AVERAGE SALES PRICE (ASP) FOR MEDICARE ... - Janssen CNS
AVERAGE SALES PRICE (ASP) FOR MEDICARE ... - Janssen CNS
AVERAGE SALES PRICE (ASP) FOR MEDICARE ... - Janssen CNS
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>AVERAGE</strong> <strong>SALES</strong> <strong>PRICE</strong> (<strong>ASP</strong>)<br />
<strong>FOR</strong> <strong>MEDICARE</strong> DRUG PROGRAM<br />
3rd QUARTER 2010 UPDATE<br />
When RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is administered in a physician office and covered under<br />
Medicare Part B, it is reimbursed based on Average Sales Price (<strong>ASP</strong>) + 6% 1<br />
• <strong>ASP</strong> is based on quarterly sales data provided by manufacturers 2<br />
• <strong>ASP</strong> = Gross Sales - (Discounts + Chargebacks + Rebates) 2<br />
Total Number of Units Sold<br />
• Manufacturers submit <strong>ASP</strong> data to Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) by specific<br />
deadlines following the end of each quarterly period. CMS uses this data to determine the Medicare<br />
reimbursement rate for the subsequent quarter. This results in a 2 quarter lag between the quarter in<br />
which the sales occur and the time when the sales are reflected in a revised reimbursement rate. For<br />
example, 1st quarter sales become the basis for 3rd quarter reimbursement. 3<br />
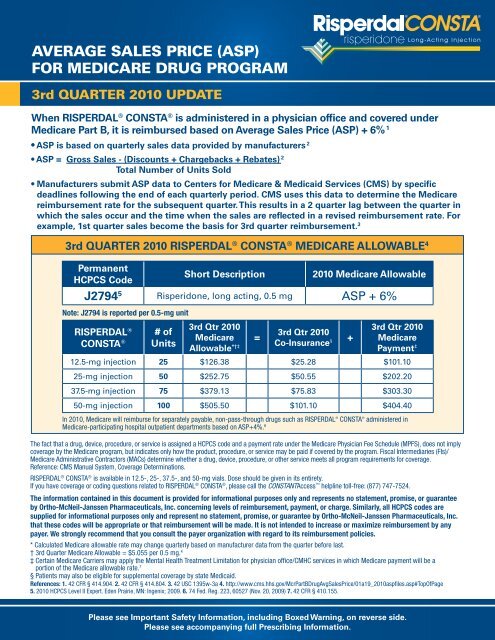
3rd QUARTER 2010 RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® <strong>MEDICARE</strong> ALLOWABLE 4<br />
Permanent<br />
HCPCS Code<br />
Short Description 2010 Medicare Allowable<br />
J2794 5 Risperidone, long acting, 0.5 mg <strong>ASP</strong> + 6%<br />
Note: J2794 is reported per 0.5-mg unit<br />
RISPERDAL ®<br />
CONSTA ®<br />
# of<br />
Units<br />
3rd Qtr 2010<br />
Medicare<br />
Allowable *†‡<br />
In 2010, Medicare will reimburse for separately payable, non-pass-through drugs such as RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® administered in<br />
Medicare-participating hospital outpatient departments based on <strong>ASP</strong>+4%. 6<br />
The fact that a drug, device, procedure, or service is assigned a HCPCS code and a payment rate under the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS), does not imply<br />
coverage by the Medicare program, but indicates only how the product, procedure, or service may be paid if covered by the program. Fiscal Intermediaries (FIs)/<br />
Medicare Administrative Contractors (MACs) determine whether a drug, device, procedure, or other service meets all program requirements for coverage.<br />
Reference: CMS Manual System, Coverage Determinations.<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is available in 12.5-, 25-, 37.5-, and 50-mg vials. Dose should be given in its entirety.<br />
If you have coverage or coding questions related to RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , please call the CONSTANTAccess helpline toll-free: (877) 747-7524.<br />
The information contained in this document is provided for informational purposes only and represents no statement, promise, or guarantee<br />
by Ortho-McNeil-<strong>Janssen</strong> Pharmaceuticals, Inc. concerning levels of reimbursement, payment, or charge. Similarly, all HCPCS codes are<br />
supplied for informational purposes only and represent no statement, promise, or guarantee by Ortho-McNeil-<strong>Janssen</strong> Pharmaceuticals, Inc.<br />
that these codes will be appropriate or that reimbursement will be made. It is not intended to increase or maximize reimbursement by any<br />
payer. We strongly recommend that you consult the payer organization with regard to its reimbursement policies.<br />
* Calculated Medicare allowable rate may change quarterly based on manufacturer data from the quarter before last.<br />
† 3rd Quarter Medicare Allowable = $5.055 per 0.5 mg. 4<br />
‡ Certain Medicare Carriers may apply the Mental Health Treatment Limitation for physician office/CMHC services in which Medicare payment will be a<br />
portion of the Medicare allowable rate. 7<br />
§ Patients may also be eligible for supplemental coverage by state Medicaid.<br />
References: 1. 42 CFR § 414.904. 2. 42 CFR § 414.804. 3. 42 USC 1395w-3a 4. http://www.cms.hhs.gov/McrPartBDrugAvgSalesPrice/01a19_2010aspfiles.asp#TopOfPage<br />
5. 2010 HCPCS Level II Expert. Eden Prairie, MN: Ingenix; 2009. 6. 74 Fed. Reg. 223, 60527 (Nov. 20, 2009) 7. 42 CFR § 410.155.<br />
Please see Important Safety Information, including Boxed Warning, on reverse side.<br />
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information.<br />
=<br />
3rd Qtr 2010<br />
Co-Insurance §<br />
+<br />
3rd Qtr 2010<br />
Medicare<br />
Payment ‡<br />
12.5-mg injection 25 $126.38 $25.28 $101.10<br />
25-mg injection 50 $252.75 $50.55 $202.20<br />
37.5-mg injection 75 $379.13 $75.83 $303.30<br />
50-mg injection 100 $505.50 $101.10 $404.40
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) long-acting injection is indicated for the treatment of schizophrenia and for the maintenance treatment of<br />
Bipolar I Disorder.<br />
IMPORTANT SAFETY IN<strong>FOR</strong>MATION <strong>FOR</strong> RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone)<br />
WARNING: Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis<br />
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. Analyses of<br />
17 placebo-controlled trials (modal duration of 10 weeks), largely in patients taking atypical antipsychotic drugs, revealed a risk<br />
of death in the drug-treated patients of between 1.6 to 1.7 times the risk of death in placebo-treated patients. Over the course of a<br />
typical 10-week controlled trial, the rate of death in drug-treated patients was about 4.5%, compared to a rate of about 2.6% in the<br />
placebo group. Although the causes of death were varied, most of the deaths appeared to be either cardiovascular (e.g., heart failure,<br />
sudden death) or infectious (e.g., pneumonia) in nature. Observational studies suggest that, similar to atypical antipsychotic drugs,<br />
treatment with conventional antipsychotic drugs may increase mortality. The extent to which the findings of increased mortality in<br />
observational studies may be attributed to the antipsychotic drug as opposed to some characteristic(s) of the patients is not clear.<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis.<br />
Contraindications: RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to the product.<br />
Cerebrovascular Adverse Events (CAEs): CAEs (e.g., stroke, transient ischemia attacks), including fatalities, were reported in placebo-controlled trials in elderly<br />
patients with dementia-related psychosis taking oral risperidone. The incidence of CAEs was significantly higher than with placebo. RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is not<br />
approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis.<br />
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS): NMS, a potentially fatal symptom complex, has been reported with the use of antipsychotic medications. Clinical<br />
manifestations include muscle rigidity, fever, altered mental status, and evidence of autonomic instability (see full Prescribing Information). Management should<br />
include immediate discontinuation of antipsychotic drugs and other drugs not essential to concurrent therapy, intensive symptomatic treatment and close medical<br />
monitoring, and treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems.<br />
Tardive Dyskinesia (TD): TD is a syndrome of potentially irreversible, involuntary, dyskinetic movements that may develop in patients treated with antipsychotic<br />
medications. The risk of developing TD and the likelihood that dyskinetic movements will become irreversible are believed to increase with duration of treatment<br />
and total cumulative dose, but can develop after relatively brief treatment at low doses. Elderly women patients appeared to be at increased risk for TD, although<br />
it is impossible to predict which patients will develop the syndrome. Prescribing should be consistent with the need to minimize the risk of TD (see full Prescribing<br />
Information). Discontinue drug if clinically appropriate. The syndrome may remit, partially or completely, if antipsychotic treatment is withdrawn.<br />
Hyperglycemia and Diabetes: Hyperglycemia, some cases extreme and associated with ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar coma or death has been reported in<br />
patients treated with atypical antipsychotics (APS), including RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® . Patients starting treatment with APS who have or are at risk for diabetes<br />
mellitus should undergo fasting blood glucose testing at the beginning of and during treatment. Patients who develop symptoms of hyperglycemia should also<br />
undergo fasting blood glucose testing. All patients treated with atypical antipsychotics should be monitored for symptoms of hyperglycemia. Some patients<br />
require continuation of anti-diabetic treatment despite discontinuation of the suspect drug.<br />
Hyperprolactinemia: As with other drugs that antagonize dopamine D 2 receptors, risperidone elevates prolactin levels and the elevation persists during chronic<br />
administration. Risperidone is associated with higher levels of prolactin elevation than other antipsychotic agents.<br />
Orthostatic Hypotension and Syncope: RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® may induce orthostatic hypotension associated with dizziness, tachycardia, and in some<br />
patients, syncope, especially during the initial dose-titration period. RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® should be used with caution in patients with known cardiovascular<br />
disease (e.g., heart failure, history of MI or ischemia, conduction abnormalities), cerebrovascular disease or conditions that would predispose patients to hypotension<br />
(e.g., dehydration, hypovolemia) and additionally elderly patients with renal or hepatic impairment. Monitoring should be considered in patients for whom this may be<br />
of concern.<br />
Leukopenia, Neutropenia and Agranulocytosis have been reported with antipsychotics, including RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® . Patients with a history of clinically<br />
significant low white blood cell count (WBC) or drug-induced leukopenia/neutropenia should have frequent complete blood cell counts during the first few months<br />
of therapy. At the first sign of a clinically significant decline in WBC, and in the absence of other causative factors, discontinuation of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® should<br />
be considered. Patients with clinically significant neutropenia should be carefully monitored for fever or other symptoms or signs of infection and treated promptly if<br />
such symptoms or signs occur. Patients with severe neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ®<br />
(risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION<br />
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING IN<strong>FOR</strong>MATION<br />
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® .<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION<br />
Initial U.S. Approval: 2003<br />
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-<br />
RELATED PSYCHOSIS<br />
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.<br />
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic<br />
drugs are at an increased risk of death. RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is not approved<br />
for use in patients with dementia-related psychosis. (5.1)<br />
-----------------------------------RECENT MAJOR CHANGES ------------------------------<br />
Indications and Usage, Bipolar Disorder (1.2) May 2009<br />
Dosage and Administration, Bipolar Disorder (2.2) May 2009<br />
Warnings and Precautions, Leukopenia, Neutropenia,<br />
and Agranulocytosis (5.8) July 2009<br />
Warnings and Precautions, Suicide (5.17) May 2009<br />
---------------------------------INDICATIONS AND USAGE----------------------------------<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is an atypical antipsychotic indicated:<br />
• for the treatment of schizophrenia. (1.1)<br />
• as monotherapy or as adjunctive therapy to lithium or valproate for the<br />
maintenance treatment of Bipolar I Disorder. (1.2)<br />
--------------------------------DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION---------------------------<br />
• For patients who have never taken oral RISPERDAL ® , tolerability should<br />
be established with oral RISPERDAL ® prior to initiating treatment with<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® . (2)<br />
• Administer by deep intramuscular (IM) deltoid or gluteal injection. Each injection<br />
should be administered by a health care professional using the appropriate<br />
enclosed safety needle (1-inch for deltoid administration alternating injections<br />
between the two arms and 2-inch for gluteal administration alternating<br />
injections between the two buttocks). Do not administer intravenously. (2)<br />
• 25 mg intramuscular (IM) every 2 weeks. Patients not responding to 25 mg may<br />
benefit from a higher dose of 37.5 mg or 50 mg. The maximum dose should not<br />
exceed 50 mg every 2 weeks. (2)<br />
• Oral RISPERDAL ® (or another antipsychotic medication) should be given with<br />
the first injection of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , and continued for 3 weeks (and<br />
then discontinued) to ensure adequate therapeutic plasma concentrations from<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® . (2)<br />
• Upward dose adjustment of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® should not be made more<br />
frequently than every 4 weeks. Clinical effects of each upward dose adjustment<br />
should not be anticipated earlier than 3 weeks after injection. (2)<br />
• Avoid inadvertent administration into a blood vessel. (5.15)<br />
• See Full Prescribing Information Section 2.8 for instructions for use.<br />
-------------------------------DOSAGE <strong>FOR</strong>MS AND STRENGTHS--------------------------<br />
Vial kits: 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 37.5 mg, and 50 mg (3)<br />
-------------------------------------CONTRAINDICATIONS------------------------------------<br />
• Known hypersensitivity to the product (4)<br />
------------------------------WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS------------------------------<br />
• Cerebrovascular events, including stroke, in elderly patients with dementiarelated<br />
psychosis. RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is not approved for use in patients<br />
with dementia-related psychosis (5.2)<br />
• Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome: Manage with immediate discontinuation and<br />
close monitoring (5.3)<br />
• Tardive Dyskinesia: Discontinue treatment if clinically appropriate (5.4)<br />
• Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus- in some cases extreme and associated<br />
with ketoacidosis or hyperosmolar coma or death, has been reported in patients<br />
taking risperidone. Patients with diabetes mellitus should have glucose levels<br />
monitored regularly. Patients with risk factors for diabetes mellitus should<br />
undergo fasting glucose testing at the beginning of treatment and periodically<br />
during treatment. All patients taking risperidone should be monitored for<br />
symptoms of hyperglycemia. Symptomatic patients should undergo fasting<br />
glucose testing. (5.5)<br />
• Hyperprolactinemia: Risperidone treatment may elevate prolactin levels.<br />
Long-standing hyperprolactinemia, when associated with hypogonadism, can<br />
lead to decreased bone density in men and women. (5.6)<br />
• Orthostatic hypotension: associated with dizziness, tachycardia, bradycardia, and<br />
syncope can occur, especially during initial dose titration with oral risperidone.<br />
Use caution in patients with cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular disease,<br />
and conditions that could affect hemodynamic responses. (5.7)<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION<br />
• Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis have been reported with<br />
antipsychotics, including RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® . Patients with history of a<br />
clinically significant low white blood cell count (WBC) or a drug-induced<br />
leukopenia/neutropenia should have their complete blood cell count (CBC)<br />
monitored frequently during the first few months of therapy and discontinuation<br />
of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® should be considered at the first sign of a clinically<br />
significant decline in WBC in the absence of other causative factors. (5.8)<br />
• Potential for cognitive and motor impairment: has potential to impair judgment,<br />
thinking, and motor skills. Use caution when operating machinery, including<br />
automobiles. (5.9)<br />
• Seizures: Use cautiously in patients with a history of seizures or with conditions<br />
that potentially lower the seizure threshold. (5.10)<br />
• Dysphagia: Esophageal dysmotility and aspiration can occur. Use cautiously in<br />
patients at risk for aspiration pneumonia. (5.11)<br />
• Priapism: has been reported. Severe priapism may require surgical intervention.<br />
(5.12)<br />
• Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP): has been reported. (5.13)<br />
• Avoid inadvertent administration into a blood vessel (5.15)<br />
• Suicide: There is increased risk of suicide attempt in patients with schizophrenia<br />
or bipolar disorder, and close supervision of high-risk patients should<br />
accompany drug therapy. (5.17)<br />
• Increased sensitivity in patients with Parkinson’s disease or those with dementia<br />
with Lewy bodies: has been reported. Manifestations include mental status<br />
changes, motor impairment, extrapyramidal symptoms, and features consistent<br />
with Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome. (5.18)<br />
• Diseases or conditions that could affect metabolism or hemodynamic responses:<br />
Use with caution in patients with such medical conditions (e.g., recent<br />
myocardial infarction or unstable cardiac disease) (5.18)<br />
-------------------------------------ADVERSE REACTIONS------------------------------------<br />
The most common adverse reactions in clinical trials in patients with schizophrenia<br />
(≥ 5%) were headache, parkinsonism, dizziness, akathisia, fatigue, constipation,<br />
dyspepsia, sedation, weight increased, pain in extremity, and dry mouth. The most<br />
common adverse reactions in clinical trials in patients with bipolar disorder were<br />
weight increased (5% in monotherapy trial) and tremor and parkinsonism ( ≥ 10% in<br />
adjunctive therapy trial). (6)<br />
The most common adverse reactions that were associated with discontinuation<br />
from clinical trials in patients with schizophrenia were agitation, depression,<br />
anxiety, and akathisia. Adverse reactions that were associated with discontinuation<br />
from bipolar disorder trials were hyperglycemia (one subject monotherapy trial)<br />
and hypokinesia and tardive dyskinesia (one subject each in adjunctive therapy<br />
trial). (6)<br />
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact <strong>Janssen</strong>, Division of<br />
Ortho-McNeil-<strong>Janssen</strong> Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-JANSSEN (1-800-526-7736) or<br />
FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch<br />
-------------------------------------DRUG INTERACTIONS------------------------------------<br />
• Due to <strong>CNS</strong> effects, use caution when administering with other centrally-acting<br />
drugs. Avoid alcohol. (7.1)<br />
• Due to hypotensive effects, hypotensive effects of other drugs with this potential<br />
may be enhanced. (7.2)<br />
• Effects of levodopa and dopamine agonists may be antagonized. (7.3)<br />
• Cimetidine and ranitidine increase the bioavailability of risperidone. (7.5)<br />
• Clozapine may decrease clearance of risperidone. (7.6)<br />
• Fluoxetine and paroxetine increase plasma concentrations of risperidone. (7.11)<br />
• Carbamazepine and other enzyme inducers decrease plasma concentrations of<br />
risperidone. (7.12)<br />
--------------------------------USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS-----------------------------<br />
• Renal or Hepatic Impairment: dose appropriately with oral RISPERDAL ® prior to<br />
initiating treatment with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® . A lower starting dose of<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® of 12.5 mg may be appropriate in some patients. (2.4)<br />
• Nursing Mothers: should not breast feed. (8.3)<br />
• Pediatric Use: safety and effectiveness not established in patients less than<br />
18 years of age. (8.4)<br />
• Elderly: dosing for otherwise healthy elderly patients is the same as for healthy<br />
nonelderly. Elderly may be more predisposed to orthostatic effects than<br />
nonelderly. (8.5)<br />
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING IN<strong>FOR</strong>MATION.<br />
Revised: 04/2010<br />
FULL PRESCRIBING IN<strong>FOR</strong>MATION: CONTENTS*<br />
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH<br />
DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS<br />
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE<br />
1.1 Schizophrenia<br />
1.2 Bipolar Disorder<br />
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION<br />
2.1 Schizophrenia<br />
2.2 Bipolar Disorder<br />
2.3 General Dosing Information<br />
2.4 Dosage in Special Populations<br />
2.5 Reinitiation of Treatment in Patients Previously Discontinued
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION<br />
2.6 Switching from Other Antipsychotics<br />
2.7 Co-Administration of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® with Certain Other<br />
Medications<br />
2.8 Instructions for Use<br />
3 DOSAGE <strong>FOR</strong>MS AND STRENGTHS<br />
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS<br />
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS<br />
5.1 Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related<br />
Psychosis<br />
5.2 Cerebrovascular Adverse Events, Including Stroke, in Elderly Patients<br />
with Dementia-Related Psychosis<br />
5.3 Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)<br />
5.4 Tardive Dyskinesia<br />
5.5 Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus<br />
5.6 Hyperprolactinemia<br />
5.7 Orthostatic Hypotension<br />
5.8 Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis<br />
5.9 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment<br />
5.10 Seizures<br />
5.11 Dysphagia<br />
5.12 Priapism<br />
5.13 Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP)<br />
5.14 Body Temperature Regulation<br />
5.15 Administration<br />
5.16 Antiemetic Effect<br />
5.17 Suicide<br />
5.18 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness<br />
5.19 Osteodystrophy and Tumors in Animals<br />
5.20 Monitoring: Laboratory Tests<br />
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS<br />
6.1 Commonly-Observed Adverse Reactions in Double-Blind,<br />
Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials - Schizophrenia<br />
6.2 Commonly-Observed Adverse Reactions in Double-Blind,<br />
Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials – Bipolar Disorder<br />
6.3 Other Adverse Reactions Observed During the Premarketing Evaluation<br />
of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ®<br />
6.4 Discontinuations Due to Adverse Reactions<br />
6.5 Dose Dependency of Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials<br />
6.6 Changes in Body Weight<br />
6.7 Changes in ECG<br />
6.8 Pain Assessment and Local Injection Site Reactions<br />
6.9 Postmarketing Experience<br />
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS<br />
7.1 Centrally-Acting Drugs and Alcohol<br />
7.2 Drugs with Hypotensive Effects<br />
7.3 Levodopa and Dopamine Agonists<br />
7.4 Amitriptyline<br />
7.5 Cimetidine and Ranitidine<br />
7.6 Clozapine<br />
7.7 Lithium<br />
7.8 Valproate<br />
7.9 Digoxin<br />
7.10 Topiramate<br />
7.11 Drugs That Inhibit CYP 2D6 and Other CYP Isozymes<br />
7.12 Carbamazepine and Other CYP 3A4 Enzyme Inducers<br />
7.13 Drugs Metabolized by CYP 2D6<br />
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS<br />
8.1 Pregnancy<br />
8.2 Labor and Delivery<br />
8.3 Nursing Mothers<br />
8.4 Pediatric Use<br />
8.5 Geriatric Use<br />
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE<br />
9.1 Controlled Substance<br />
9.2 Abuse<br />
9.3 Dependence<br />
10 OVERDOSAGE<br />
10.1 Human Experience<br />
10.2 Management of Overdosage<br />
11 DESCRIPTION<br />
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY<br />
12.1 Mechanism of Action<br />
12.2 Pharmacodynamics<br />
12.3 Pharmacokinetics<br />
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY<br />
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility<br />
14 CLINICAL STUDIES<br />
14.1 Schizophrenia<br />
14.2 Bipolar Disorder - Monotherapy<br />
14.3 Bipolar Disorder - Adjunctive Therapy<br />
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING<br />
17 PATIENT COUNSELING IN<strong>FOR</strong>MATION<br />
17.1 Orthostatic Hypotension<br />
17.2 Interference with Cognitive and Motor Performance<br />
17.3 Pregnancy<br />
17.4 Nursing<br />
17.5 Concomitant Medication<br />
17.6 Alcohol<br />
*Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed<br />
FULL PRESCRIBING IN<strong>FOR</strong>MATION<br />
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-<br />
RELATED PSYCHOSIS<br />
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic<br />
drugs are at an increased risk of death. Analyses of 17 placebo-controlled trials<br />
(modal duration of 10 weeks), largely in patients taking atypical antipsychotic<br />
drugs, revealed a risk of death in drug-treated patients of between 1.6 to<br />
1.7 times the risk of death in placebo-treated patients. Over the course of a<br />
typical 10-week controlled trial, the rate of death in drug-treated patients was<br />
about 4.5%, compared to a rate of about 2.6% in the placebo group. Although<br />
the causes of death were varied, most of the deaths appeared to be either<br />
cardiovascular (e.g., heart failure, sudden death) or infectious (e.g., pneumonia)<br />
in nature. Observational studies suggest that, similar to atypical antipsychotic<br />
drugs, treatment with conventional antipsychotic drugs may increase mortality.<br />
The extent to which the findings of increased mortality in observational studies<br />
may be attributed to the antipsychotic drug as opposed to some characteristic(s)<br />
of the patients is not clear. RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) is not approved<br />
for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis. [See Warnings<br />
and Precautions (5.1)]<br />
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE<br />
1.1 Schizophrenia<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) is indicated for the treatment of schizophrenia<br />
[see Clinical Studies (14.1)].<br />
1.2 Bipolar Disorder<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is indicated as monotherapy or as adjunctive therapy to<br />
lithium or valproate for the maintenance treatment of Bipolar I Disorder [see Clinical<br />
Studies (14.2, 14.3)].<br />
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION<br />
For patients who have never taken oral RISPERDAL ® , it is recommended to<br />
establish tolerability with oral RISPERDAL ® prior to initiating treatment with<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® .<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® should be administered every 2 weeks by deep intramuscular<br />
(IM) deltoid or gluteal injection. Each injection should be administered by a health<br />
care professional using the appropriate enclosed safety needle [see Dosage and<br />
Administration (2.8)]. For deltoid administration, use the 1-inch needle alternating<br />
injections between the two arms. For gluteal administration, use the 2-inch needle<br />
alternating injections between the two buttocks. Do not administer intravenously.<br />
2.1 Schizophrenia<br />
The recommended dose for the treatment of schizophrenia is 25 mg IM every<br />
2 weeks. Although dose response for effectiveness has not been established for<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , some patients not responding to 25 mg may benefit from a<br />
higher dose of 37.5 mg or 50 mg. The maximum dose should not exceed 50 mg<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® every 2 weeks. No additional benefit was observed with<br />
dosages greater than 50 mg RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® ; however, a higher incidence<br />
of adverse effects was observed.<br />
The efficacy of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® in the treatment of schizophrenia has not<br />
been evaluated in controlled clinical trials for longer than 12 weeks. Although<br />
controlled studies have not been conducted to answer the question of how long<br />
patients with schizophrenia should be treated with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , oral<br />
risperidone has been shown to be effective in delaying time to relapse in longer-term<br />
use. It is recommended that responding patients be continued on treatment with<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® at the lowest dose needed. The physician who elects to<br />
use RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® for extended periods should periodically re-evaluate<br />
the long-term risks and benefits of the drug for the individual patient.<br />
2.2 Bipolar Disorder<br />
The recommended dose for monotherapy or adjunctive therapy to lithium or<br />
valproate for the maintenance treatment of Bipolar I Disorder is 25 mg IM every<br />
2 weeks. Some patients may benefit from a higher dose of 37.5 mg or 50 mg.<br />
Dosages above 50 mg have not been studied in this population. The physician who<br />
elects to use RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® for extended periods should periodically<br />
re-evaluate the long-term risks and benefits of the drug for the individual patient.<br />
2.3 General Dosing Information<br />
A lower initial dose of 12.5 mg may be appropriate when clinical factors warrant<br />
dose adjustment, such as in patients with hepatic or renal impairment, for certain<br />
drug interactions that increase risperidone plasma concentrations [see Drug<br />
Interactions (7.11)] or in patients who have a history of poor tolerability to<br />
psychotropic medications. The efficacy of the 12.5 mg dose has not been investigated<br />
in clinical trials.
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION<br />
Oral RISPERDAL ® (or another antipsychotic medication) should be given with the<br />
first injection of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® and continued for 3 weeks (and then<br />
discontinued) to ensure that adequate therapeutic plasma concentrations are<br />
maintained prior to the main release phase of risperidone from the injection site<br />
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].<br />
Upward dose adjustment should not be made more frequently than every 4 weeks.<br />
The clinical effects of this dose adjustment should not be anticipated earlier than<br />
3 weeks after the first injection with the higher dose.<br />
In patients with clinical factors such as hepatic or renal impairment or certain drug<br />
interactions that increase risperidone plasma concentrations [see Drug Interactions<br />
(7.11)], dose reduction as low as 12.5 mg may be appropriate. The efficacy of the<br />
12.5 mg dose has not been investigated in clinical trials.<br />
Do not combine two different dose strengths of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® in a single<br />
administration.<br />
2.4 Dosage in Special Populations<br />
Elderly<br />
For elderly patients treated with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , the recommended dosage<br />
is 25 mg IM every 2 weeks. Oral RISPERDAL ® (or another antipsychotic medication)<br />
should be given with the first injection of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® and should be<br />
continued for 3 weeks to ensure that adequate therapeutic plasma concentrations<br />
are maintained prior to the main release phase of risperidone from the injection site<br />
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].<br />
Renal or Hepatic Impairment<br />
Patients with renal or hepatic impairment should be treated with titrated doses of oral<br />
RISPERDAL ® prior to initiating treatment with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® . The<br />
recommended starting dose is 0.5 mg oral RISPERDAL ® twice daily during the first<br />
week, which can be increased to 1 mg twice daily or 2 mg once daily during the<br />
second week. If a total daily dose of at least 2 mg oral RISPERDAL ® is well tolerated,<br />
an injection of 25 mg RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® can be administered every 2 weeks.<br />
Oral supplementation should be continued for 3 weeks after the first injection until<br />
the main release of risperidone from the injection site has begun. In some patients,<br />
slower titration may be medically appropriate. Alternatively, a starting dose of<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® of 12.5 mg may be appropriate. The efficacy of the 12.5 mg<br />
dose has not been investigated in clinical trials.<br />
Patients with renal impairment may have less ability to eliminate risperidone than<br />
normal adults. Patients with impaired hepatic function may have an increase in the<br />
free fraction of the risperidone, possibly resulting in an enhanced effect [see Clinical<br />
Pharmacology (12.3)]. Elderly patients and patients with a predisposition to<br />
hypotensive reactions or for whom such reactions would pose a particular risk<br />
should be instructed in nonpharmacologic interventions that help to reduce the<br />
occurrence of orthostatic hypotension (e.g., sitting on the edge of the bed for<br />
several minutes before attempting to stand in the morning and slowly rising from a<br />
seated position). These patients should avoid sodium depletion or dehydration, and<br />
circumstances that accentuate hypotension (alcohol intake, high ambient<br />
temperature, etc.). Monitoring of orthostatic vital signs should be considered [see<br />
Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].<br />
2.5 Reinitiation of Treatment in Patients Previously Discontinued<br />
There are no data to specifically address reinitiation of treatment. When restarting<br />
patients who have had an interval off treatment with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® ,<br />
supplementation with oral RISPERDAL ® (or another antipsychotic medication)<br />
should be administered.<br />
2.6 Switching from Other Antipsychotics<br />
There are no systematically collected data to specifically address switching patients<br />
from other antipsychotics to RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , or concerning concomitant<br />
administration with other antipsychotics. Previous antipsychotics should be<br />
continued for 3 weeks after the first injection of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® to ensure<br />
that therapeutic concentrations are maintained until the main release phase of<br />
risperidone from the injection site has begun [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].<br />
For patients who have never taken oral RISPERDAL ® , it is recommended to<br />
establish tolerability with oral RISPERDAL ® prior to initiating treatment with<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® . As recommended with other antipsychotic medications,<br />
the need for continuing existing EPS medication should be re-evaluated periodically.<br />
2.7 Co-Administration of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® with Certain Other<br />
Medications<br />
Co-administration of carbamazepine and other CYP 3A4 enzyme inducers (e.g.,<br />
phenytoin, rifampin, phenobarbital) with risperidone would be expected to cause<br />
decreases in the plasma concentrations of the sum of risperidone and<br />
9-hydroxyrisperidone combined, which could lead to decreased efficacy of<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® treatment. The dose of risperidone needs to be titrated<br />
accordingly for patients receiving these enzyme inducers, especially during<br />
initiation or discontinuation of therapy with these inducers [see Drug Interactions<br />
(7.11)]. At the initiation of therapy with carbamazepine or other known CYP 3A4<br />
hepatic enzyme inducers, patients should be closely monitored during the first<br />
4-8 weeks, since the dose of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® may need to be adjusted. A dose<br />
increase, or additional oral RISPERDAL ® , may need to be considered. On<br />
discontinuation of carbamazepine or other CYP 3A4 hepatic enzyme inducers, the<br />
dosage of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® should be re-evaluated and, if necessary,<br />
decreased. Patients may be placed on a lower dose of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ®<br />
between 2 to 4 weeks before the planned discontinuation of carbamazepine or other<br />
CYP 3A4 inducers to adjust for the expected increase in plasma concentrations of<br />
risperidone plus 9-hydroxyrisperidone. For patients treated with the recommended<br />
dose of 25 mg RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® and discontinuing from carbamazepine or other<br />
CYP3A4 enzyme inducers, it is recommended to continue treatment with the 25-mg<br />
dose unless clinical judgment necessitates lowering the RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® dose<br />
to 12.5 mg or necessitates interruption of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® treatment. The<br />
efficacy of the12.5 mg dose has not been investigated in clinical trials.<br />
Fluoxetine and paroxetine, CYP 2D6 inhibitors, have been shown to increase the<br />
plasma concentration of risperidone 2.5-2.8 fold and 3-9 fold respectively. Fluoxetine<br />
did not affect the plasma concentration of 9-hydroxyrisperidone. Paroxetine<br />
lowered the concentration of 9-hydroxyrisperidone by about 10%. The dose of<br />
risperidone needs to be titrated accordingly when fluoxetine or paroxetine is<br />
co-administered. When either concomitant fluoxetine or paroxetine is initiated or<br />
discontinued, the physician should re-evaluate the dose of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® .<br />
When initiation of fluoxetine or paroxetine is considered, patients may be placed<br />
on a lower dose of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® between 2 to 4 weeks before the planned<br />
start of fluoxetine or paroxetine therapy to adjust for the expected increase in<br />
plasma concentrations of risperidone. When fluoxetine or paroxetine is initiated in<br />
patients receiving the recommended dose of 25 mg RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , it is<br />
recommended to continue treatment with the 25 mg dose unless clinical judgment<br />
necessitates lowering the RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® dose to 12.5 mg or necessitates<br />
interruption of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® treatment. When RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is<br />
initiated in patients already receiving fluoxetine or paroxetine, a starting dose of<br />
12.5 mg can be considered. The efficacy of the 12.5 mg dose has not been<br />
investigated in clinical trials. The effects of discontinuation of concomitant<br />
fluoxetine or paroxetine therapy on the pharmacokinetics of risperidone and<br />
9-hydroxyrisperidone have not been studied. [See Drug Interactions (7.11)]<br />
2.8 Instructions for Use<br />
Dose pack components include:<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® must be reconstituted only in the diluent supplied in<br />
the dose pack, and must be administered with only the appropriate needle<br />
supplied in the dose pack for gluteal (2-inch needle) or deltoid (1-inch needle)<br />
administration. All components are required for administration. Do not<br />
substitute any components of the dose pack. To assure that the intended dose<br />
of risperidone is delivered, the full contents from the vial must be administered.<br />
Administration of partial contents may not deliver the intended dose of<br />
risperidone.<br />
Remove the dose pack of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® from the refrigerator and allow it<br />
to come to room temperature prior to reconstitution.<br />
1. Flip off the plastic colored cap from the vial.<br />
2. Peel back the blister pouch and<br />
remove the SmartSite ® Needle-<br />
Free Vial Access Device by<br />
holding the white luer cap. Do not<br />
touch the spike tip of the access<br />
device at any time.<br />
3. Place vial on a hard surface. Hold the base of the vial.<br />
Orient the SmartSite ® Access Device vertically over the<br />
vial so that the spike tip is at the center of the vial’s<br />
rubber stopper. With a straight downward push, press<br />
the spike tip of the SmartSite ® Access Device through<br />
the center of the vial’s rubber stopper until the device<br />
securely snaps onto the vial top.<br />
4. Swab the syringe connection point (blue circle) of the<br />
SmartSite ® Access Device with preferred antiseptic<br />
prior to attaching the syringe to the SmartSite ® Access<br />
Device.
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION<br />
5. The prefilled syringe has a white tip consisting of 2<br />
parts: a white collar and a smooth white cap. To open<br />
the syringe, hold the syringe by the white collar and<br />
snap off the smooth white cap (DO NOT TWIST OFF<br />
THE WHITE CAP). Remove the white cap together with<br />
the rubber tip cap inside.<br />
For all syringe assembly steps, hold the syringe only by<br />
the white collar located at the tip of the syringe. Be<br />
careful to not overtighten components when assembling.<br />
Overtightening connections may cause syringe<br />
component parts to loosen from the syringe body.<br />
6. While holding the white collar of the syringe, insert<br />
and press the syringe tip into the blue circle of the<br />
SmartSite ® Access Device and twist in a clockwise<br />
motion to secure the connection of the syringe to the<br />
SmartSite ® Access Device (avoid over-twisting). Hold<br />
the skirt of the SmartSite ® Access Device during<br />
attachment to prevent it from spinning. Keep the<br />
syringe and SmartSite ® Access Device aligned.<br />
7. Inject the entire contents of the syringe containing the<br />
diluent into the vial.<br />
8. Shake the vial vigorously while holding the plunger rod<br />
down with the thumb for a minimum of 10 seconds to<br />
ensure a homogeneous suspension. When properly<br />
mixed, the suspension appears uniform, thick, and<br />
milky in color. The microspheres will be visible in liquid,<br />
but no dry microspheres remain.<br />
9. Do not store the vial after reconstitution or the<br />
suspension may settle. If 2 minutes pass before<br />
injection, re-suspend by shaking vigorously.<br />
10. Invert the vial completely and slowly withdraw the<br />
suspension from the vial into the syringe. Tear section<br />
of the vial label at the perforation and apply detached<br />
label to syringe for identification purposes.<br />
11. While holding the white collar of the syringe, unscrew<br />
the syringe from the SmartSite ® Access Device.<br />
Discard both the vial and vial access device<br />
appropriately.<br />
12. Select the appropriate needle:<br />
For GLUTEAL injection, select the 20G TW 2-inch<br />
needle (longer needle with yellow colored hub in<br />
blister with yellow print)<br />
For DELTOID injection, select the 21G UTW 1-inch<br />
needle (shorter needle with green colored hub in<br />
blister with green print)<br />
13. Peel the blister pouch of the Needle-Pro ® safety<br />
device open halfway. Grasp the transparent needle<br />
sheath using the plastic peel pouch. To prevent<br />
contamination, be careful not to touch the orange<br />
Needle-Pro ® safety device’s Luer connector. While<br />
holding the white collar of the syringe, attach the Luer<br />
connection of the orange Needle-Pro ® safety device<br />
to the syringe with an easy clockwise twisting motion.<br />
14. While continuing to hold the white collar of the<br />
syringe, grasp the transparent needle sheath and seat<br />
the needle firmly on the orange Needle-Pro ® safety<br />
device with a push and a clockwise twist.<br />
15. If 2 minutes pass before injection, re-suspend by<br />
shaking vigorously.<br />
16. While holding the white collar of the syringe, pull the<br />
transparent needle sheath straight away from the<br />
needle. DO NOT TWIST the sheath as the Luer<br />
connections may be loosened.<br />
17. Tap the syringe gently to make any air bubbles rise to<br />
the top. Remove air in syringe by depressing the<br />
plunger rod while holding the needle in an upright<br />
position. Inject the entire contents of the syringe<br />
intramuscularly (IM) into the selected gluteal or deltoid<br />
muscle of the patient within 2 minutes to avoid settling.<br />
Gluteal injection should be made into the upper-outer<br />
quadrant of the gluteal area. DO NOT ADMINISTER<br />
INTRAVENOUSLY.<br />
WARNING: To avoid a needle stick injury with a contaminated needle:<br />
• Do not use free hand to press the Needle-Pro ® safety device over the needle.<br />
• Do not intentionally disengage the Needle-Pro ® safety device.<br />
• Do not attempt to straighten the needle or engage Needle-Pro ® safety device if<br />
the needle is bent or damaged.<br />
• Do not mishandle the Needle-Pro ® safety device, as it may cause the needle to<br />
protrude from the Needle-Pro ® safety device.<br />
18. After injection is complete,<br />
press the needle into the<br />
orange Needle-Pro ® safety<br />
device using a one-handed<br />
technique. Perform a<br />
one-handed technique by<br />
GENTLY pressing the orange<br />
Needle-Pro ® safety device<br />
against a table top or other<br />
hard, flat surface. AS THE ORANGE NEEDLE-PRO ® SAFETY DEVICE IS PRESSED,<br />
THE NEEDLE WILL FIRMLY ENGAGE INTO THE ORANGE NEEDLE-PRO ® SAFETY<br />
DEVICE. Visually confirm that the needle is fully engaged into the orange<br />
Needle-Pro ® safety device before discarding. Discard needle appropriately. Also<br />
discard the other (unused) needle provided in the dose pack.<br />
Upon suspension of the microspheres in the diluent, it is recommended to use<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® immediately. If RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is not administered<br />
within 2 minutes of reconstitution, settling of the microspheres will occur and<br />
resuspension by shaking is necessary prior to administration. Keeping the vial<br />
upright, shake vigorously back and forth for as long as it takes to resuspend the<br />
microspheres. Once in suspension, the product may remain at room temperature<br />
(do not expose to temperatures above 77°F (25°C)). RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® must<br />
be used within 6 hours of suspension.<br />
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and<br />
discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.<br />
3 DOSAGE <strong>FOR</strong>MS AND STRENGTHS<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is available in dosage strengths of 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 37.5 mg,<br />
and 50 mg risperidone. It is provided as a dose pack, consisting of a vial containing<br />
the risperidone microspheres, a pre-filled syringe containing 2 mL of diluent for<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , a SmartSite ® Needle-Free Vial Access Device, and two<br />
Needle-Pro ® safety needles for intramuscular injection (a 21 G UTW 1-inch needle<br />
with needle protection device for deltoid administration and a 20 G TW 2-inch<br />
needle with needle protection device for gluteal administration).<br />
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) is contraindicated in patients with a known<br />
hypersensitivity to the product.<br />
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS<br />
5.1 Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis<br />
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs<br />
are at an increased risk of death. RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) is not<br />
approved for the treatment of dementia-related psychosis (see Boxed Warning).<br />
5.2 Cerebrovascular Adverse Events, Including Stroke, in Elderly Patients with<br />
Dementia-Related Psychosis<br />
Cerebrovascular adverse events (e.g., stroke, transient ischemic attack), including<br />
fatalities, were reported in patients (mean age 85 years; range 73-97) in trials of oral<br />
risperidone in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis. In placebocontrolled<br />
trials, there was a significantly higher incidence of cerebrovascular<br />
adverse events in patients treated with oral risperidone compared to patients<br />
treated with placebo. RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is not approved for the treatment of<br />
patients with dementia-related psychosis [See also Boxed Warning and Warnings<br />
and Precautions (5.1)]<br />
5.3 Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)<br />
A potentially fatal symptom complex sometimes referred to as Neuroleptic<br />
Malignant Syndrome (NMS) has been reported in association with antipsychotic
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION<br />
drugs. Clinical manifestations of NMS are hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered<br />
mental status, and evidence of autonomic instability (irregular pulse or blood<br />
pressure, tachycardia, diaphoresis, and cardiac dysrhythmia). Additional signs may<br />
include elevated creatine phosphokinase, myoglobinuria (rhabdomyolysis), and<br />
acute renal failure.<br />
The diagnostic evaluation of patients with this syndrome is complicated. In arriving<br />
at a diagnosis, it is important to identify cases in which the clinical presentation<br />
includes both serious medical illness (e.g., pneumonia, systemic infection, etc.) and<br />
untreated or inadequately treated extrapyramidal signs and symptoms (EPS). Other<br />
important considerations in the differential diagnosis include central anticholinergic<br />
toxicity, heat stroke, drug fever, and primary central nervous system pathology.<br />
The management of NMS should include: (1) immediate discontinuation of<br />
antipsychotic drugs and other drugs not essential to concurrent therapy; (2)<br />
intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring; and (3) treatment of any<br />
concomitant serious medical problems for which specific treatments are available.<br />
There is no general agreement about specific pharmacological treatment regimens<br />
for uncomplicated NMS.<br />
If a patient requires antipsychotic drug treatment after recovery from NMS, the<br />
potential reintroduction of drug therapy should be carefully considered. The patient<br />
should be carefully monitored, since recurrences of NMS have been reported.<br />
5.4 Tardive Dyskinesia<br />
A syndrome of potentially irreversible, involuntary, dyskinetic movements may<br />
develop in patients treated with antipsychotic drugs. Although the prevalence of<br />
the syndrome appears to be highest among the elderly, especially elderly women,<br />
it is impossible to rely upon prevalence estimates to predict, at the inception of<br />
antipsychotic treatment, which patients are likely to develop the syndrome. Whether<br />
antipsychotic drug products differ in their potential to cause tardive dyskinesia is<br />
unknown.<br />
The risk of developing tardive dyskinesia and the likelihood that it will become<br />
irreversible are believed to increase as the duration of treatment and the total<br />
cumulative dose of antipsychotic drugs administered to the patient increase.<br />
However, the syndrome can develop, although much less commonly, after relatively<br />
brief treatment periods at low doses.<br />
There is no known treatment for established cases of tardive dyskinesia, although<br />
the syndrome may remit, partially or completely, if antipsychotic treatment is<br />
withdrawn. Antipsychotic treatment, itself, however, may suppress (or partially<br />
suppress) the signs and symptoms of the syndrome and thereby may possibly mask<br />
the underlying process. The effect that symptomatic suppression has upon the<br />
long-term course of the syndrome is unknown.<br />
Given these considerations, RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® should be prescribed in a<br />
manner that is most likely to minimize the occurrence of tardive dyskinesia. Chronic<br />
antipsychotic treatment should generally be reserved for patients who suffer from<br />
a chronic illness that: (1) is known to respond to antipsychotic drugs, and (2) for<br />
whom alternative, equally effective, but potentially less harmful treatments are not<br />
available or appropriate. In patients who do require chronic treatment, the smallest<br />
dose and the shortest duration of treatment producing a satisfactory clinical<br />
response should be sought. The need for continued treatment should be reassessed<br />
periodically.<br />
If signs and symptoms of tardive dyskinesia appear in a patient treated with<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , drug discontinuation should be considered. However, some<br />
patients may require treatment with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® despite the presence<br />
of the syndrome.<br />
5.5 Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus<br />
Hyperglycemia, in some cases extreme and associated with ketoacidosis or<br />
hyperosmolar coma or death, has been reported in patients treated with atypical<br />
antipsychotics including RISPERDAL ® . Assessment of the relationship between<br />
atypical antipsychotic use and glucose abnormalities is complicated by the<br />
possibility of an increased background risk of diabetes mellitus in patients with<br />
schizophrenia and the increasing incidence of diabetes mellitus in the general<br />
population. Given these confounders, the relationship between atypical<br />
antipsychotic use and hyperglycemia-related adverse events is not completely<br />
understood. However, epidemiological studies suggest an increased risk of<br />
treatment-emergent hyperglycemia-related adverse events in patients treated with<br />
the atypical antipsychotics. Precise risk estimates for hyperglycemia-related<br />
adverse events in patients treated with atypical antipsychotics are not available.<br />
Patients with an established diagnosis of diabetes mellitus who are started on<br />
atypical antipsychotics should be monitored regularly for worsening of glucose<br />
control. Patients with risk factors for diabetes mellitus (e.g., obesity, family history<br />
of diabetes) who are starting treatment with atypical antipsychotics should undergo<br />
fasting blood glucose testing at the beginning of treatment and periodically during<br />
treatment. Any patient treated with atypical antipsychotics should be monitored for<br />
symptoms of hyperglycemia including polydipsia, polyuria, polyphagia, and<br />
weakness. Patients who develop symptoms of hyperglycemia during treatment with<br />
atypical antipsychotics should undergo fasting blood glucose testing. In some<br />
cases, hyperglycemia has resolved when the atypical antipsychotic was<br />
discontinued; however, some patients required continuation of anti-diabetic<br />
treatment despite discontinuation of the suspect drug.<br />
5.6 Hyperprolactinemia<br />
As with other drugs that antagonize dopamine D2 receptors, risperidone elevates<br />
prolactin levels and the elevation persists during chronic administration.<br />
Risperidone is associated with higher levels of prolactin elevation than other<br />
antipsychotic agents.<br />
Hyperprolactinemia may suppress hypothalamic GnRH, resulting in reduced<br />
pituitary gonadotropin secretion. This, in turn, may inhibit reproductive function by<br />
impairing gonadal steroidogenesis in both female and male patients. Galactorrhea,<br />
amenorrhea, gynecomastia, and impotence have been reported in patients<br />
receiving prolactin-elevating compounds. Long-standing hyperprolactinemia when<br />
associated with hypogonadism may lead to decreased bone density in both female<br />
and male subjects.<br />
Tissue culture experiments indicate that approximately one-third of human breast<br />
cancers are prolactin dependent in vitro, a factor of potential importance if the<br />
prescription of these drugs is contemplated in a patient with previously detected<br />
breast cancer. An increase in pituitary gland, mammary gland, and pancreatic islet<br />
cell neoplasia (mammary adenocarcinomas, pituitary and pancreatic adenomas)<br />
was observed in the risperidone carcinogenicity studies conducted in mice and<br />
rats [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. Neither clinical studies nor epidemiologic<br />
studies conducted to date have shown an association between chronic<br />
administration of this class of drugs and tumorigenesis in humans; the available<br />
evidence is considered too limited to be conclusive at this time.<br />
5.7 Orthostatic Hypotension<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® may induce orthostatic hypotension associated with<br />
dizziness, tachycardia, and in some patients, syncope, especially during the initial<br />
dose-titration period with oral risperidone, probably reflecting its alpha-adrenergic<br />
antagonistic properties. Syncope was reported in 0.8% (12/1499 patients) of patients<br />
treated with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® in multiple-dose studies. Patients should be<br />
instructed in nonpharmacologic interventions that help to reduce the occurrence<br />
of orthostatic hypotension (e.g., sitting on the edge of the bed for several minutes<br />
before attempting to stand in the morning and slowly rising from a seated position).<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® should be used with particular caution in (1) patients with<br />
known cardiovascular disease (history of myocardial infarction or ischemia, heart<br />
failure, or conduction abnormalities), cerebrovascular disease, and conditions<br />
which would predispose patients to hypotension, e.g., dehydration and<br />
hypovolemia, and (2) in the elderly and patients with renal or hepatic impairment.<br />
Monitoring of orthostatic vital signs should be considered in all such patients, and<br />
a dose reduction should be considered if hypotension occurs. Clinically significant<br />
hypotension has been observed with concomitant use of oral RISPERDAL ® and<br />
antihypertensive medication.<br />
5.8 Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis<br />
Class Effect: In clinical trial and/or postmarketing experience, events of leukopenia/<br />
neutropenia have been reported temporally related to antipsychotic agents,<br />
including RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® . Agranulocytosis has also been reported.<br />
Possible risk factors for leukopenia/neutropenia include pre-existing low white<br />
blood cell count (WBC) and a history of drug-induced leukopenia/neutropenia.<br />
Patients with a history of a clinically significant low WBC or a drug-induced<br />
leukopenia/neutropenia should have their complete blood count (CBC) monitored<br />
frequently during the first few months of therapy and discontinuation of<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® should be considered at the first sign of a clinically<br />
significant decline in WBC in the absence of other causative factors.<br />
Patients with clinically significant neutropenia should be carefully monitored for<br />
fever or other symptoms or signs of infection and treated promptly if such symptoms<br />
or signs occur. Patients with severe neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION<br />
prescribing RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® for patients who will be exposed to temperature<br />
extremes.<br />
5.15 Administration<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® should be injected into the deltoid or gluteal muscle, and<br />
care must be taken to avoid inadvertent injection into a blood vessel. [See Dosage<br />
and Administration (2) and Adverse Reactions (6.8)]<br />
5.16 Antiemetic Effect<br />
Risperidone has an antiemetic effect in animals; this effect may also occur in<br />
humans, and may mask signs and symptoms of overdosage with certain drugs or<br />
of conditions such as intestinal obstruction, Reye’s syndrome, and brain tumor.<br />
5.17 Suicide<br />
There is an increased risk of suicide attempt in patients with schizophrenia or bipolar<br />
disorder, and close supervision of high-risk patients should accompany drug therapy.<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is to be administered by a health care professional [see<br />
Dosage and Administration (2)]; therefore, suicide due to an overdose is unlikely.<br />
5.18 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness<br />
Clinical experience with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® in patients with certain concomitant<br />
systemic illnesses is limited. Patients with Parkinson’s Disease or Dementia with<br />
Lewy Bodies who receive antipsychotics, including RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , are<br />
reported to have an increased sensitivity to antipsychotic medications.<br />
Manifestations of this increased sensitivity have been reported to include confusion,<br />
obtundation, postural instability with frequent falls, extrapyramidal symptoms, and<br />
clinical features consistent with the neuroleptic malignant syndrome.<br />
Caution is advisable when using RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® in patients with diseases<br />
or conditions that could affect metabolism or hemodynamic responses.<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® has not been evaluated or used to any appreciable extent<br />
in patients with a recent history of myocardial infarction or unstable heart disease.<br />
Patients with these diagnoses were excluded from clinical studies during the<br />
product’s premarket testing.<br />
Increased plasma concentrations of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone occur<br />
in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION<br />
experiencing adverse events, events were grouped in standardized categories<br />
using MedDRA terminology.<br />
Throughout this section, adverse reactions are reported. Adverse reactions are<br />
adverse events that were considered to be reasonably associated with the use of<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (adverse drug reactions) based on the comprehensive<br />
assessment of the available adverse event information. A causal association for<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® often cannot be reliably established in individual cases.<br />
Further, because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions,<br />
adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly<br />
compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates<br />
observed in clinical practice.<br />
The majority of all adverse reactions were mild to moderate in severity.<br />
6.1 Commonly-Observed Adverse Reactions in Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled<br />
Clinical Trials - Schizophrenia<br />
Table 1 lists the adverse reactions reported in 2% or more of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® -<br />
treated patients with schizophrenia in one 12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled<br />
trial.<br />
Table 1. Adverse Reactions in ≥ 2% of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® -Treated Patients<br />
with Schizophrenia in a 12-Week Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial<br />
Percentage of Patients Reporting Event<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® Placebo<br />
System/Organ Class 25 mg 50 mg<br />
Adverse Reaction (N=99) (N=103) (N=98)<br />
Eye disorders<br />
Vision blurred 2 3 0<br />
Gastrointestinal disorders<br />
Constipation 5 7 1<br />
Dry mouth 0 7 1<br />
Dyspepsia 6 6 0<br />
Nausea 3 4 5<br />
Toothache 1 3 0<br />
Salivary hypersecretion 4 1 0<br />
General disorders and administration<br />
site conditions<br />
Fatigue* 3 9 0<br />
Edema peripheral 2 3 1<br />
Pain 4 1 0<br />
Pyrexia 2 1 0<br />
Infections and infestations<br />
Upper respiratory tract infection 2 0 1<br />
Investigations<br />
Weight increased 5 4 2<br />
Weight decreased 4 1 1<br />
Musculoskeletal and connective<br />
tissue disorders<br />
Pain in extremity 6 2 1<br />
Nervous system disorders<br />
Headache 15 21 12<br />
Parkinsonism* 8 15 9<br />
Dizziness 7 11 6<br />
Akathisia* 4 11 6<br />
Sedation* 5 6 3<br />
Tremor 0 3 0<br />
Syncope 2 1 0<br />
Hypoesthesia 2 0 0<br />
Respiratory, thoracic and<br />
mediastinal disorders<br />
Cough 4 2 3<br />
Sinus congestion 2 0 0<br />
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders<br />
Acne 2 2 0<br />
Dry skin 2 0 0<br />
* Fatigue includes fatigue and asthenia. Parkinsonism includes extrapyramidal<br />
disorder, musculoskeletal stiffness, muscle rigidity, and bradykinesia. Akathisia<br />
includes akathisia and restlessness. Sedation includes sedation and somnolence.<br />
6.2 Commonly-Observed Adverse Reactions in Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled<br />
Clinical Trials – Bipolar Disorder<br />
Table 2 lists the treatment-emergent adverse reactions reported in 2% or more of<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® -treated patients in the 24-month double-blind, placebocontrolled<br />
treatment period of the trial assessing the efficacy and safety of<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® when administered as monotherapy for maintenance<br />
treatment in patients with Bipolar I Disorder.<br />
Table 2. Adverse Reactions in ≥2% of Patients with Bipolar I Disorder Treated<br />
with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® as Monotherapy in a 24-Month Double-Blind,<br />
Placebo-Controlled Trial<br />
Percentage of Patients Reporting Event<br />
System/Organ Class RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® Placebo<br />
Adverse Reaction (N=154) (N=149)<br />
Investigations<br />
Weight increased 5 1<br />
Nervous system disorders<br />
Dizziness 3 1<br />
Vascular disorders<br />
Hypertension 3 1<br />
Table 3 lists the treatment-emergent adverse reactions reported in 4% or more of<br />
patients in the 52-week double-blind, placebo-controlled treatment phase of a trial<br />
assessing the efficacy and safety of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® when administered as<br />
adjunctive maintenance treatment in patients with bipolar disorder.<br />
Table 3. Adverse Reactions in ≥ 4% of Patients with Bipolar Disorder Treated<br />
with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® as Adjunctive Therapy in a 52-Week Double-Blind,<br />
Placebo-Controlled Trial<br />
Percentage of Patients Reporting Event<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® + Placebo +<br />
System/Organ Class Treatment as Usuala Treatment as Usuala Adverse Reaction (N=72) (N=67)<br />
General disorders and administration<br />
site conditions<br />
Gait abnormal 4 0<br />
Infections and infestations<br />
Upper respiratory tract infection 6 3<br />
Investigations<br />
Weight increased 7 1<br />
Metabolism and nutrition disorders<br />
Decreased appetite 6 1<br />
Increased appetite 4 0<br />
Musculoskeletal and connective<br />
tissue disorders<br />
Arthralgia 4 3<br />
Nervous system disorders<br />
Tremor 24 16<br />
Parkinsonismb 15 6<br />
Dyskinesiab 6 3<br />
Sedationc 7 1<br />
Disturbance in attention 4 0<br />
Reproductive system and breast disorders<br />
Amenorrhea 4 1<br />
Respiratory, thoracic and<br />
mediastinal disorders<br />
Cough 4 1<br />
a Patients received double-blind RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® or placebo in addition to<br />
continuing their treatment as usual, which included mood stabilizers,<br />
antidepressants, and/or anxiolytics.<br />
b Parkinsonism includes muscle rigidity, hypokinesia, cogwheel rigidity, and<br />
bradykinesia. Dyskinesia includes muscle twitching and dyskinesia.<br />
c Sedation includes sedation and somnolence.<br />
6.3 Other Adverse Reactions Observed During the Premarketing Evaluation of<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ®<br />
The following additional adverse reactions occurred in < 2% of the<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® -treated patients in the above schizophrenia double-blind,<br />
placebo-controlled trial dataset, in < 2% of the RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® -treated<br />
patients in the above double-blind, placebo-controlled period of the monotherapy<br />
bipolar disorder trial dataset, or in < 4% of the RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® -treated<br />
patients in the above double-blind, placebo-controlled period of the adjunctive<br />
treatment bipolar disorder trial dataset. The following also includes additional<br />
adverse reactions reported at any frequency in RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® -treated<br />
patients who participated in the open-label phases of the above bipolar disorder<br />
studies and in other studies, including double-blind, active controlled and<br />
open-label studies in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.<br />
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: anemia, neutropenia<br />
Cardiac disorders: tachycardia, atrioventricular block first degree, palpitations,<br />
sinus bradycardia, bundle branch block left, bradycardia, sinus tachycardia, bundle<br />
branch block right<br />
Ear and labyrinth disorders: ear pain, vertigo<br />
Endocrine disorders: hyperprolactinemia<br />
Eye disorders: conjunctivitis, visual acuity reduced<br />
Gastrointestinal disorders: diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain upper, abdominal<br />
pain, stomach discomfort, gastritis
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION<br />
General disorders and administration site conditions: injection site pain, chest<br />
discomfort, chest pain, influenza like illness, sluggishness, malaise, induration,<br />
injection site induration, injection site swelling, injection site reaction, face edema<br />
Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity<br />
Infections and infestations: nasopharyngitis, influenza, bronchitis, urinary tract<br />
infection, rhinitis, respiratory tract infection, ear infection, pneumonia, lower<br />
respiratory tract infection, pharyngitis, sinusitis, viral infection, infection, localized<br />
infection, cystitis, gastroenteritis, subcutaneous abscess<br />
Injury and poisoning: fall, procedural pain<br />
Investigations: blood prolactin increased, alanine aminotransferase increased,<br />
electrocardiogram abnormal, gamma-glutamyl transferase increased, blood<br />
glucose increased, hepatic enzyme increased, aspartate aminotransferase<br />
increased, electrocardiogram QT prolonged, glucose urine present<br />
Metabolism and nutritional disorders: anorexia, hyperglycemia<br />
Musculoskeletal, connective tissue and bone disorders: posture abnormal, myalgia,<br />
back pain, buttock pain, muscular weakness, neck pain, musculoskeletal chest pain<br />
Nervous system disorders: coordination abnormal, dystonia, tardive dyskinesia,<br />
drooling, paresthesia, dizziness postural, convulsion, akinesia, hypokinesia,<br />
dysarthria<br />
Psychiatric disorders: insomnia, agitation, anxiety, sleep disorder, depression, initial<br />
insomnia, libido decreased, nervousness<br />
Renal and urinary disorders: urinary incontinence<br />
Reproductive system and breast disorders: galactorrhea, oligomenorrhea, erectile<br />
dysfunction, sexual dysfunction, ejaculation disorder, gynecomastia, breast<br />
discomfort, menstruation irregular, menstruation delayed, menstrual disorder,<br />
ejaculation delayed<br />
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: nasal congestion, pharyngolaryngeal<br />
pain, dyspnea, rhinorrhea<br />
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: rash, eczema, pruritus generalized,<br />
pruritus<br />
Vascular disorders: hypotension, orthostatic hypotension<br />
6.4 Discontinuations Due to Adverse Reactions<br />
Schizophrenia<br />
Approximately 11% (22/202) of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® -treated patients in the<br />
12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled schizophrenia trial discontinued<br />
treatment due to an adverse event, compared with 13% (13/98) who received<br />
placebo. The adverse reactions associated with discontinuation in two or more<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® -treated patients were: agitation (3%), depression (2%),<br />
anxiety (1%), and akathisia (1%).<br />
Bipolar Disorder<br />
In the 24-month double-blind, placebo-controlled treatment period of the trial<br />
assessing the efficacy and safety of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® when administered as<br />
monotherapy for maintenance treatment in patients with bipolar I disorder, 1 (0.6%)<br />
of 154 RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® -treated patients discontinued due to an adverse<br />
reaction (hyperglycemia).<br />
In the 52-week double-blind phase of the placebo-controlled trial in which<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® was administered as adjunctive therapy to patients with<br />
bipolar disorder in addition to continuing with their treatment as usual, approximately<br />
4% (3/72) of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® -treated patients discontinued treatment due to<br />
an adverse event, compared with 1.5% (1/67) of placebo-treated patients. Adverse<br />
reactions associated with discontinuation in RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® -treated<br />
patients were: hypokinesia (one patient) and tardive dyskinesia (one patient).<br />
6.5 Dose Dependency of Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials<br />
Extrapyramidal Symptoms:<br />
Two methods were used to measure extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) in the 12-week<br />
double-blind, placebo-controlled trial comparing three doses of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ®<br />
(25 mg, 50 mg, and 75 mg) with placebo in patients with schizophrenia, including: (1) the<br />
incidence of spontaneous reports of EPS symptoms; and (2) the change from baseline<br />
to endpoint on the total score (sum of the subscale scores for parkinsonism, dystonia,<br />
and dyskinesia) of the Extrapyramidal Symptom Rating Scale (ESRS).<br />
As shown in Table 1, the overall incidence of EPS-related adverse reactions<br />
(akathisia, dystonia, parkinsonism, and tremor) in patients treated with 25 mg<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® was comparable to that of patients treated with placebo;<br />
the incidence of EPS-related adverse reactions was higher in patients treated with<br />
50 mg RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® .<br />
The median change from baseline to endpoint in total ESRS score showed no<br />
worsening in patients treated with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® compared with patients<br />
treated with placebo: 0 (placebo group); -1 (25-mg group, significantly less than the<br />
placebo group); and 0 (50-mg group).<br />
Dystonia<br />
Class Effect: Symptoms of dystonia, prolonged abnormal contractions of muscle<br />
groups, may occur in susceptible individuals during the first few days of treatment.<br />
Dystonic symptoms include: spasm of the neck muscles, sometimes progressing to<br />
tightness of the throat, swallowing difficulty, difficulty breathing, and/or protrusion of<br />
the tongue. While these symptoms can occur at low doses, they occur more frequently<br />
and with greater severity with high potency and at higher doses of first generation<br />
antipsychotic drugs. An elevated risk of acute dystonia is observed in males and<br />
younger age groups.<br />
6.6 Changes in Body Weight<br />
In the 12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in patients with schizophrenia,<br />
9% of patients treated with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , compared with 6% of patients<br />
treated with placebo, experienced a weight gain of >7% of body weight at endpoint.<br />
In the 24-month double-blind, placebo-controlled treatment period of a trial<br />
assessing the efficacy and safety of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® when administered as<br />
monotherapy for maintenance treatment in patients with bipolar I disorder, 11.6%<br />
of patients treated with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® compared with 2.8% of patients<br />
treated with placebo experienced a weight gain of >7% of body weight at endpoint.<br />
In the 52-week double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in patients with bipolar disorder,<br />
26.8% of patients treated with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® as adjunctive treatment in<br />
addition to continuing their treatment as usual, compared with 27.3% of patients<br />
treated with placebo in addition to continuing their treatment as usual, experienced<br />
a weight gain of >7% of body weight at endpoint.<br />
6.7 Changes in ECG<br />
The electrocardiograms of 202 schizophrenic patients treated with 25 mg or 50 mg<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® and 98 schizophrenic patients treated with placebo in the<br />
12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled trial were evaluated. Compared with placebo,<br />
there were no statistically significant differences in QTc intervals (using Fridericia’s and<br />
linear correction factors) during treatment with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® .<br />
The electrocardiograms of 227 patients with Bipolar I Disorder were evaluated in<br />
the 24-month double-blind, placebo-controlled period. There were no clinically<br />
relevant differences in QTc intervals (using Fridericia’s and linear correction factors)<br />
during treatment with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® compared to placebo.<br />
The electrocardiograms of 85 patients with bipolar disorder were evaluated in the<br />
52-week double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. There were no statistically<br />
significant differences in QTc intervals (using Fridericia’s and linear correction<br />
factors) during treatment with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® 25 mg, 37.5 mg, or 50 mg<br />
when administered as adjunctive treatment in addition to continuing treatment as<br />
usual compared to placebo.<br />
6.8 Pain Assessment and Local Injection Site Reactions<br />
The mean intensity of injection pain reported by patients with schizophrenia using a<br />
visual analog scale (0 = no pain to 100 = unbearably painful) decreased in all<br />
treatment groups from the first to the last injection (placebo: 16.7 to 12.6; 25 mg: 12.0<br />
to 9.0; 50 mg: 18.2 to 11.8). After the sixth injection (Week 10), investigator ratings<br />
indicated that 1% of patients treated with 25 mg or 50 mg RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ®<br />
experienced redness, swelling, or induration at the injection site.<br />
In a separate study to observe local-site tolerability in which RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ®<br />
was administered into the deltoid muscle every 2 weeks over a period of 8 weeks,<br />
no patient discontinued treatment due to local injection site pain or reaction.<br />
Clinician ratings indicated that only mild redness, swelling, or induration at the<br />
injection site was observed in subjects treated with 37.5 mg or 50 mg<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® at 2 hours after deltoid injection. All ratings returned to<br />
baseline at the predose assessment of the next injection 2 weeks later. No moderate<br />
or severe reactions were observed in any subject.<br />
6.9 Postmarketing Experience<br />
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of<br />
risperidone; because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of<br />
uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency: agranulocytosis,<br />
alopecia, anaphylactic reaction, angioedema, atrial fibrillation, diabetes mellitus,<br />
diabetic ketoacidosis in patients with impaired glucose metabolism, hypoglycemia,<br />
hypothermia, inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion, intestinal obstruction,<br />
jaundice, mania, pancreatitis, priapism, QT prolongation, sleep apnea syndrome,<br />
thrombocytopenia, urinary retention, and water intoxication. In addition, the<br />
following adverse reactions have been observed during post approval use of<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® : cerebrovascular disorders, including cerebrovascular<br />
accidents, and diabetes mellitus aggravated.<br />
Retinal artery occlusion after injection of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® has been reported<br />
during postmarketing surveillance. This has been reported in the presence of<br />
abnormal arteriovenous anastomosis.<br />
Serious injection site reactions including abscess, cellulitis, cyst, hematoma,<br />
necrosis, nodule, and ulcer have been reported with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ®<br />
during postmarketing surveillance. Isolated cases required surgical intervention.<br />
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS<br />
The interactions of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® with coadministration of other drugs<br />
have not been systematically evaluated. The drug interaction data provided in this<br />
section is based on studies with oral RISPERDAL ® .<br />
7.1 Centrally-Acting Drugs and Alcohol<br />
Given the primary <strong>CNS</strong> effects of risperidone, caution should be used when<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is administered in combination with other centrally-acting<br />
drugs or alcohol.<br />
7.2 Drugs with Hypotensive Effects<br />
Because of its potential for inducing hypotension, RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® may enhance<br />
the hypotensive effects of other therapeutic agents with this potential.<br />
7.3 Levodopa and Dopamine Agonists<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® may antagonize the effects of levodopa and dopamine<br />
agonists.
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION<br />
7.4 Amitriptyline<br />
Amitriptyline did not affect the pharmacokinetics of risperidone or of risperidone<br />
and 9-hydroxyrisperidone combined following concomitant administration with oral<br />
RISPERDAL ® .<br />
7.5 Cimetidine and Ranitidine<br />
Cimetidine and ranitidine increased the bioavailability of oral risperidone by 64%<br />
and 26%, respectively. However, cimetidine did not affect the AUC of risperidone<br />
and 9-hydroxyrisperidone combined, whereas ranitidine increased the AUC of<br />
risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone combined by 20%.<br />
7.6 Clozapine<br />
Chronic administration of clozapine with risperidone may decrease the clearance<br />
of risperidone.<br />
7.7 Lithium<br />
Repeated doses of oral RISPERDAL ® (3 mg twice daily) did not affect the exposure<br />
(AUC) or peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) of lithium (n=13).<br />
7.8 Valproate<br />
Repeated doses of oral RISPERDAL ® (4 mg once daily) did not affect the pre-dose<br />
or average plasma concentrations and exposure (AUC) of valproate (1000 mg/day<br />
in three divided doses) compared to placebo (n=21). However, there was a<br />
20% increase in valproate peak plasma concentration (Cmax) after concomitant<br />
administration of oral RISPERDAL ® .<br />
7.9 Digoxin<br />
Oral RISPERDAL ® (0.25 mg twice daily) did not show a clinically relevant effect on<br />
the pharmacokinetics of digoxin.<br />
7.10 Topiramate<br />
Oral RISPERDAL ® administered at doses from 1-6 mg/day concomitantly with<br />
topiramate 400 mg/day resulted in a 23% decrease in risperidone Cmax and a 33%<br />
decrease in risperidone AUC0-12 hour at steady state. Minimal reductions in the<br />
exposure to risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone combined, and no change for<br />
9-hydroxyrisperidone were observed. This interaction is unlikely to be of clinical<br />
significance. There was no clinically relevant effect of oral RISPERDAL ® on the<br />
pharmacokinetics of topiramate.<br />
7.11 Drugs That Inhibit CYP 2D6 and Other CYP Isozymes<br />
Risperidone is metabolized to 9-hydroxyrisperidone by CYP 2D6, an enzyme that is<br />
polymorphic in the population and that can be inhibited by a variety of psychotropic<br />
and other drugs [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Drug interactions that reduce<br />
the metabolism of risperidone to 9-hydroxyrisperidone would increase the plasma<br />
concentrations of risperidone and lower the concentrations of 9-hydroxyrisperidone.<br />
Analysis of clinical studies involving a modest number of poor metabolizers<br />
(n=˜ 70 patients) does not suggest that poor and extensive metabolizers have different<br />
rates of adverse effects. No comparison of effectiveness in the two groups has<br />
been made.<br />
In vitro studies showed that drugs metabolized by other CYP isozymes, including<br />
1A1, 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, and 3A4, are only weak inhibitors of risperidone metabolism.<br />
Fluoxetine and Paroxetine<br />
Fluoxetine (20 mg once daily) and paroxetine (20 mg once daily), CYP 2D6 inhibitors,<br />
have been shown to increase the plasma concentration of risperidone 2.5-2.8 fold<br />
and 3-9 fold respectively. Fluoxetine did not affect the plasma concentration of<br />
9-hydroxyrisperidone. Paroxetine lowered the concentration of 9-hydroxyrisperidone<br />
by about 10%. When either concomitant fluoxetine or paroxetine is initiated or<br />
discontinued, the physician should re-evaluate the dose of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® .<br />
When initiation of fluoxetine or paroxetine is considered, patients may be placed<br />
on a lower dose of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® between 2 to 4 weeks before the planned<br />
start of fluoxetine or paroxetine therapy to adjust for the expected increase in<br />
plasma concentrations of risperidone. When fluoxetine or paroxetine is initiated in<br />
patients receiving the recommended dose of 25 mg RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , it is<br />
recommended to continue treatment with the 25-mg dose unless clinical judgment<br />
necessitates lowering the RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® dose to 12.5 mg or necessitates<br />
interruption of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® treatment. When RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is<br />
initiated in patients already receiving fluoxetine or paroxetine, a starting dose of<br />
12.5 mg can be considered. The efficacy of the 12.5 mg dose has not been<br />
investigated in clinical trials. [See also DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.5)]. The<br />
effects of discontinuation of concomitant fluoxetine or paroxetine therapy on the<br />
pharmacokinetics of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone have not been studied.<br />
Erythromycin<br />
There were no significant interactions between oral RISPERDAL ® and erythromycin.<br />
7.12 Carbamazepine and Other CYP 3A4 Enzyme Inducers<br />
Carbamazepine co-administration with oral RISPERDAL ® decreased the steadystate<br />
plasma concentrations of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone by about 50%.<br />
Plasma concentrations of carbamazepine did not appear to be affected.<br />
Co-administration of other known CYP 3A4 enzyme inducers (e.g., phenytoin,<br />
rifampin, and phenobarbital) with risperidone may cause similar decreases in the<br />
combined plasma concentrations of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone, which<br />
could lead to decreased efficacy of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® treatment. At the<br />
initiation of therapy with carbamazepine or other known hepatic enzyme inducers,<br />
patients should be closely monitored during the first 4–8 weeks, since the dose of<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® may need to be adjusted. A dose increase, or additional<br />
oral RISPERDAL ® , may need to be considered. On discontinuation of carbamazepine<br />
or other CYP 3A4 hepatic enzyme inducers, the dosage of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ®<br />
should be re-evaluated and, if necessary, decreased. Patients may be placed on<br />
a lower dose of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® between 2 to 4 weeks before the<br />
planned discontinuation of carbamazepine or other CYP 3A4 enzyme inducers to<br />
adjust for the expected increase in plasma concentrations of risperidone plus<br />
9-hydroxyrisperidone. For patients treated with the recommended dose of 25 mg<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® and discontinuing from carbamazepine or other CYP 3A4<br />
enzyme inducers, it is recommended to continue treatment with the 25-mg dose<br />
unless clinical judgment necessitates lowering the RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® dose to<br />
12.5 mg or necessitates interruption of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® treatment. The<br />
efficacy of the 12.5 mg dose has not been investigated in clinical trials. [See also<br />
DOSAGE AND ADMINSTRATION (2.5)]<br />
7.13 Drugs Metabolized by CYP 2D6<br />
In vitro studies indicate that risperidone is a relatively weak inhibitor of CYP 2D6.<br />
Therefore, RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is not expected to substantially inhibit<br />
the clearance of drugs that are metabolized by this enzymatic pathway. In<br />
drug interaction studies, oral RISPERDAL ® did not significantly affect the<br />
pharmacokinetics of donepezil and galantamine, which are metabolized by CYP 2D6.<br />
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS<br />
8.1 Pregnancy<br />
Pregnancy Category C.<br />
The teratogenic potential of oral risperidone was studied in three embryofetal<br />
development studies in Sprague-Dawley and Wistar rats (0.63-10 mg/kg or 0.4 to<br />
6 times the oral maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] on a mg/m2 basis)<br />
and in one embryofetal development study in New Zealand rabbits (0.31-5 mg/kg or<br />
0.4 to 6 times the oral MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). The incidence of malformations<br />
was not increased compared to control in offspring of rats or rabbits given 0.4 to<br />
6 times the oral MRHD on a mg/m2 basis. In three reproductive studies in rats (two<br />
peri/post-natal development studies and a multigenerational study), there was an<br />
increase in pup deaths during the first 4 days of lactation at doses of 0.16-5 mg/kg<br />
or 0.1 to 3 times the oral MRHD on a mg/m2 basis. It is not known whether these<br />
deaths were due to a direct effect on the fetuses or pups or to effects on the dams.<br />
There was no no-effect dose for increased rat pup mortality. In one peri/post-natal<br />
development study, there was an increase in stillborn rat pups at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg<br />
or 1.5 times the oral MRHD on a mg/m2 basis. In a cross-fostering study in Wistar<br />
rats, toxic effects on the fetus or pups, as evidenced by a decrease in the number<br />
of live pups and an increase in the number of dead pups at birth (Day 0), and a<br />
decrease in birth weight in pups of drug-treated dams were observed. In addition,<br />
there was an increase in deaths by Day 1 among pups of drug-treated dams,<br />
regardless of whether or not the pups were cross-fostered. Risperidone also<br />
appeared to impair maternal behavior in that pup body weight gain and survival (from<br />
Days 1 to 4 of lactation) were reduced in pups born to control but reared by<br />
drug-treated dams. These effects were all noted at the one dose of risperidone<br />
tested, i.e., 5 mg/kg or 3 times the oral MRHD on a mg/m2 basis.<br />
No studies were conducted with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® .<br />
Placental transfer of risperidone occurs in rat pups. There are no adequate and<br />
well-controlled studies in pregnant women. However, there was one report of a case<br />
of agenesis of the corpus callosum in an infant exposed to risperidone in utero. The<br />
causal relationship to oral RISPERDAL ® therapy is unknown. Reversible extrapyramidal<br />
symptoms in the neonate were observed following postmarketing use of risperidone<br />
during the last trimester of pregnancy.<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® should be used during pregnancy only if the potential<br />
benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.<br />
8.2 Labor and Delivery<br />
The effect of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® on labor and delivery in humans is unknown.<br />
8.3 Nursing Mothers<br />
Risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone are also excreted in human breast milk.<br />
Therefore, women should not breast-feed during treatment with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ®<br />
and for at least 12 weeks after the last injection.<br />
8.4 Pediatric Use<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® has not been studied in children younger than 18 years old.<br />
8.5 Geriatric Use<br />
In an open-label study, 57 clinically stable, elderly patients (≥ 65 years old) with<br />
schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder received RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® every<br />
2 weeks for up to 12 months. In general, no differences in the tolerability of<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® were observed between otherwise healthy elderly and<br />
nonelderly patients. Therefore, dosing recommendations for otherwise healthy<br />
elderly patients are the same as for nonelderly patients. Because elderly patients<br />
exhibit a greater tendency to orthostatic hypotension than nonelderly patients,<br />
elderly patients should be instructed in nonpharmacologic interventions that help<br />
to reduce the occurrence of orthostatic hypotension (e.g., sitting on the edge of the<br />
bed for several minutes before attempting to stand in the morning and slowly rising<br />
from a seated position). In addition, monitoring of orthostatic vital signs should be<br />
considered in elderly patients for whom orthostatic hypotension is of concern [see<br />
Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION<br />
Concomitant use with Furosemide in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related<br />
Psychosis<br />
In two of four placebo-controlled trials in elderly patients with dementia-related<br />
psychosis, a higher incidence of mortality was observed in patients treated with<br />
furosemide plus oral risperidone when compared to patients treated with oral<br />
risperidone alone or with oral placebo plus furosemide. No pathological mechanism<br />
has been identified to explain this finding, and no consistent pattern for cause<br />
of death was observed. An increase of mortality in elderly patients with<br />
dementia-related psychosis was seen with the use of oral risperidone regardless<br />
of concomitant use with furosemide. RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is not approved for<br />
the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis. [See Boxed Warning<br />
and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]<br />
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE<br />
9.1 Controlled Substance<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) is not a controlled substance.<br />
9.2 Abuse<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® has not been systematically studied in animals or humans<br />
for its potential for abuse. Because RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is to be administered<br />
by health care professionals, the potential for misuse or abuse by patients is low.<br />
9.3 Dependence<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® has not been systematically studied in animals or humans<br />
for its potential for tolerance or physical dependence.<br />
10 OVERDOSAGE<br />
10.1 Human Experience<br />
No cases of overdose were reported in premarketing studies with<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® . Because RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is to be administered by<br />
health care professionals, the potential for overdosage by patients is low.<br />
In premarketing experience with oral RISPERDAL ® , there were eight reports of<br />
acute RISPERDAL ® overdosage, with estimated doses ranging from 20 to 300 mg<br />
and no fatalities. In general, reported signs and symptoms were those resulting<br />
from an exaggeration of the drug’s known pharmacological effects, i.e., drowsiness<br />
and sedation, tachycardia and hypotension, and extrapyramidal symptoms. One<br />
case, involving an estimated overdose of 240 mg, was associated with hyponatremia,<br />
hypokalemia, prolonged QT, and widened QRS. Another case, involving an estimated<br />
overdose of 36 mg, was associated with a seizure.<br />
Postmarketing experience with oral RISPERDAL ® includes reports of acute<br />
overdose, with estimated doses of up to 360 mg. In general, the most frequently<br />
reported signs and symptoms are those resulting from an exaggeration of the<br />
drug’s known pharmacological effects, i.e., drowsiness, sedation, tachycardia,<br />
hypotension, and extrapyramidal symptoms. Other adverse reactions reported since<br />
market introduction related to oral RISPERDAL ® overdose include prolonged QT<br />
interval and convulsions. Torsade de pointes has been reported in association with<br />
combined overdose of oral RISPERDAL ® and paroxetine.<br />
10.2 Management of Overdosage<br />
In case of acute overdosage, establish and maintain an airway and ensure adequate<br />
oxygenation and ventilation. Cardiovascular monitoring should commence immediately<br />
and should include continuous electrocardiographic monitoring to detect possible<br />
arrhythmias. If antiarrhythmic therapy is administered, disopyramide, procainamide,<br />
and quinidine carry a theoretical hazard of QT prolonging effects that might be additive<br />
to those of risperidone. Similarly, it is reasonable to expect that the alpha-blocking<br />
properties of bretylium might be additive to those of risperidone, resulting in<br />
problematic hypotension.<br />
There is no specific antidote to risperidone. Therefore, appropriate supportive<br />
measures should be instituted. The possibility of multiple drug involvement should<br />
be considered. Hypotension and circulatory collapse should be treated with<br />
appropriate measures, such as intravenous fluids and/or sympathomimetic agents<br />
(epinephrine and dopamine should not be used, since beta stimulation may worsen<br />
hypotension in the setting of risperidone-induced alpha blockade). In cases of<br />
severe extrapyramidal symptoms, anticholinergic medication should be<br />
administered. Close medical supervision and monitoring should continue until the<br />
patient recovers.<br />
11 DESCRIPTION<br />
Risperidone is a psychotropic agent belonging to the chemical class of<br />
benzisoxazole derivatives. The chemical designation is 3-[2-[4-(6-fluoro-<br />
1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl]ethyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-2-methyl-4H-pyrido[1,2a]pyrimidin-4-one.<br />
Its molecular formula is C23H27FN4O2 and its molecular weight is<br />
410.49. The structural formula is:<br />
Risperidone is practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in methylene chloride, and<br />
soluble in methanol and 0.1 N HCl.<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) Long-Acting Injection is a combination of<br />
extended-release microspheres for injection and diluent for parenteral use.<br />
The extended-release microspheres formulation is a white to off-white, free-flowing<br />
powder that is available in dosage strengths of 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 37.5 mg, or 50 mg<br />
risperidone per vial. Risperidone is micro-encapsulated in 7525 polylactideco-glycolide<br />
(PLG) at a concentration of 381 mg risperidone per gram of microspheres.<br />
The diluent for parenteral use is a clear, colorless solution. Composition of the<br />
diluent includes polysorbate 20, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, disodium<br />
hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, citric acid anhydrous, sodium chloride, sodium<br />
hydroxide, and water for injection. The microspheres are suspended in the diluent<br />
prior to injection.<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is provided as a dose pack, consisting of a vial containing<br />
the microspheres, a pre-filled syringe containing the diluent, a SmartSite ®<br />
Needle-Free Vial Access Device, and two Needle-Pro ® safety needles (a 21 G UTW<br />
1-inch needle with needle protection device for deltoid administration and a 20 G TW<br />
2-inch needle with needle protection device for gluteal administration).<br />
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY<br />
12.1 Mechanism of Action<br />
The mechanism of action of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , as with other drugs used to<br />
treat schizophrenia, is unknown. However, it has been proposed that the drug’s<br />
therapeutic activity in schizophrenia is mediated through a combination of dopamine<br />
Type 2 (D2) and serotonin Type 2 (5HT2) receptor antagonism.<br />
RISPERDAL ® is a selective monoaminergic antagonist with high affinity (Ki of 0.12 to<br />
7.3 nM) for the serotonin Type 2 (5HT2), dopamine Type 2 (D2), α1 and α2 adrenergic,<br />
and H1 histaminergic receptors. RISPERDAL ® acts as an antagonist at other receptors,<br />
but with lower potency. RISPERDAL ® has low to moderate affinity (Ki of 47 to 253 nM)<br />
for the serotonin 5HT1C, 5HT1D, and 5HT1A receptors, weak affinity (Ki of 620 to<br />
800 nM) for the dopamine D1 and haloperidol-sensitive sigma site, and no affinity<br />
(when tested at concentrations >10-5 M) for cholinergic muscarinic or β1 and β2<br />
adrenergic receptors.<br />
12.2 Pharmacodynamics<br />
The clinical effect from RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® results from the combined<br />
concentrations of risperidone and its major metabolite, 9-hydroxyrisperidone<br />
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Antagonism at receptors other than D2 and 5HT2 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)] may explain some of the other effects of<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® .<br />
12.3 Pharmacokinetics<br />
Absorption<br />
After a single intramuscular (gluteal) injection of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , there is<br />
a small initial release of the drug (< 1% of the dose), followed by a lag time of 3<br />
weeks. The main release of the drug starts from 3 weeks onward, is maintained<br />
from 4 to 6 weeks, and subsides by 7 weeks following the intramuscular (IM)<br />
injection. Therefore, oral antipsychotic supplementation should be given during the<br />
first 3 weeks of treatment with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® to maintain therapeutic<br />
levels until the main release of risperidone from the injection site has begun [see<br />
Dosage and Administration (2)]. Following single doses of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® ,<br />
the pharmacokinetics of risperidone, 9-hydroxyrisperidone (the major metabolite),<br />
and risperidone plus 9-hydroxy risperidone were linear in the dosing range of<br />
12.5 mg to 50 mg.<br />
The combination of the release profile and the dosage regimen (IM injections every<br />
2 weeks) of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® results in sustained therapeutic concentrations.<br />
Steady-state plasma concentrations are reached after 4 injections and are<br />
maintained for 4 to 6 weeks after the last injection. Following multiple doses of 25 mg<br />
and 50 mg RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , plasma concentrations of risperidone,<br />
9-hydroxyrisperidone, and risperidone plus 9-hydroxyrisperidone were linear.<br />
Deltoid and gluteal intramuscular injections at the same doses are bioequivalent<br />
and, therefore, interchangeable.<br />
Distribution<br />
Once absorbed, risperidone is rapidly distributed. The volume of distribution is<br />
1-2 L/kg. In plasma, risperidone is bound to albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein. The<br />
plasma protein binding of risperidone is approximately 90%, and that of its major<br />
metabolite, 9-hydroxyrisperidone, is 77%. Neither risperidone nor 9-hydroxyrisperidone<br />
displaces each other from plasma binding sites. High therapeutic concentrations<br />
of sulfamethazine (100 mcg/mL), warfarin (10 mcg/mL), and carbamazepine (10 mcg/mL)<br />
caused only a slight increase in the free fraction of risperidone at 10 ng/mL and of<br />
9-hydroxyrisperidone at 50 ng/mL, changes of unknown clinical significance.<br />
Metabolism and Drug Interactions<br />
Risperidone is extensively metabolized in the liver. The main metabolic pathway is<br />
through hydroxylation of risperidone to 9-hydroxyrisperidone by the enzyme, CYP<br />
2D6. A minor metabolic pathway is through N-dealkylation. The main metabolite,<br />
9-hydroxyrisperidone, has similar pharmacological activity as risperidone.<br />
Consequently, the clinical effect of the drug results from the combined concentrations<br />
of risperidone plus 9-hydroxyrisperidone.<br />
CYP 2D6, also called debrisoquin hydroxylase, is the enzyme responsible for<br />
metabolism of many neuroleptics, antidepressants, antiarrhythmics, and other<br />
drugs. CYP 2D6 is subject to genetic polymorphism (about 6%-8% of Caucasians,<br />
and a very low percentage of Asians, have little or no activity and are “poor<br />
metabolizers”) and to inhibition by a variety of substrates and some non-substrates,<br />
notably quinidine. Extensive CYP 2D6 metabolizers convert risperidone rapidly into<br />
9-hydroxyrisperidone, whereas poor CYP 2D6 metabolizers convert it much more
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION<br />
slowly. Although extensive metabolizers have lower risperidone and higher<br />
9-hydroxyrisperidone concentrations than poor metabolizers, the pharmacokinetics<br />
of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone combined, after single and multiple doses,<br />
are similar in extensive and poor metabolizers.<br />
The interactions of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® with coadministration of other drugs<br />
have not been systematically evaluated in human subjects. Drug interactions are<br />
based primarily on experience with oral RISPERDAL ® . Risperidone could be subject<br />
to two kinds of drug-drug interactions. First, inhibitors of CYP 2D6 interfere with<br />
conversion of risperidone to 9-hydroxyrisperidone [see Drug Interactions (7.11)].<br />
This occurs with quinidine, giving essentially all recipients a risperidone<br />
pharmacokinetic profile typical of poor metabolizers. The therapeutic benefits and<br />
adverse effects of RISPERDAL ® in patients receiving quinidine have not been<br />
evaluated, but observations in a modest number (n=˜70) of poor metabolizers given<br />
oral RISPERDAL ® do not suggest important differences between poor and extensive<br />
metabolizers. Second, co-administration of carbamazepine and other known<br />
enzyme inducers (e.g., phenytoin, rifampin, and phenobarbital) with oral<br />
RISPERDAL ® cause a decrease in the combined plasma concentrations of<br />
risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone [see Drug Interactions (7.12)]. It would also<br />
be possible for risperidone to interfere with metabolism of other drugs metabolized<br />
by CYP 2D6. Relatively weak binding of risperidone to the enzyme suggests this is<br />
unlikely [see Drug Interactions (7.11)].<br />
Excretion<br />
Risperidone and its metabolites are eliminated via the urine and, to a much lesser<br />
extent, via the feces. As illustrated by a mass balance study of a single 1 mg oral<br />
dose of 14C-risperidone administered as solution to three healthy male volunteers,<br />
total recovery of radioactivity at 1 week was 84%, including 70% in the urine and<br />
14% in the feces.<br />
The apparent half-life of risperidone plus 9-hydroxyrisperidone following<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® administration is 3 to 6 days, and is associated with a<br />
monoexponential decline in plasma concentrations. This half-life of 3-6 days is related<br />
to the erosion of the microspheres and subsequent absorption of risperidone. The<br />
clearance of risperidone and risperidone plus 9-hydroxyrisperidone was 13.7 L/h and<br />
5.0 L/h in extensive CYP 2D6 metabolizers, and 3.3 L/h and 3.2 L/h in poor CYP 2D6<br />
metabolizers, respectively. No accumulation of risperidone was observed during<br />
long-term use (up to 12 months) in patients treated every 2 weeks with 25 mg or 50 mg<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® . The elimination phase is complete approximately 7 to 8 weeks<br />
after the last injection.<br />
Renal Impairment<br />
In patients with moderate to severe renal disease treated with oral RISPERDAL ® ,<br />
clearance of the sum of risperidone and its active metabolite decreased by 60%<br />
compared with young healthy subjects. Although patients with renal impairment<br />
were not studied with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , it is recommended that patients with<br />
renal impairment be carefully titrated on oral RISPERDAL ® before treatment with<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is initiated at a dose of 25 mg. A lower initial dose of 12.5 mg<br />
may be appropriate when clinical factors warrant dose adjustment, such as in<br />
patients with renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].<br />
Hepatic Impairment<br />
While the pharmacokinetics of oral RISPERDAL ® in subjects with liver disease were<br />
comparable to those in young healthy subjects, the mean free fraction of risperidone<br />
in plasma was increased by about 35% because of the diminished concentration<br />
of both albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein. Although patients with hepatic<br />
impairment were not studied with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , it is recommended that<br />
patients with hepatic impairment be carefully titrated on oral RISPERDAL ® before<br />
treatment with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is initiated at a dose of 25 mg. A lower initial<br />
dose of 12.5 mg may be appropriate when clinical factors warrant dose adjustment,<br />
such as in patients with hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].<br />
Elderly<br />
In an open-label trial, steady-state concentrations of risperidone plus<br />
9-hydroxyrisperidone in otherwise healthy elderly patients (≥ 65 years old) treated<br />
with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® for up to 12 months fell within the range of values<br />
observed in otherwise healthy nonelderly patients. Dosing recommendations are<br />
the same for otherwise healthy elderly patients and nonelderly patients [see Dosage<br />
and Administration (2)].<br />
Race and Gender Effects<br />
No specific pharmacokinetic study was conducted to investigate race and gender<br />
effects, but a population pharmacokinetic analysis did not identify important<br />
differences in the disposition of risperidone due to gender (whether or not corrected<br />
for body weight) or race.<br />
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY<br />
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility<br />
Carcinogenesis - Oral<br />
Carcinogenicity studies were conducted in Swiss albino mice and Wistar rats.<br />
Risperidone was administered in the diet at doses of 0.63, 2.5, and 10 mg/kg for<br />
18 months to mice and for 25 months to rats. These doses are equivalent to 2.4, 9.4,<br />
and 37.5 times the oral maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) for<br />
schizophrenia (16 mg/day) on a mg/kg basis, or 0.2, 0.75, and 3 times the oral MRHD<br />
(mice) or 0.4, 1.5, and 6 times the oral MRHD (rats) on a mg/m2 basis. A maximum<br />
tolerated dose was not achieved in male mice. There was a significant increase in<br />
pituitary gland adenomas in female mice at doses 0.75 and 3 times the oral MRHD<br />
on a mg/m2 basis. There was a significant increase in endocrine pancreatic<br />
adenomas in male rats at doses 1.5 and 6 times the oral MRHD on a mg/m2 basis.<br />
Mammary gland adenocarcinomas were significantly increased in female mice at<br />
all doses tested (0.2, 0.75, and 3 times the oral MRHD on a mg/m2 basis), in female<br />
rats at all doses tested (0.4, 1.5, and 6 times the oral MRHD on a mg/m2 basis), and<br />
in male rats at a dose 6 times the oral MRHD on a mg/m2 basis.<br />
Carcinogenesis - Intramuscular<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® was evaluated in a 24-month carcinogenicity study in which<br />
SPF Wistar rats were treated every 2 weeks with intramuscular (IM) injections of<br />
either 5 mg/kg or 40 mg/kg of risperidone. These doses are 1 and 8 times the MRHD<br />
(50 mg) on a mg/m2 basis. A control group received injections of 0.9% NaCl, and a<br />
vehicle control group was injected with placebo microspheres. There was a<br />
significant increase in pituitary gland adenomas, endocrine pancreas adenomas,<br />
and adrenomedullary pheochromocytomas at 8 times the IM MRHD on a mg/m2 basis. The incidence of mammary gland adenocarcinomas was significantly<br />
increased in female rats at both doses (1 and 8 times the IM MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). A significant increase in renal tubular tumors (adenoma, adenocarcinomas)<br />
was observed in male rats at 8 times the IM MRHD on a mg/m2 basis. Plasma<br />
exposures (AUC) in rats were 0.3 and 2 times (at 5 and 40 mg/kg, respectively) the<br />
expected plasma exposure (AUC) at the IM MRHD.<br />
Dopamine D2 receptor antagonists have been shown to chronically elevate prolactin<br />
levels in rodents. Serum prolactin levels were not measured during the<br />
carcinogenicity studies of oral risperidone; however, measurements taken during<br />
subchronic toxicity studies showed that oral risperidone elevated serum prolactin<br />
levels 5- to 6-fold in mice and rats at the same doses used in the oral carcinogenicity<br />
studies. Serum prolactin levels increased in a dose-dependent manner up to 6- and<br />
1.5-fold in male and female rats, respectively, at the end of the 24-month treatment<br />
with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® every 2 weeks. Increases in the incidence of pituitary<br />
gland, endocrine pancreas, and mammary gland neoplasms have been found in<br />
rodents after chronic administration of other antipsychotic drugs and may be<br />
prolactin-mediated.<br />
The relevance for human risk of the findings of prolactin-mediated endocrine tumors<br />
in rodents is unknown [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].<br />
Mutagenesis<br />
No evidence of mutagenic potential for oral risperidone was found in the in vitro<br />
Ames reverse mutation test, in vitro mouse lymphoma assay, in vitro rat hepatocyte<br />
DNA-repair assay, in vivo oral micronucleus test in mice, the sex-linked recessive<br />
lethal test in Drosophila, or the in vitro chromosomal aberration test in human<br />
lymphocytes or in Chinese hamster cells.<br />
In addition, no evidence of mutagenic potential was found in the in vitro Ames<br />
reverse mutation test for RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® .<br />
Impairment of Fertility<br />
Oral risperidone (0.16 to 5 mg/kg) was shown to impair mating, but not fertility, in<br />
Wistar rats in three reproductive studies (two mating and fertility studies and a<br />
multigenerational study) at doses 0.1 to 3 times the oral maximum recommended<br />
human dose (MRHD) (16 mg/day) on a mg/m2 basis. The effect appeared to be in<br />
females, since impaired mating behavior was not noted in the mating and fertility study<br />
in which males only were treated. In a subchronic study in Beagle dogs in which oral<br />
risperidone was administered at doses of 0.31 to 5 mg/kg, sperm motility and<br />
concentration were decreased at doses 0.6 to 10 times the oral MRHD on a mg/m2 basis. Dose-related decreases were also noted in serum testosterone at the same<br />
doses. Serum testosterone and sperm values partially recovered, but remained<br />
decreased after treatment was discontinued. No no-effect doses were noted in either<br />
rat or dog.<br />
No mating and fertility studies were conducted with RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® .<br />
14 CLINICAL STUDIES<br />
14.1 Schizophrenia<br />
The effectiveness of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® in the treatment of schizophrenia was<br />
established, in part, on the basis of extrapolation from the established effectiveness<br />
of the oral formulation of risperidone. In addition, the effectiveness of<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® in the treatment of schizophrenia was established<br />
in a 12-week, placebo-controlled trial in adult psychotic inpatients and outpatients<br />
who met the DSM-IV criteria for schizophrenia.<br />
Efficacy data were obtained from 400 patients with schizophrenia who were<br />
randomized to receive injections of 25 mg, 50 mg, or 75 mg RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ®<br />
or placebo every 2 weeks. During a 1-week run-in period, patients were<br />
discontinued from other antipsychotics and were titrated to a dose of 4 mg oral<br />
RISPERDAL ® . Patients who received RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® were given doses of<br />
oral RISPERDAL ® (2 mg for patients in the 25-mg group, 4 mg for patients in the<br />
50-mg group, and 6 mg for patients in the 75-mg group) for the 3 weeks after the<br />
first injection to provide therapeutic plasma concentrations until the main release<br />
phase of risperidone from the injection site had begun. Patients who received<br />
placebo injections were given placebo tablets.<br />
Efficacy was evaluated using the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS),<br />
a validated, multi-item inventory, composed of five subscales to evaluate positive<br />
symptoms, negative symptoms, disorganized thoughts, uncontrolled hostility/<br />
excitement, and anxiety/depression.<br />
The primary efficacy variable in this trial was change from baseline to endpoint in<br />
the total PANSS score. The mean total PANSS score at baseline for schizophrenic<br />
patients in this study was 81.5.
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) LONG-ACTING INJECTION<br />
Total PANSS scores showed significant improvement in the change from baseline to<br />
endpoint in schizophrenic patients treated with each dose of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ®<br />
(25 mg, 50 mg, or 75 mg) compared with patients treated with placebo. While there<br />
were no statistically significant differences between the treatment effects for the three<br />
dose groups, the effect size for the 75 mg dose group was actually numerically less<br />
than that observed for the 50 mg dose group.<br />
Subgroup analyses did not indicate any differences in treatment outcome as a<br />
function of age, race, or gender.<br />
14.2 Bipolar Disorder - Monotherapy<br />
The effectiveness of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® for the maintenance treatment of<br />
Bipolar I Disorder was established in a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled<br />
study of adult patients who met DSM-IV criteria for Bipolar Disorder Type I, who<br />
were stable on medications or experiencing an acute manic or mixed episode.<br />
A total of 501 patients were treated during a 26-week open-label period with<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (starting dose of 25 mg, and titrated, if deemed clinically<br />
desirable, to 37.5 mg or 50 mg; in patients not tolerating the 25 mg dose, the dose<br />
could be reduced to 12.5 mg). In the open-label phase, 303 (60%) patients were<br />
judged to be stable and were randomized to double-blind treatment with either the<br />
same dose of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® or placebo and monitored for relapse. The<br />
primary endpoint was time to relapse to any mood episode (depression, mania,<br />
hypomania, or mixed).<br />
Time to relapse was delayed in patients receiving RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ®<br />
monotherapy as compared to placebo. The majority of relapses were due to manic<br />
rather than depressive symptoms. Based on their bipolar disorder history, subjects<br />
entering this study had had, on average, more manic episodes than depressive<br />
episodes.<br />
14.3 Bipolar Disorder - Adjunctive Therapy<br />
The effectiveness of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® as an adjunct to treatment with lithium<br />
or valproate for the maintenance treatment of Bipolar Disorder was established in<br />
a multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of adult patients<br />
who met DSM-IV criteria for Bipolar Disorder Type I and who experienced at least<br />
4 episodes of mood disorder requiring psychiatric/clinical intervention in the<br />
previous 12 months, including at least 2 episodes in the 6 months prior to the start<br />
of the study.<br />
A total of 240 patients were treated during a 16-week open-label period with<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (starting dose of 25 mg, and titrated, if deemed clinically<br />
desirable, to 37.5 mg or 50 mg), as adjunctive therapy in addition to continuing their<br />
treatment as usual for their bipolar disorder, which consisted of mood stabilizers<br />
(primarily lithium and valproate), antidepressants, and/or anxiolytics. All oral<br />
antipsychotics were discontinued after the first three weeks of the initial<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® injection. In the open-label phase, 124 (51.7%) were judged<br />
to be stable for at least the last 4 weeks and were randomized to double-blind<br />
treatment with either the same dose of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® or placebo in<br />
addition to continuing their treatment as usual and monitored for relapse during a<br />
52-week period. The primary endpoint was time to relapse to any new mood episode<br />
(depression, mania, hypomania, or mixed).<br />
Time to relapse was delayed in patients receiving adjunctive therapy with<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® as compared to placebo. The relapse types were about half<br />
depressive and half manic or mixed episodes.<br />
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® (risperidone) is available in dosage strengths of 12.5 mg,<br />
25 mg, 37.5 mg, or 50 mg risperidone. It is provided as a dose pack, consisting of a<br />
vial containing the risperidone microspheres, a pre-filled syringe containing 2 mL of<br />
diluent for RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® , a SmartSite ® Needle-Free Vial Access Device,<br />
and two Needle-Pro ® safety needles for intramuscular injection (a 21 G UTW 1-inch<br />
needle with needle protection device for deltoid administration and a 20 G TW 2-inch<br />
needle with needle protection device for gluteal administration).<br />
12.5-mg vial/kit (NDC 50458-309-11): 41 mg (equivalent to 12.5 mg of risperidone)<br />
of a white to off-white powder provided in a vial with a violet flip-off cap<br />
(NDC 50458-309-01).<br />
25-mg vial/kit (NDC 50458-306-11): 78 mg (equivalent to 25 mg of risperidone)<br />
of a white to off-white powder provided in a vial with a pink flip-off cap<br />
(NDC 50458-306-01).<br />
37.5-mg vial/kit (NDC 50458-307-11): 116 mg (equivalent to 37.5 mg of risperidone)<br />
of a white to off-white powder provided in a vial with a green flip-off cap<br />
(NDC 50458-307-01).<br />
50-mg vial/kit (NDC 50458-308-11): 152 mg (equivalent to 50 mg of risperidone) of a<br />
white to off-white powder provided in a vial with a blue flip-off cap<br />
(NDC 50458-308-01).<br />
Storage and Handling<br />
The entire dose pack should be stored in the refrigerator (36°-46°F; 2°-8°C) and<br />
protected from light.<br />
If refrigeration is unavailable, RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® can be stored at temperatures<br />
not exceeding 77°F (25°C) for no more than 7 days prior to administration. Do not<br />
expose unrefrigerated product to temperatures above 77°F (25°C).<br />
Keep out of reach of children.<br />
17 PATIENT COUNSELING IN<strong>FOR</strong>MATION<br />
Physicians are advised to discuss the following issues with patients for whom they<br />
prescribe RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® .<br />
17.1 Orthostatic Hypotension<br />
Patients should be advised of the risk of orthostatic hypotension and instructed in<br />
nonpharmacologic interventions that help to reduce the occurrence of orthostatic<br />
hypotension (e.g., sitting on the edge of the bed for several minutes before<br />
attempting to stand in the morning and slowly rising from a seated position) [see<br />
Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].<br />
17.2 Interference with Cognitive and Motor Performance<br />
Because RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® has the potential to impair judgment, thinking, or<br />
motor skills, patients should be cautioned about operating hazardous machinery,<br />
including automobiles, until they are reasonably certain that treatment with<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® does not affect them adversely [see Warnings and<br />
Precautions (5.9)].<br />
17.3 Pregnancy<br />
Patients should be advised to notify their physician if they become pregnant or<br />
intend to become pregnant during therapy and for at least 12 weeks after the last<br />
injection of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].<br />
17.4 Nursing<br />
Patients should be advised not to breast-feed an infant during treatment and for at<br />
least 12 weeks after the last injection of RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® [see Use in Specific<br />
Populations (8.3)].<br />
17.5 Concomitant Medication<br />
Patients should be advised to inform their physicians if they are taking, or plan to<br />
take, any prescription or over-the-counter drugs, since there is a potential for<br />
interactions [see Drug Interactions (7)].<br />
17.6 Alcohol<br />
Patients should be advised to avoid alcohol during treatment with<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].<br />
10130505<br />
Revised April 2010<br />
© Ortho-McNeil-<strong>Janssen</strong> Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2007<br />
Risperidone is manufactured by:<br />
<strong>Janssen</strong> Pharmaceutical Ltd.<br />
Wallingstown, Little Island, County Cork, Ireland<br />
Microspheres are manufactured by:<br />
Alkermes, Inc.<br />
Wilmington, Ohio<br />
Diluent is manufactured by:<br />
Vetter Pharma Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG<br />
Ravensburg or Langenargen, Germany or<br />
Cilag AG<br />
Schaffhausen, Switzerland or<br />
Ortho Biotech Products, L.P.<br />
Raritan, NJ<br />
RISPERDAL ® CONSTA ® is manufactured for:<br />
<strong>Janssen</strong>, Division of Ortho-McNeil-<strong>Janssen</strong> Pharmaceuticals, Inc.<br />
Titusville, NJ 08560