Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
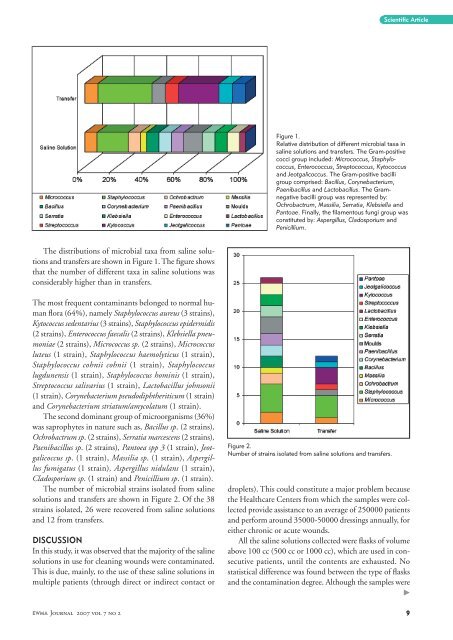
The distributions of microbial taxa from saline solutions<br />
and transfers are shown in Figure 1. The figure shows<br />
that the number of different taxa in saline solutions was<br />
considerably higher than in transfers.<br />
The most frequent contaminants belonged to normal human<br />
flora (64%), namely Staphylococcus aureus (3 strains),<br />
Kytococcus sedentarius (3 strains), Staphylococcus epidermidis<br />
(2 strains), Enterococcus faecalis (2 strains), Klebsiella pneumoniae<br />
(2 strains), Micrococcus sp. (2 strains), Micrococcus<br />
luteus (1 strain), Staphylococcus haemolyticus (1 strain),<br />
Staphylococcus cohnii cohnii (1 strain), Staphylococcus<br />
lugdunensis (1 strain), Staphylococcus hominis (1 strain),<br />
Streptococcus salivarius (1 strain), Lactobacillus johnsonii<br />
(1 strain), Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum (1 strain)<br />
and Corynebacterium striatum/amycolatum (1 strain).<br />
The second dominant group of microorganisms (36%)<br />
was saprophytes in nature such as, Bacillus sp. (2 strains),<br />
Ochrobactrum sp. (2 strains), Serratia marcescens (2 strains),<br />
Paenibacillus sp. (2 strains), Pantoea spp 3 (1 strain), Jeotgalicoccus<br />
sp. (1 strain), Massilia sp. (1 strain), Aspergillus<br />
fumigatus (1 strain), Aspergillus nidulans (1 strain),<br />
Cladosporium sp. (1 strain) and Penicillium sp. (1 strain).<br />
The number of microbial strains isolated from saline<br />
solutions and transfers are shown in Figure 2. Of the 38<br />
strains isolated, 26 were recovered from saline solutions<br />
and 12 from transfers.<br />
DISCUSSION<br />
In this study, it was observed that the majority of the saline<br />
solutions in use for cleaning wounds were contaminated.<br />
This is due, mainly, to the use of these saline solutions in<br />
multiple patients (through direct or indirect contact or<br />
<strong>EWMA</strong> Journal 2007 vol 7 no 2<br />
Figure 1.<br />
Relative distribution of different microbial taxa in<br />
saline solutions and transfers. The Gram-positive<br />
cocci group included: Micrococcus, Staphylococcus,<br />
Enterococcus, Streptococcus, Kytococcus<br />
and Jeotgalicoccus. The Gram-positive bacilli<br />
group comprised: Bacillus, Corynebacterium,<br />
Paenibacillus and Lactobacillus. The Gramnegative<br />
bacilli group was represented by:<br />
Ochrobactrum, Massilia, Serratia, Klebsiella and<br />
Pantoae. Finally, the filamentous fungi group was<br />
constituted by: Aspergillus, Cladosporium and<br />
Penicillium.<br />
Figure 2.<br />
Number of strains isolated from saline solutions and transfers.<br />
Scientific Article<br />
droplets). This could constitute a major problem because<br />
the Healthcare Centers from which the samples were collected<br />
provide assistance to an average of 250000 patients<br />
and perform around 35000-50000 dressings annually, for<br />
either chronic or acute wounds.<br />
All the saline solutions collected were flasks of volume<br />
above 100 cc (500 cc or 1000 cc), which are used in consecutive<br />
patients, until the contents are exhausted. No<br />
statistical difference was found between the type of flasks<br />
and the contamination degree. Although the samples were<br />
�