</strong> Gupta Wiley Eastern ,19603. Boundary Layer Theory: H.Schlicht<strong>in</strong>g 6 th Ed. McGraw Hill ,19864. Fluid Mechanics: Frank M.White 2 nd Ed. McGraw Hill,19865. Foundations <strong>of</strong> Fluid Mechanics: S.W.Yuan Prentice Hall______________________________________________________________________________________ME-201 Strength <strong>of</strong> Materials – IPART-A1. Simple stresses <strong>and</strong> stra<strong>in</strong>s : Concept <strong>of</strong> stress <strong>and</strong> stra<strong>in</strong>; St. Vernants pr<strong>in</strong>ciple, stress <strong>and</strong> stra<strong>in</strong>diagram, Hooke’s law, Young’s modulus, Poisson ratio, stress at a po<strong>in</strong>t, stress <strong>and</strong> stra<strong>in</strong>s <strong>in</strong> barssubjected to axial load<strong>in</strong>g. Modulus <strong>of</strong> elasticity, stress produced <strong>in</strong> compound bars subject to axialload<strong>in</strong>g. Temperature stress <strong>and</strong> stra<strong>in</strong> calculations due to applications <strong>of</strong> axial loads <strong>and</strong> variation<strong>of</strong> temperature <strong>in</strong> s<strong>in</strong>gle <strong>and</strong> compound bars. Compound stress <strong>and</strong> stra<strong>in</strong>s, the two dimensional7
Punjab <strong>Tech</strong>nical University PTU/DA/6 th August 2011B.<strong>Tech</strong> <strong>Aeronautical</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>system; stress at a po<strong>in</strong>t on a plane, pr<strong>in</strong>cipal stresses <strong>and</strong> pr<strong>in</strong>cipal planes; Mohr’s circle <strong>of</strong> stress;ellipse <strong>of</strong> stress <strong>and</strong> their applications. Generalized Hook's Law, pr<strong>in</strong>cipal stresses related topr<strong>in</strong>cipal stra<strong>in</strong>s2. Bend<strong>in</strong>g moment <strong>and</strong> shear force diagrams: S.F <strong>and</strong> B.M def<strong>in</strong>itions. BM <strong>and</strong> SF diagrams forcantilevers, simply supported beams with or without overhangs <strong>and</strong> calculation <strong>of</strong> maximum BM<strong>and</strong> SF <strong>and</strong> the po<strong>in</strong>t <strong>of</strong> contraflexure under the follow<strong>in</strong>g loads:a) Concentrated loadsb) Uniformity distributed loads over the whole span or part <strong>of</strong> spanc) Comb<strong>in</strong>ation <strong>of</strong> concentrated loads (two or three) <strong>and</strong> uniformly distributed loadsd) Uniformity vary<strong>in</strong>g loadse) Application <strong>of</strong> momentsRelation between rate <strong>of</strong> load<strong>in</strong>g, shear force <strong>and</strong> bend<strong>in</strong>g moment3. Theory <strong>of</strong> bend<strong>in</strong>g stresses <strong>in</strong> beams due to bend<strong>in</strong>g: assumptions <strong>in</strong> the simple bend<strong>in</strong>g theory,derivation <strong>of</strong> formula: its application to beams <strong>of</strong> rectangular, circular <strong>and</strong> channel, I & T-sections,: Comb<strong>in</strong>ed direct <strong>and</strong> bend<strong>in</strong>g stresses <strong>in</strong> aforementioned sections, composite / flitchedbeams.4. Torsion: Derivation <strong>of</strong> torsion equation <strong>and</strong> its assumptions. Applications <strong>of</strong> the equation to thehollow <strong>and</strong> solid circular shafts, torsional rigidity, comb<strong>in</strong>ed torsion <strong>and</strong> bend<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> circular shaftspr<strong>in</strong>cipal stress <strong>and</strong> maximum shear stresses under comb<strong>in</strong>ed load<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> bend<strong>in</strong>g <strong>and</strong> torsion,analysis <strong>of</strong> close-coiled-helical spr<strong>in</strong>gs.PART-B5. Th<strong>in</strong> cyl<strong>in</strong>ders <strong>and</strong> spheres : Derivation <strong>of</strong> formulae <strong>and</strong> calculation <strong>of</strong> hoop stress, longitud<strong>in</strong>alstress <strong>in</strong> a cyl<strong>in</strong>der, effects <strong>of</strong> jo<strong>in</strong>ts, change <strong>in</strong> diameter, length <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>ternal volume; pr<strong>in</strong>cipalstresses <strong>in</strong> sphere <strong>and</strong> change <strong>in</strong> diameter <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>ternal volume6. Columns <strong>and</strong> struts : Columns <strong>and</strong> failure <strong>of</strong> columns : Euler’s formuls; Rank<strong>in</strong>e- Gordon’sformula, Johnson’s empirical formula for axially loaded columns <strong>and</strong> their applications.7. Slope <strong>and</strong> deflection : Relationship between moment, slope <strong>and</strong> deflection, Moment area method;method <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>tegration; M<strong>ac</strong>aulay’s method: Use <strong>of</strong> all these methods to calculate slope <strong>and</strong>deflection for the follow<strong>in</strong>g :a) Cantileversb) Simply supported beams with or without overhangc) Under concentrated loads, uniformly distributed loads or comb<strong>in</strong>ation <strong>of</strong> concentrated <strong>and</strong>uniformly distributed loads8
Suggested Read<strong>in</strong>gs/ Books:Punjab <strong>Tech</strong>nical University PTU/DA/6 th August 2011B.<strong>Tech</strong> <strong>Aeronautical</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>1. Strength <strong>of</strong> Materials by Ferd<strong>in</strong><strong>and</strong> P S<strong>in</strong>ger <strong>and</strong> Andrew Pytel,Harper <strong>and</strong> Row H.2. Kogakusha Publishers, New York3. Mechanics <strong>of</strong> Materials by SI Version, end edition by Ferd<strong>in</strong><strong>and</strong> P. Beer <strong>and</strong> E4. Russel Johnston (Jr); McGraw Hill, India5. Mechanics <strong>of</strong> Materials-SI Version 2nd Edition by EP Popov, Prentice Hall India6. Introduction to Solid Mechanics by D.H Shames, Prentice Hall Inc.7. Elements <strong>of</strong> strength <strong>of</strong> Materials by Timoshenko <strong>and</strong> Young8. Strength <strong>of</strong> Materials by DS Bedi; Khanna book Publish<strong>in</strong>g Company, New Delhi.9. Strength <strong>of</strong> materials by R.S Lehri <strong>and</strong> A.S. Lehri, S.K Kataria <strong>and</strong> Sons._____________________________________________________________________________________ME-207 M<strong>ac</strong>h<strong>in</strong>e Draw<strong>in</strong>g1. Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples <strong>of</strong> draw<strong>in</strong>g, requirements <strong>of</strong> production draw<strong>in</strong>g, section<strong>in</strong>g <strong>and</strong> conventionalrepresentation, dimension<strong>in</strong>g, symbols <strong>of</strong> st<strong>and</strong>ard tolerances, m<strong>ac</strong>h<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g symbols,Introduction <strong>and</strong> familiarization <strong>of</strong> the code IS:296.2. FASTENERS : Various types <strong>of</strong> screw threads, types <strong>of</strong> nuts <strong>and</strong> bolts, screwedfasteners, weld<strong>in</strong>g jo<strong>in</strong>ts <strong>and</strong> riveted jo<strong>in</strong>ts3. Assembly <strong>and</strong> Dis-assembly <strong>of</strong> the follow<strong>in</strong>g manually <strong>and</strong> us<strong>in</strong>g computer aideddraft<strong>in</strong>g.a) Coupl<strong>in</strong>gs: Solid or rigid Coupl<strong>in</strong>g, Protected type flange coupl<strong>in</strong>g, P<strong>in</strong> typeflexible coupl<strong>in</strong>g, muff coupl<strong>in</strong>g, Oldham, universal coupl<strong>in</strong>g, claw coupl<strong>in</strong>g, conefriction clutch, free h<strong>and</strong> sketch <strong>of</strong> s<strong>in</strong>gle plate friction clutch.b) Knuckle <strong>and</strong> cotter jo<strong>in</strong>tsc) Pipe <strong>and</strong> Pipe fitt<strong>in</strong>gs: flanged jo<strong>in</strong>ts, spigot an socket jo<strong>in</strong>t, union jo<strong>in</strong>t, hydraulican expansion jo<strong>in</strong>td) IC Eng<strong>in</strong>e Parts : Piston, connect<strong>in</strong>g rode) Boiler Mount<strong>in</strong>gs : steam stop valve, feed check valve, safety valve, blow <strong>of</strong>f cock.f) Bear<strong>in</strong>gs : swivel bear<strong>in</strong>g, thrust bear<strong>in</strong>g, plummer block, angular plumber blockg) Miscellaneous : Screw J<strong>ac</strong>k, Drill Press Vice, Crane hook.Draft<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> simple mechanical components on computer.NOTE :Draw<strong>in</strong>g Pr<strong>ac</strong>tice is to be done as per IS:296 code.9
Punjab <strong>Tech</strong>nical University PTU/DA/6 th August 2011B.<strong>Tech</strong> <strong>Aeronautical</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>First angle projection to be used. Draw<strong>in</strong>gs should conta<strong>in</strong> bill <strong>of</strong> materials <strong>and</strong> should illustratef<strong>in</strong>ish. The syllabus given above <strong>in</strong>dicates the broad outl<strong>in</strong>es <strong>and</strong> the scope <strong>of</strong> the subject to becovered. It is not necessary to cover all the draw<strong>in</strong>g exercises <strong>of</strong> the types <strong>of</strong> m<strong>ac</strong>h<strong>in</strong>e toolsmentioned above.Suggested Read<strong>in</strong>gs/ Books:1. Text-book <strong>of</strong> M<strong>ac</strong>h<strong>in</strong>e Draw<strong>in</strong>g by V Lakshmi Narayanan <strong>and</strong> Mathur2. M<strong>ac</strong>h<strong>in</strong>e Draw<strong>in</strong>g by PS Gill, BD Kataria <strong>and</strong> Sons, Ludhiana3. M<strong>ac</strong>h<strong>in</strong>e Draw<strong>in</strong>g by ND Bhatt, Charotar publications4. M<strong>ac</strong>h<strong>in</strong>e Draw<strong>in</strong>g by N Sidheshwar, Tata McGraw Hill_______________________________________________________________________________________ME-211 Strength <strong>of</strong> Materials Lab1. To perform tensile test <strong>in</strong> ductile <strong>and</strong> brittle materials <strong>and</strong> to draw stress-stra<strong>in</strong> curve <strong>and</strong>to determ<strong>in</strong>e various mechanical properties.2. To perform compression test on C.I. <strong>and</strong> to determ<strong>in</strong>e ultimate compressive strength.3. To perform shear test on different materials <strong>and</strong> determ<strong>in</strong>e ultimate shear strength.4. To perform any one hardness test (Rockwell, Br<strong>in</strong>ell & Vicker’s test) <strong>and</strong> determ<strong>in</strong>ehardness <strong>of</strong> materials.5. To perform imp<strong>ac</strong>t test to determ<strong>in</strong>e imp<strong>ac</strong>t strength.6. To perform torsion test <strong>and</strong> to determ<strong>in</strong>e various mechanical properties.7. Study <strong>of</strong> performance <strong>of</strong> Fatigue & Creep tests8. To perform bend<strong>in</strong>g test on beam (wooden or any other material) <strong>and</strong> to determ<strong>in</strong>e theYoung's modulus <strong>and</strong> Modulus <strong>of</strong> rupture9. To perform Torsion test <strong>and</strong> close coiled helical spr<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> tension <strong>and</strong> compression <strong>and</strong> todeterm<strong>in</strong>e modulus <strong>of</strong> rigidity/stiffness10. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation <strong>of</strong> Buck<strong>in</strong>g loads <strong>of</strong> long columns with different end conditions._____________________________________________________________________________________ME-214 Fluid Mechanics –I Lab1. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the met<strong>ac</strong>entric height <strong>of</strong> a float<strong>in</strong>g vessel under loaded <strong>and</strong> unloadedconditions.2. To study the flow through a variable area duct <strong>and</strong> verify Bernoulli’s energy equation.3. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the coefficient <strong>of</strong> discharge for an obstruction flow meter (venturimeter/orifice meter)4. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the discharge coefficient for a Vee- notch or rectangular notch.10
Punjab <strong>Tech</strong>nical University PTU/DA/6 th August 2011B.<strong>Tech</strong> <strong>Aeronautical</strong> <strong>Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g</strong>5. To study the transition from lam<strong>in</strong>ar to turbulent flow <strong>and</strong> to ascerta<strong>in</strong> the lower criticalReynolds number.6. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the hydraulic coefficients for flow through an orifice.7. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the friction coefficients for pipes <strong>of</strong> different diameters.8. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the head loss <strong>in</strong> a pipe l<strong>in</strong>e due to sudden expansion/ sudden contr<strong>ac</strong>tion/bend.9. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the velocity distribution for pipel<strong>in</strong>e flow with a pitot static probe.11