Epoprostenol - Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust
Epoprostenol - Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust
Epoprostenol - Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
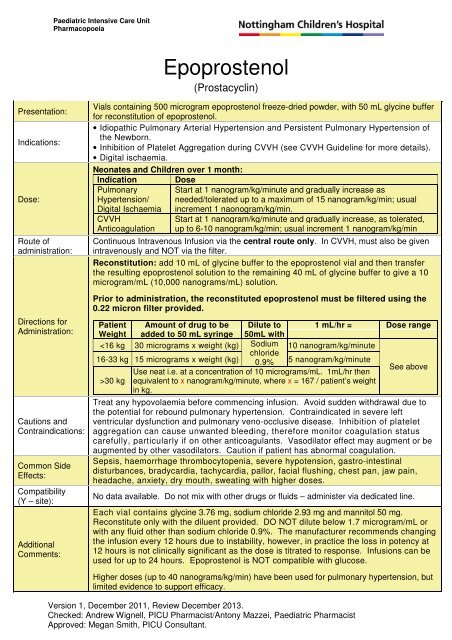
Paediatric Intensive Care UnitPharmacopoeia<strong>Epoprostenol</strong>(Prostacyclin)Presentation:Indications:Dose:Route ofadministration:Directions forAdministration:Cautions andContraindications:Common SideEffects:Compatibility(Y – site):AdditionalComments:Vials containing 500 microgram epoprostenol freeze-dried powder, with 50 mL glycine bufferfor reconstitution of epoprostenol.• Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension ofthe Newborn.• Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation during CVVH (see CVVH Guideline for more details).• Digital ischaemia.Neonates and Children over 1 month:Indication DosePulmonary Start at 1 nanogram/kg/minute and gradually increase asHypertension/ needed/tolerated up to a maximum of 15 nanogram/kg/min; usualDigital Ischaemia increment 1 naonogram/kg/min.CVVHAnticoagulationStart at 1 nanogram/kg/minute and gradually increase, as tolerated,up to 6-10 nanogram/kg/min; usual increment 1 nanogram/kg/minContinuous Intravenous Infusion via the central route only. In CVVH, must also be givenintravenously and NOT via the filter.Reconstitution: add 10 mL of glycine buffer to the epoprostenol vial and then transferthe resulting epoprostenol solution to the remaining 40 mL of glycine buffer to give a 10microgram/mL (10,000 nanograms/mL) solution.Prior to administration, the reconstituted epoprostenol must be filtered using the0.22 micron filter provided.Patient Amount of drug to be Dilute to 1 mL/hr = Dose rangeWeight added to 50 mL syringe 50mL with30 kg equivalent to x nanogram/kg/minute, where x = 167 / patient’s weightin kg.Treat any hypovolaemia before commencing infusion. Avoid sudden withdrawal due tothe potential for rebound pulmonary hypertension. Contraindicated in severe leftventricular dysfunction and pulmonary veno-occlusive disease. Inhibition of plateletaggregation can cause unwanted bleeding, therefore monitor coagulation statuscarefully, particularly if on other anticoagulants. Vasodilator effect may augment or beaugmented by other vasodilators. Caution if patient has abnormal coagulation.Sepsis, haemorrhage thrombocytopenia, severe hypotension, gastro-intestinaldisturbances, bradycardia, tachycardia, pallor, facial flushing, chest pan, jaw pain,headache, anxiety, dry mouth, sweating with higher doses.No data available. Do not mix with other drugs or fluids – administer via dedicated line.Each vial contains glycine 3.76 mg, sodium chloride 2.93 mg and mannitol 50 mg.Reconstitute only with the diluent provided. DO NOT dilute below 1.7 microgram/mL orwith any fluid other than sodium chloride 0.9%. The manufacturer recommends changingthe infusion every 12 hours due to instability, however, in practice the loss in potency at12 hours is not clinically significant as the dose is titrated to response. Infusions can beused for up to 24 hours. <strong>Epoprostenol</strong> is NOT compatible with glucose.Higher doses (up to 40 nanograms/kg/min) have been used for pulmonary hypertension, butlimited evidence to support efficacy.Version 1, December 2011, Review December 2013.Checked: Andrew Wignell, PICU Pharmacist/Antony Mazzei, Paediatric PharmacistApproved: Megan Smith, PICU Consultant.
Paediatric Intensive Care UnitPharmacopoeiaReferences1. Medicines for Children, 2 nd Edition, 2003.2. BNF for Children, 2011-2012.3. Guy’s and Thomas’ Paediatric Formulary, 8 th Edition, 2010.4. <strong>University</strong> College <strong>Hospitals</strong> Injectable Medicines Administration Guide, 3 rd Edition, 2010.5. Trissel LA (ed), Handbook on Injectable Drugs. [online] London: Pharmaceutical Press accessedvia www.medicinescomplete.com (accessed on 26/11/2011).6. Medusa Injectable Medicines Guide: accessed via http://medusa.wales.nhs.uk/ (accessed on26/11/2011).7. Paediatric Injectable Drugs. Accessed via http://www.medicinescomplete.com/mc/ (accessed7/12/11)8. Lexicomp: Paediatric and Neonatal Dosage Handbook, 18 th Edition, 2011.Version 1, December 2011, Review December 2013.Checked: Andrew Wignell, PICU Pharmacist/Antony Mazzei, Paediatric PharmacistApproved: Megan Smith, PICU Consultant.