SPH4U: Lecture 8 Notes - The Burns Home Page
SPH4U: Lecture 8 Notes - The Burns Home Page
SPH4U: Lecture 8 Notes - The Burns Home Page
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
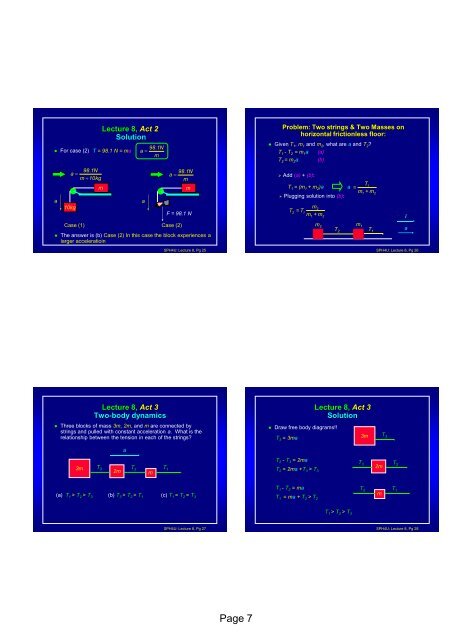
<strong>Lecture</strong> 8, Act 2Solution• For case (2) T = 98.1 N = maa98.1Na m 10kg10kgCase (1)m98.1Na m• <strong>The</strong> answer is (b) Case (2) In this case the block experiences alarger acceleratioina98.1Na mmF = 98.1 NCase (2)<strong>SPH4U</strong>: <strong>Lecture</strong> 8, Pg 25Problem: Two strings & Two Masses onhorizontal frictionless floor:• Given T 1 , m 1 and m 2 , what are a and T 2 ?T 1 - T 2 = m 1 a (a)T 2 = m 2 a (b)‣ Add (a) + (b):T1T 1 = (m 1 + m 2 )a a =m1+ m‣ Plugging solution into (b):m2T2= T1m + m12m 2m 1T 2 T 12a<strong>SPH4U</strong>: <strong>Lecture</strong> 8, Pg 26i<strong>Lecture</strong> 8, Act 3Two-body dynamics• Three blocks of mass 3m, 2m, and m are connected bystrings and pulled with constant acceleration a. What is therelationship between the tension in each of the strings?• Draw free body diagrams!!T 3 = 3ma<strong>Lecture</strong> 8, Act 3Solution3mT 3a3mT 3 T 2 T2m1mT 2 - T 3 = 2maT 3 T 2 2mT 2 = 2ma +T 3 > T 3T 2 T 1(a) T 1 > T 2 > T 3 (b) T 3 > T 2 > T 1 (c) T 1 = T 2 = T 3T 1 - T 2 = mamT 1 = ma + T 2 > T 2T 1 > T 2 > T 3<strong>SPH4U</strong>: <strong>Lecture</strong> 8, Pg 27<strong>SPH4U</strong>: <strong>Lecture</strong> 8, Pg 28<strong>Page</strong> 7